|
Haufen
{{italic title A ''Heerhaufen'', also ''Haufen'' or ''Haufe'', was the name given to unorganised or poorly organised paramilitary troops and auxiliaries in Central Europe during the Early Modern Period. The term is German and is sometimes translated "company" or "troops". The term ''Haufe'' was used especially during the peasants' wars and Thirty Years' War for a body of men, sometimes of several thousand armed peasants or '' Landsknechten'', often with as part of a grassroots democracy movement (c.f the ''Heeresversammlungs'' of antiquity), and therefore more loosely organised than the smaller and strictly military units known as ''Fähnleins''. The well known German Youth Movement song ''"Wir sind des Geyers schwarze Haufen"'' ("We are Geyer's black ''Haufen''") recalls the notion of the ''Haufen''. The German name for a forlorn hope is ''Verlorener Haufen'' ("Lost ''Haufen''"). See also * Verlorener Haufen * Baltringer Haufen * Schwarzer Haufen The Black Company o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
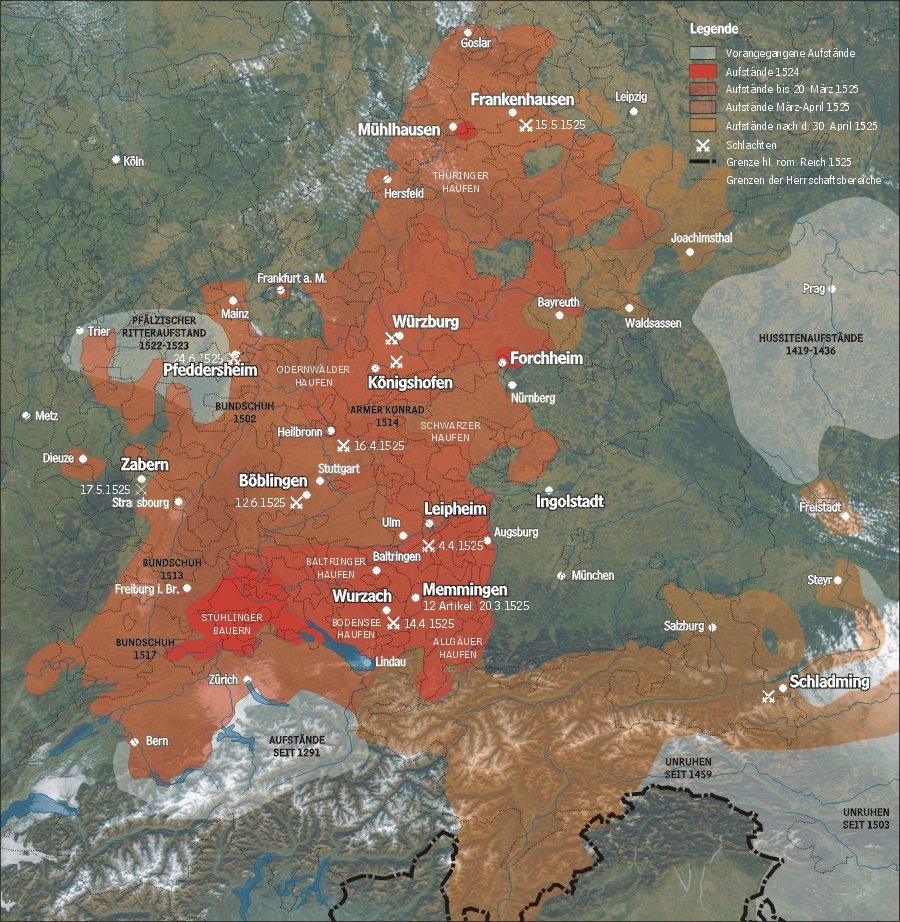
Baltringer Haufen
The Baltringer Haufen (also spelled ''Baltringer Haufe'', German for Baltringen Band, Baltringen Troop or Baltringen Mob) was prominent among several armed groups of peasants and artisan, craftsmen during the German Peasants' War of 1524–1525. The name derived from the small Upper Swabian village of Baltringen, which lies approximately south of Ulm in the district of Biberach (district), Biberach, Germany. In the early modern period the term ''Haufe(n)'' (literally: heap) denoted a lightly organised military formation particularly with regard to Landsknecht regiments. Formation of the ''Baltringer Haufen'' According to the account of a nun from nearby Heggbach Abbey, local peasants assembled and conferred in an inn at Baltringen for the first time on Christmas Eve 1524. From then on regular meetings took place, the number of attendants reaching 80 at the beginning of February 1525. Whereas in other regions the peasants met and discussed at markets, in Baltringen this occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwarzer Haufen
The Black Company or the Black Troops () was a unit of Franconian farmers and knights that fought on the side of the peasants during the Peasants' Revolt in the 1520s, during the Protestant Reformation in Germany. Name The original German name of the Black Company was . The term (black) pointed out the ideological distance of the company from the large peasant army at that time, which called itself the ( meaning "light-colored"). The German word was the name the peasants gave to their armed companies. It was never used again for an army, possibly because the word means "heap" in German and was used to refer to loosely organised armed rabbles. Formation The Black Company was formed in 1525 in Rothenburg, out of local, home guard farmers - maybe 600 men - and a company of mercenary knights. The leader of the Black Company, at least nominally, was nobleman Florian Geyer. Geyer managed to shape the Black Company into something like a company of real soldiers, instead of j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forlorn Hope
A forlorn hope is a band of soldiers or other combatants chosen to take the vanguard in a military operation, such as a suicidal assault through the kill zone of a defended position, or the first men to climb a scaling ladder against a defended fortification, where the risk of casualties is high. Such a band is also known as the (). Etymology The term comes from the Dutch , literally 'lost heap'. The term was used in military contexts to denote a troop formation. The Dutch word (in its sense of 'heap' in English) is not cognate with English 'hope': this is an example of folk etymology. The translation of as "forlorn hope" is "a quaint misunderstanding" using the nearest-sounding English words. This folk etymology has been strengthened by the fact that in Dutch, the word is a homograph meaning "hope" as well as "heap", although the two senses have different etymologies. History In the German mercenary armies of the , these troops were called the , which has the same mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florian Geyer
Florian Geyer von Giebelstadt (also spelled ''Geier''; ''c''. 1490 – 10 June 1525) was a German nobleman, diplomat, and knight. He became widely known for leading peasants during the German Peasants' War. Early life Florian Geyer was born around 1490 at Geyer Castle in Giebelstadt, Lower Franconia. After the deaths of his father Dietrich (in 1492) and of his two older brothers, Florian Geyer inherited the family castle and fortune. In 1512 and 1513, he was a guest at the court of King Henry VIII in England, where he may have been exposed to the reformist ideas of John Wycliffe and the Lollards. In 1517, after refusing to pay 350-year-old interest claims from Neumünster Collegiate Church, Geyer was excommunicated. In 1519, Geyer served under Casimir Margrave of Brandeburg-Kulmbach in the army of the Swabian League against Ulrich Duke of Württemberg and Götz von Berlichingen in Möckmühl. Later that year Brandeburg-Kulmbach sent Geyer to his brother Albrecht Duke of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramilitary
A paramilitary is an organization whose structure, tactics, training, subculture, and (often) function are similar to those of a professional military, but is not part of a country's official or legitimate armed forces. Paramilitary units carry out duties that a country's military or police forces are unable or unwilling to handle. Other organizations may be considered paramilitaries by structure alone, despite being unarmed or lacking a combat role. Overview Though a paramilitary is, by definition, not a military, it is usually equivalent to a light infantry force in terms of strength, firepower, and organizational structure. Paramilitaries use "military" equipment (such as long guns and armored personnel carriers; usually military surplus resources), skills (such as battlefield medicine and bomb disposal), and tactics (such as urban warfare and close-quarters combat) that are compatible with their purpose, often combining them with skills from other relevant fields such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliaries
Auxiliaries are support personnel that assist the military or police but are organised differently from regular forces. Auxiliary may be military volunteers undertaking support functions or performing certain duties such as garrison troops, usually on a part-time basis. Unlike a military reserve force, an auxiliary force does not necessarily have the same degree of training or ranking structure as regular soldiers, and it may or may not be integrated into a fighting force. Some auxiliaries, however, are militias composed of former active duty military personnel and actually have better training and combat experience than their regular counterparts. Historically, the designation ''auxiliary'' has also been given to foreign or allied troops in the service of a nation at war, most famously the eponymous '' Auxilia'' serving the Roman Empire. In the context of colonial troops, locally-recruited irregulars were often described as auxiliaries. Historical usage Roman auxiliari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area's history. The concept of "Central Europe" appeared in the 19th century. Central Europe comprised most of the territories of the Holy Roman Empire and those of the two neighboring kingdoms of Poland and Hungary. Hungary and parts of Poland were later part of the Habsburg monarchy, which also significantly shaped the history of Central Europe. Unlike their Western European (Portugal, Spain et al.) and Eastern European (Russia) counterparts, the Central European nations never had any notable colonies (either overseas or adjacent) due to their inland location and other factors. It has often been argued that one of the contributing causes of both World War I and World War II was Germany's lack of original overseas colonies. After Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peasants' War
This is a chronological list of conflicts in which peasants played a significant role. Background The history of peasant wars spans over two thousand years. A variety of factors fueled the emergence of the peasant revolt phenomenon, including: *Tax resistance *Social inequality *Religious war *National liberation *Resistance against serfdom *Redistribution of land *External factors such as plague and famine Later peasant revolts such as the Telangana Rebellion were also influenced by agrarian socialist ideologies such as Maoism. The majority of peasant rebellions ended prematurely and were unsuccessful. Peasants suffered from limited funding and lacked the training and organisational capabilities of professional armies. Chronological list The list gives the name, the date, the peasant allies and enemies, and the result of these conflicts following this legend: : : : : See also * Servile Wars * Peasant movement * Popular revolts in late-medieval Europe * Maoism * Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle, famine, and disease, while some areas of what is now modern Germany experienced population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. Until the 20th century, historians generally viewed it as a continuation of the religious struggle initiated by the 16th-century Reformation within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Lutheran and Catholic states, but over the next 50 years the expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries destabilised the settlement. While most modern commentators accept differences over religion and Imperial authority were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landsknecht
The (singular: , ), also rendered as Landsknechts or Lansquenets, were Germanic mercenaries used in pike and shot formations during the early modern period. Consisting predominantly of pikemen and supporting foot soldiers, their front line was formed by ''Doppelsöldner'' ("double-pay men") renowned for their use of '' Zweihänder'' and arquebus. Originally organized by Emperor Maximilian I and Georg von Frundsberg, they formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire's Imperial Army from the late 1400s to the early 1600s, fighting in the Habsburg-Valois wars, the Habsburg-Ottoman wars, and the European wars of religion. Although prone to mutiny if unpaid and divided within their ranks between Catholics and Lutherans, the ''Landsknechte'' were well-armed, experienced, and fierce warriors. In addition, they were recruitable in large numbers throughout Germany and Austria by the Holy Roman Emperor and thus guaranteed both quantity and quality to the Imperial military f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grassroots Democracy
Grassroots democracy is a tendency towards designing political processes that shift as much decision-making authority as practical to the organization's lowest geographic or social level of organization. Grassroots organizations can have a variety of structures; depending on the type of organization and what the members want. These can be non-structured and non-hierarchical organizations that are run by all members, or by whichever member wishes to do something. To cite a specific hypothetical example, a national grassroots organization would place as much decision-making power as possible in the hands of local chapters or common members instead of the head office. The principle is that for democratic power to be best exercised it must be vested in a local community and common members and instead of isolated, atomized individuals, at the top of the organization. Grassroots organizations can inhabit participatory systems. Grassroots systems differ from representative Rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |