|
Harvard Mark II
The Harvard Mark II, also known as the Aiken Relay Calculator, was an electromechanical computer built under the direction of Howard Aiken at Harvard University, completed in 1947. It was financed by the United States Navy and used for ballistic calculations at Naval Proving Ground Dahlgren. Howard Aiken and Grace Hopper worked together to build and program the Mark II. Overview The contract to build the Mark II was signed with Harvard in February 1945, after the successful demonstration of the Mark I in 1944. It was completed and debugged in 1947, and delivered to the US Navy Proving Ground at Dahlgren, Virginia in March 1948, becoming fully operational by the end of that year. The Mark II was constructed with high-speed electromagnetic relays instead of the electro-mechanical counters used in the Mark I, making it much faster than its predecessor. It weighed and occupied over of floor space. Its addition time was 0.125 seconds (8 Hz) and the multiplication time was 0. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Aiken
Howard Hathaway Aiken (March 8, 1900 – March 14, 1973) was an American physicist and a pioneer in computing, being the original conceptual designer behind IBM's Harvard Mark I computer. Biography Aiken studied at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and later obtained his Ph.D. in physics at Harvard University in 1939. During this time, he encountered differential equations that he could only solve numerically. Inspired by Charles Babbage's difference engine, he envisioned an electro-mechanical computing device that could do much of the tedious work for him. This computer was originally called the ASCC (Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator) and later renamed Harvard Mark I. With engineering, construction, and funding from IBM, the machine was completed and installed at Harvard in February 1944.Cohen, I. Bernard (1999). ''Howard Aiken: Portrait of a Computer Pioneer''. MIT Press. pp.73–114. Richard Milton Bloch, Robert Campbell and Grace Hopper joined the project l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stored-program Computer
A stored-program computer is a computer that stores program instructions in electronically or optically accessible memory. This contrasts with systems that stored the program instructions with plugboards or similar mechanisms. The definition is often extended with the requirement that the treatment of programs and data in memory be interchangeable or uniform. Description In principle, stored-program computers have been designed with various architectural characteristics. A computer with a von Neumann architecture stores program data and instruction data in the same memory, while a computer with a Harvard architecture has separate memories for storing program and data. However, the term ''stored-program computer'' is sometimes used as a synonym for the von Neumann architecture. Jack Copeland considers that it is "historically inappropriate, to refer to electronic stored-program digital computers as 'von Neumann machines'". Hennessy and Patterson wrote that the early Harvard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
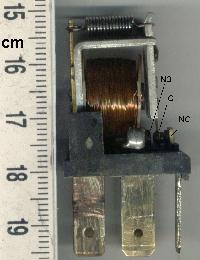
Electro-mechanical Computers
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems interact with each other. This process is especially prominent in systems such as those of DC or AC rotating electrical machines which can be designed and operated to generate power from a mechanical process ( generator) or used to power a mechanical effect (motor). Electrical engineering in this context also encompasses electronics engineering. Electromechanical devices are ones which have both electrical and mechanical processes. Strictly speaking, a manually operated switch is an electromechanical component due to the mechanical movement causing an electrical output. Though this is true, the term is usually understood to refer to devices which involve an electrical signal to create mechanical movement, or vice versa mechanical movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1940s Computers
Year 194 ( CXCIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Septimius and Septimius (or, less frequently, year 947 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 194 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Septimius Severus and Decimus Clodius Septimius Albinus Caesar become Roman Consuls. * Battle of Issus: Septimius Severus marches with his army (12 legions) to Cilicia, and defeats Pescennius Niger, Roman governor of Syria. Pescennius retreats to Antioch, and is executed by Severus' troops. * Septimius Severus besieges Byzantium (194–196); the city walls suffer extensive damage. Asia * Battle of Yan Province: Warlords Cao Cao and Lü Bu fight for control over Yan Province; the battle lasts for over 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Mark IV
The Harvard Mark IV was an electronic stored-program computer built by Harvard University under the supervision of Howard Aiken for the United States Air Force. The computer was finished being built in 1952. It stayed at Harvard, where the Air Force used it extensively. The Mark IV was all electronic. The Mark IV used magnetic drum and had 200 registers of ferrite magnetic-core memory (one of the first computers to do so). It separated the storage of data and instructions in what is known as the Harvard architecture. See also * Harvard Mark I * Harvard Mark II * Harvard Mark III * List of vacuum tube computers * Howard Aiken * Harvard (World War II advanced trainer aircraft) References Further reading *''A History of Computing Technology'', Michael R. Williams, 1997, IEEE Computer Society Press The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated discip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Architecture
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with separate storage and signal pathways for instructions and data. It contrasts with the von Neumann architecture, where program instructions and data share the same memory and pathways. The term originated from the Harvard Mark I relay-based computer, which stored instructions on punched tape (24 bits wide) and data in electro-mechanical counters. These early machines had data storage entirely contained within the central processing unit, and provided no access to the instruction storage as data. Programs needed to be loaded by an operator; the processor could not initialize itself. Modern processors appear to the user to be systems with von Neumann architectures, with the program code stored in the same main memory as the data. For performance reasons, internally and largely invisible to the user, most designs have separate processor caches for the instructions and data, with separate pathways into the processor fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instruction Set
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA), also called computer architecture, is an abstract model of a computer. A device that executes instructions described by that ISA, such as a central processing unit (CPU), is called an ''implementation''. In general, an ISA defines the supported instructions, data types, registers, the hardware support for managing main memory, fundamental features (such as the memory consistency, addressing modes, virtual memory), and the input/output model of a family of implementations of the ISA. An ISA specifies the behavior of machine code running on implementations of that ISA in a fashion that does not depend on the characteristics of that implementation, providing binary compatibility between implementations. This enables multiple implementations of an ISA that differ in characteristics such as performance, physical size, and monetary cost (among other things), but that are capable of running the same machine code, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Computer Bug, 1945
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1). First or 1st may also refer to: *World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement Arts and media Music * 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and record producer Albums * ''1st'' (album), a 1983 album by Streets * ''1st'' (Rasmus EP), a 1995 EP by The Rasmus, frequently identified as a single * '' 1ST'', a 2021 album by SixTones * ''First'' (Baroness EP), an EP by Baroness * ''First'' (Ferlyn G EP), an EP by Ferlyn G * ''First'' (David Gates album), an album by David Gates * ''First'' (O'Bryan album), an album by O'Bryan * ''First'' (Raymond Lam album), an album by Raymond Lam * ''First'', an album by Denise Ho Songs * "First" (Cold War Kids song), a song by Cold War Kids * "First" (Lindsay Lohan song), a song by Lindsay Lohan * "First", a song by Everglow from ''Last Melody'' * "First", a song by Lauren Daigle * "First", a song by Niki & Gabi * "First", a song by Jonas Brot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grace Hopper
Grace Brewster Hopper (; December 9, 1906 – January 1, 1992) was an American computer scientist, mathematician, and United States Navy rear admiral. One of the first programmers of the Harvard Mark I computer, she was a pioneer of computer programming who invented one of the first linkers. Hopper was the first to devise the theory of machine-independent programming languages, and the FLOW-MATIC programming language she created using this theory was later extended to create COBOL, an early high-level programming language still in use today. Prior to joining the Navy, Hopper earned a Ph.D. in mathematics from Yale University and was a professor of mathematics at Vassar College. Hopper attempted to enlist in the Navy during World War II but was rejected because she was 34 years old. She instead joined the Navy Reserves. Hopper began her computing career in 1944 when she worked on the Harvard Mark I team led by Howard H. Aiken. In 1949, she joined the Eckert–Mauchly Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Surface Warfare Center Dahlgren Division
The United States Naval Surface Warfare Center Dahlgren Division (NSWCDD), named for Rear Admiral John A. Dahlgren, is located in King George County, Virginia, in close proximity to the largest fleet concentration area in the Navy. NSWCDD is part of the Naval Surface Warfare Centers under the Naval Sea Systems Command (NAVSEA). NSWCDD was initially established 16 October 1918 as a remote extension of Maryland's Indian Head Proving Ground used for testing naval guns. The Dahlgren site was named the Lower Station, Dahlgren Naval Proving Ground when it first opened. The location on the Potomac River was specifically chosen for the development of a long ballistic test range on the Potomac River, required for the testing of modern, high-powered munitions.http://namdc.ahf.nmci.navy.mil/site%20pages/news/03-29-13_NSF_Dahlgren_profile_2013.pdf The NSWCDD employs approximately 4,700 scientists, engineers and support personnel at the Dalhgren organization and more than 350 at NSWCDD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |