|
Harold Redler
Lieutenant Harold Bolton Redler (27 January 1897 – 21 June 1918) was a British World War I flying ace credited with ten aerial victories. His most notable triumph was over a leading German ace, Adolf von Tutschek, whom he killed in action. Early life and family Harold Bolton Redler was born in West Monkton, Somerset, the eldest son of Daniel Bolton Redler and Annie Pethick (née Crocker). Redler's grandfather Thomas John Redler, was a grain merchant and miller. Around 1900 Daniel and his brother Arnold broke away from the family business to form their own company Daniel Redler & Co. Ltd., initially at the City Flour Mill, Worcester, but then moved to Sharpness, Gloucestershire, in 1909. The brothers later went their separate ways; with Arnold inventing a system of handling bulk materials, and later founding the Redler company, now part of the Schenck Process Group, while Daniel relocated to South Africa, where he was a founder and director of the Tiger Oats & National Mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of St Augustine, West Monkton
The Church of St Augustine in West Monkton, Somerset, England, dates from the 13th century and has been designated as a Grade I listed building. The parish church has an tower, of four stories, with no pinnacles or fancy tracery on the windows, giving the tower a slender, austere look compared to the medieval Somerset towers of churches in nearby Taunton, for example. Nikolaus Pevsner proposes that St Augustine's tower is older than the surrounding church towers, with a tower arch that may date to 1300 as part of a previous church building. The churchyard includes a stocks and whipping post under a canopy. See also * List of Grade I listed buildings in Taunton Deane * List of towers in Somerset * List of ecclesiastical parishes in the Diocese of Bath and Wells The ecclesiastical parishes within the Diocese of Bath and Wells cover the majority of the English county of Somerset and small areas of Devon, Dorset, Gloucestershire and Wiltshire. The episcopal seat of the Bish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nieuport 23
Nieuport, later Nieuport-Delage, was a French aeroplane company that primarily built racing aircraft before World War I and fighter aircraft during World War I and between the wars. History Beginnings Originally formed as Nieuport-Duplex in 1902 for the manufacture of engine components the company was reformed in 1909 as the Société Générale d'Aéro-locomotion, and its products were marketed to the aviation industry, including ignition components. During this time they built their first aircraft, a small single-seat pod and boom monoplane. This was destroyed shortly after having been flown successfully, during the Great Flood of Paris in 1909 . A second design flew before the end of 1909 and had the essential form of modern aircraft, including an enclosed fuselage with the pilot protected from the slipstream and a horizontal tail whose aerodynamic force acted downwards, balancing the weight of the engine ahead of the centre of gravity, as opposed to upwards as on contempo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
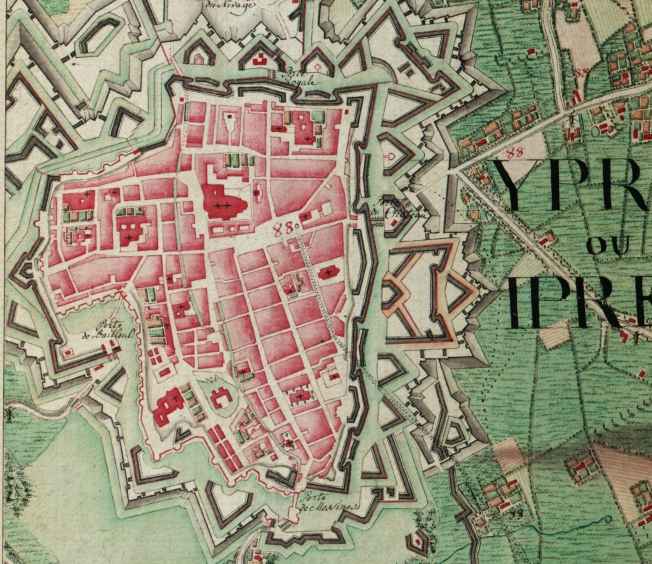
Ypres
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality comprises the city of Ypres/Ieper and the villages of Boezinge, Brielen, Dikkebus, Elverdinge, Hollebeke, Sint-Jan, Vlamertinge, Voormezele, Zillebeke, and Zuidschote. Together, they are home to about 34,900 inhabitants. During the First World War, Ypres (or "Wipers" as it was commonly known by the British troops) was the centre of the Battles of Ypres between German and Allied forces. History Origins before First World War Ypres is an ancient town, known to have been raided by the Romans in the first century BC. It is first mentioned by name in 1066 and is probably named after the river Ieperlee on the banks of which it was founded. During the Middle Ages, Ypres was a prosperous Flemish city with a population of 40,000 in 1200 A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observation Balloon
An observation balloon is a type of balloon that is employed as an aerial platform for intelligence gathering and artillery spotting. Use of observation balloons began during the French Revolutionary Wars, reaching their zenith during World War I, and they continue in limited use today. Synonyms include espionage balloon, reconnaissance balloon, or surveillance balloon. Historically, observation balloons were filled with hydrogen. The balloons were fabric envelopes filled with hydrogen gas, whose flammable nature led to the destruction of hundreds of balloons on both sides. Observers manning these observation balloons frequently had to use a parachute to evacuate their balloon when it came under attack. To avoid the potentially flammable consequences of hydrogen, observation balloons after World War I were often filled with non-flammable helium. Typically, balloons were tethered to a steel cable attached to a winch that reeled the gasbag to its desired height (usually 1,000-1,5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth War Graves Commission
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC) is an intergovernmental organisation of six independent member states whose principal function is to mark, record and maintain the graves and places of commemoration of Commonwealth of Nations military service members who died in the two World Wars. The commission is also responsible for commemorating Commonwealth civilians who died as a result of enemy action during the Second World War. The commission was founded by Sir Fabian Ware and constituted through Royal Charter in 1917 as the Imperial War Graves Commission. The change to the present name took place in 1960. The commission, as part of its mandate, is responsible for commemorating all Commonwealth war dead individually and equally. To this end, the war dead are commemorated by a name on a headstone, at an identified site of a burial, or on a memorial. War dead are commemorated uniformly and equally, irrespective of military or civil rank, race or creed. The commission i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gazetted
A gazette is an official journal, a newspaper of record, or simply a newspaper. In English and French speaking countries, newspaper publishers have applied the name ''Gazette'' since the 17th century; today, numerous weekly and daily newspapers bear the name ''The Gazette''. Etymology ''Gazette'' is a loanword from the French language, which is, in turn, a 16th-century permutation of the Italian ''gazzetta'', which is the name of a particular Venetian coin. ''Gazzetta'' became an epithet for ''newspaper'' during the early and middle 16th century, when the first Venetian newspapers cost one gazzetta. (Compare with other vernacularisms from publishing lingo, such as the British '' penny dreadful'' and the American ''dime novel''.) This loanword, with its various corruptions, persists in numerous modern languages (Slavic languages, Turkic languages). Government gazettes In England, with the 1700 founding of ''The Oxford Gazette'' (which became the ''London Gazette''), the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
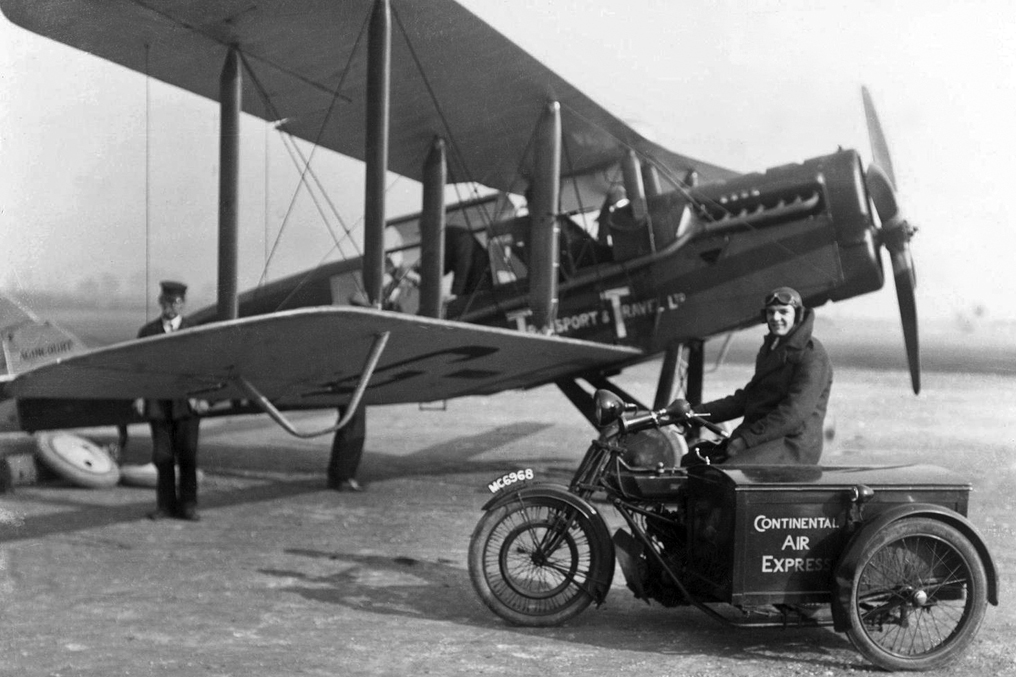
Airco DH
The Aircraft Manufacturing Company Limited (Airco) was an early British aircraft manufacturer. Established during 1912, it grew rapidly during the First World War, referring to itself as the largest aircraft company in the world by 1918. Airco produced many thousands of aircraft for both the British and Allied military air wings throughout the war, including fighters, trainers and bombers. The majority of the company's aircraft were designed in-house by Airco's chief designer Geoffrey de Havilland. Airco established the first airline in the United Kingdom, Aircraft Transport and Travel Limited, which operated as a subsidiary of Airco. On 25 August 1919, it commenced the world's first regular daily international service. Following the end of the war, the company's fortunes rapidly turned sour. The interwar period was unfavourable for aircraft manufacturers largely due to a glut of surplus aircraft from the war, while a lack of interest in aviation on the part of the Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Henderson (RAF Officer)
Captain Ian Henry David Henderson (2 October 1896 – 21 June 1918) was a British World War I flying ace credited with seven aerial victories. Biography He was the only son of Lieutenant-General Sir David Henderson (British Army officer), David Henderson, who served as Director-General of Military Aeronautics 1914–17, and as General Officer Commanding, Royal Flying Corps 1914–15, and his wife Dame Henrietta Caroline (née Dundas). Henderson graduated from the Royal Military College, Sandhurst, on 13 January 1915, and was commissioned as a second lieutenant in the Princess Louise's (Argyll and Sutherland Highlanders) regiment. He was seconded to the Royal Flying Corps, and was appointed a flying officer on 21 August 1915. He was promoted to lieutenant in his regiment on 21 January 1916, but had to wait until 1 June before receiving the same from the RFC. On 1 July he was appointed a flight commander with the acting rank of captain. Henderson was assigned to No. 19 Squadron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jasta 12
Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 12 was a World War I "hunting group" (i.e., fighter squadron) of the ''Luftstreitkräfte'', the air arm of the Imperial German Army during World War I. As one of the original German fighter squadrons, the unit would score 155 aerial victories (including three wins over observation balloons) during the war, at the expense of seventeen killed in action, eight wounded in action, and one taken prisoner of war. History Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 12 was created on 28 September 1916 from an existing ad hoc unit, Fokkerstaffel West. The new squadron mobilized on 12 October 1916 at Laon, France. It scored its first victory on 4 December 1916. The squadron was initially equipped with ill-performing Fokker D.Is. On 24 March 1917, the unit was credited with its tenth victory. The following month, Bloody April 1917, Jasta 12 downed 23 Royal Flying Corps aircraft. May saw 10 more victories. By the end of July, the jasta's scoreboard showed 74 victories. When it lost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fokker Dr
Fokker was a Dutch aircraft manufacturer named after its founder, Anthony Fokker. The company operated under several different names. It was founded in 1912 in Berlin, Germany, and became famous for its fighter aircraft in World War I. In 1919 the company moved its operations to the Netherlands. During its most successful period in the 1920s and 1930s, it dominated the civil aviation market. Fokker went into bankruptcy in 1996, and its operations were sold to competitors. History Fokker in Germany At age 20, while studying in Germany, Anthony Fokker built his initial aircraft, the ''Spin'' (Spider)—the first Dutch-built plane to fly in his home country. Taking advantage of better opportunities in Germany, he moved to Berlin, where in 1912, he founded his first company, Fokker Aeroplanbau, later moving to the Görries suburb just southwest of Schwerin (at ), where the current company was founded, as Fokker Aviatik GmbH, on 12 February 1912. World War I Fokker capitalized on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)