|
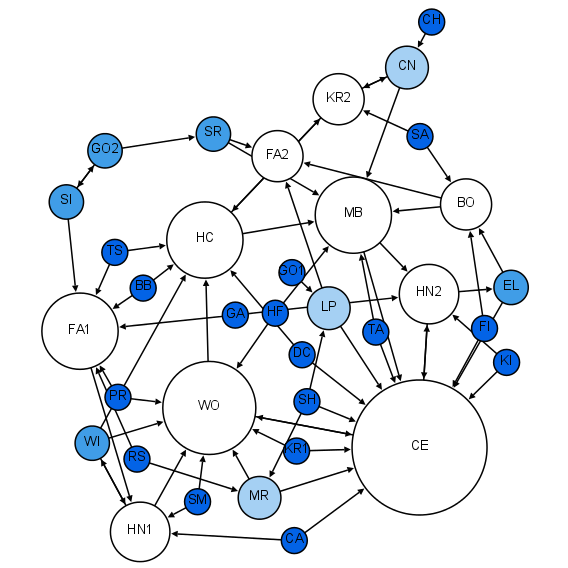
Hub (network Science)
In network science, a hub is a Node (networking), node with a number of links that greatly exceeds the average. Emergence of hubs is a consequence of a scale-free property of networks. While hubs cannot be observed in a random network, they are expected to emerge in scale-free networks. The uprise of hubs in scale-free networks is associated with power-law distribution. Hubs have a significant impact on the network topology. Hubs can be found in many real networks, such as the brain or the Internet. A hub is a component of a network with a high-degree Vertex (graph theory), node. Hubs have a significantly larger number of links in comparison with other nodes in the network. The number of links (Degree (graph theory), degrees) for a hub in a scale-free network is much higher than for the biggest node in a random network, keeping the size ''N'' of the network and average degree constant. The existence of hubs is the biggest difference between random networks and scale-free networks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Science
Network science is an academic field which studies complex networks such as telecommunication networks, computer networks, biological networks, Cognitive network, cognitive and semantic networks, and social networks, considering distinct elements or actors represented by ''nodes'' (or ''vertices'') and the connections between the elements or actors as ''links'' (or ''edges''). The field draws on theories and methods including graph theory from mathematics, statistical mechanics from physics, data mining and information visualization from computer science, inferential statistics, inferential modeling from statistics, and social structure from sociology. The United States National Research Council defines network science as "the study of network representations of physical, biological, and social phenomena leading to predictive models of these phenomena." Background and history The study of networks has emerged in diverse disciplines as a means of analyzing complex relational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilfredo Pareto
Vilfredo Federico Damaso Pareto (; ; born Wilfried Fritz Pareto; 15 July 1848 – 19 August 1923) was an Italian polymath, whose areas of interest included sociology, civil engineering, economics, political science, and philosophy. He made several important contributions to economics, particularly in the study of income distribution and in the analysis of individuals' choices, and was one of the minds behind the Lausanne School of economics. He was also responsible for popularising the use of the term '' elite'' in social analysis and contributed to elite theory. He has been described as "one of the last Renaissance scholars. Trained in physics and mathematics, he became a polymath whose genius radiated into nearly all other major fields of knowledge." He introduced the concept of Pareto efficiency and helped develop the field of microeconomics. He was also the first to claim that income follows a Pareto distribution, which is a power law probability distribution. The Paret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Law
In statistics, a power law is a Function (mathematics), functional relationship between two quantities, where a Relative change and difference, relative change in one quantity results in a relative change in the other quantity proportional to the change raised to a constant exponent: one quantity varies as a power of another. The change is independent of the initial size of those quantities. For instance, the area of a square has a power law relationship with the length of its side, since if the length is doubled, the area is multiplied by 2, while if the length is tripled, the area is multiplied by 3, and so on. Empirical examples The distributions of a wide variety of physical, biological, and human-made phenomena approximately follow a power law over a wide range of magnitudes: these include the sizes of craters on the moon and of solar flares, cloud sizes, the foraging pattern of various species, the sizes of activity patterns of neuronal populations, the frequencies of words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preferential Attachment
A preferential attachment process is any of a class of processes in which some quantity, typically some form of wealth or credit, is distributed among a number of individuals or objects according to how much they already have, so that those who are already wealthy receive more than those who are not. "Preferential attachment" is only the most recent of many names that have been given to such processes. They are also referred to under the names Yule process, cumulative advantage, the rich get richer, and the Matthew effect. They are also related to Gibrat's law. The principal reason for scientific interest in preferential attachment is that it can, under suitable circumstances, generate power law distributions. If preferential attachment is non-linear, measured distributions may deviate from a power law. These mechanisms may generate distributions which are approximately power law over transient periods. Definition A preferential attachment process is a stochastic urn p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reviews Of Modern Physics
''Reviews of Modern Physics'' (often abbreviated RMP) is a quarterly Peer review, peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Physical Society. It was established in 1929 and the current editor-in-chief is Michael Thoennessen. The journal publishes review articles, usually by established researchers, on all aspects of physics and related fields. The reviews are usually accessible to non-specialists and serve as introductory material to graduate students, which survey recent work, discuss key problems to be solved and provide perspectives toward the end. The journal has published several historically significant papers on quantum foundations, as well as the development of the Standard Model of particle physics. References External links * Academic journals established in 1929 Physics review journals Quarterly journals English-language journals American Physical Society academic journals {{physics-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erdős–Rényi Model
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Erdős–Rényi model refers to one of two closely related models for generating random graphs or the evolution of a random network. These models are named after Hungarians, Hungarian mathematicians Paul Erdős and Alfréd Rényi, who introduced one of the models in 1959. Edgar Gilbert introduced the other model contemporaneously with and independently of Erdős and Rényi. In the model of Erdős and Rényi, all graphs on a fixed vertex set with a fixed number of edges are equally likely. In the model introduced by Gilbert, also called the Erdős–Rényi–Gilbert model, each edge has a fixed probability of being present or absent, statistical independence, independently of the other edges. These models can be used in the probabilistic method to prove the existence of graphs satisfying various properties, or to provide a rigorous definition of what it means for a property to hold for almost all graphs. Definition There are two clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barabási–Albert Model
The Barabási–Albert (BA) model is an algorithm for generating random scale-free network, scale-free complex network, networks using a preferential attachment mechanism. Several natural and human-made systems, including the Internet, the World Wide Web, citation analysis, citation networks, and some social networks are thought to be approximately scale-free and certainly contain few nodes (called hubs) with unusually high degree as compared to the other nodes of the network. The BA model tries to explain the existence of such nodes in real networks. The algorithm is named for its inventors Albert-László Barabási and Réka Albert. Concepts Many observed networks (at least approximately) fall into the class of scale-free networks, meaning that they have power law, power-law (or scale-free) degree distributions, while random graph models such as the Erdős–Rényi model, Erdős–Rényi (ER) model and the Watts and Strogatz model, Watts–Strogatz (WS) model do not exhibit po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree (graph Theory)
In graph theory, the degree (or valency) of a vertex of a graph is the number of edges that are incident to the vertex; in a multigraph, a loop contributes 2 to a vertex's degree, for the two ends of the edge. The degree of a vertex v is denoted \deg(v) or \deg v. The maximum degree of a graph G is denoted by \Delta(G), and is the maximum of G's vertices' degrees. The minimum degree of a graph is denoted by \delta(G), and is the minimum of G's vertices' degrees. In the multigraph shown on the right, the maximum degree is 5 and the minimum degree is 0. In a regular graph, every vertex has the same degree, and so we can speak of ''the'' degree of the graph. A complete graph (denoted K_n, where n is the number of vertices in the graph) is a special kind of regular graph where all vertices have the maximum possible degree, n-1. In a signed graph, the number of positive edges connected to the vertex v is called positive deg(v) and the number of connected negative edges is enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Node (networking)
In Computer network, networking, a node (, ‘knot’) is either a redistribution point or a communication endpoint within telecommunication networks. A physical network node is an electronic device that is attached to a network, and is capable of creating, receiving, or transmitting information over a communication channel. In data communication, a physical network node may either be data communication equipment (such as a modem, Network hub, hub, Network bridge, bridge or Network switch, switch) or data terminal equipment (such as a digital telephone handset, a printer or a host computer). A Passivity (engineering), passive distribution point such as a distribution frame or patch panel is not a node. Computer networks In data communication, a physical network node may either be data communication equipment (DCE) such as a modem, Network hub, hub, Network bridge, bridge or Network switch, switch; or data terminal equipment (DTE) such as a digital telephone handset, a printe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (graph Theory)
In discrete mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a vertex (plural vertices) or node is the fundamental unit of which graphs are formed: an undirected graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of edges (unordered pairs of vertices), while a directed graph consists of a set of vertices and a set of arcs (ordered pairs of vertices). In a diagram of a graph, a vertex is usually represented by a circle with a label, and an edge is represented by a line or arrow extending from one vertex to another. From the point of view of graph theory, vertices are treated as featureless and indivisible objects, although they may have additional structure depending on the application from which the graph arises; for instance, a semantic network is a graph in which the vertices represent concepts or classes of objects. The two vertices forming an edge are said to be the endpoints of this edge, and the edge is said to be incident to the vertices. A vertex ''w'' is said to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Map 4096
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, internet telephony, streaming media and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable internetworking on the Internet arose from research and development commissioned in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |