|
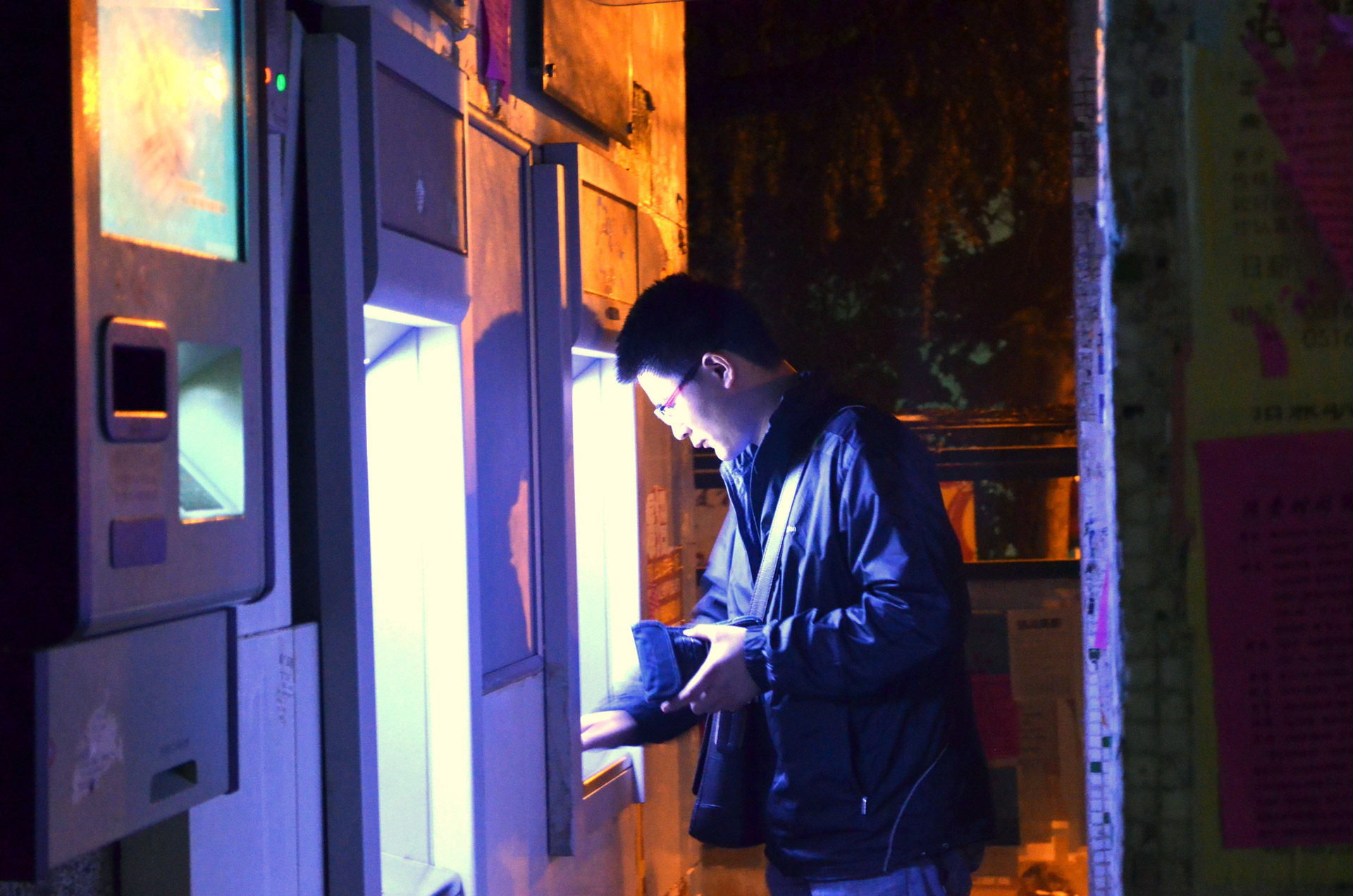
Hotspot (Wi-Fi)
A hotspot is a physical location where people can obtain Internet access, typically using Wi-Fi technology, via a wireless local-area network (WLAN) using a router connected to an Internet service provider. Public hotspots may be created by a business for use by customers, such as coffee shops or hotels. Public hotspots are typically created from wireless access points configured to provide Internet access, controlled to some degree by the venue. In its simplest form, venues that have broadband Internet access can create public wireless access by configuring an access point (AP), in conjunction with a router to connect the AP to the Internet. A single wireless router combining these functions may suffice. A private hotspot, often called tethering, may be configured on a smartphone or tablet that has a network data plan, to allow Internet access to other devices via password, Bluetooth pairing, or through the moeex protocol over USB, or even when both the hotspot devic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WI-FI Range Diagram
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, restaurants, hotels, libraries, and airports. ''Wi-Fi'' is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term "''Wi-Fi Certified''" to products that successfully complete interoperability certification testing. Non-compliant hardware is simply referred to as WLAN, and it may or may not work with "''Wi-Fi Certified''" devices. the Wi-Fi Alliance consisted of more than 800 companies from around the world. over 3.05 billion Wi-Fi-enabled devices are shipped globally each year. Wi-Fi uses m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geolocation
Geopositioning is the process of determining or estimating the geographic position of an object or a person. Geopositioning yields a set of Geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinates (such as latitude and longitude) in a given map datum. Geographic positions may also be expressed indirectly, as a distance in linear referencing or as a bearing and range from a known landmark. In turn, positions can determine a meaningful location, such as a street address. Geoposition is sometimes referred to as ''geolocation'', and the process of geopositioning may also be described as ''geo-localization''. Specific instances include: * animal geotracking, the process of inferring the location of animals over time; * positioning system, the mechanisms for the determination of geographic positions in general; * internet geolocation, geolocating a device connected to the internet; * and mobile phone tracking. Geofencing ''Geofencing'' involves creating a virtual geographic boundary (a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WPA3
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) (Wireless Protected Access), Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2), and Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) are the three security certification programs developed after 2000 by the Wi-Fi Alliance to secure wireless computer networks. The Alliance defined these in response to serious weaknesses researchers had found in the previous system, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP). WPA (sometimes referred to as the TKIP standard) became available in 2003. The Wi-Fi Alliance intended it as an intermediate measure in anticipation of the availability of the more secure and complex WPA2, which became available in 2004 and is a common shorthand for the full IEEE 802.11i (or IEEE 802.11i-2004) standard. In January 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance announced the release of WPA3, which has several security improvements over WPA2. As of 2023, most computers that connect to a wireless network have support for using WPA, WPA2, or WPA3. All versions thereof, at least as implemented throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encrypted Communication
Secure communication is when two entities are communicating and do not want a third party to listen in. For this to be the case, the entities need to communicate in a way that is unsusceptible to eavesdropping or Signals intelligence, interception. Secure communication includes means by which people can share information with varying degrees of certainty that third parties cannot intercept what is said. Other than spoken face-to-face communication with no possible eavesdropper, it is probable that no communication is guaranteed to be secure in this sense, although practical obstacles such as legislation, resources, technical issues (interception and encryption), and the sheer volume of communication serve to limit surveillance. With many communications taking place over long distance and mediated by technology, and increasing awareness of the importance of interception issues, technology and its compromise are at the heart of this debate. For this reason, this article focuses on co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opportunistic Wireless Encryption
Opportunistic Wireless Encryption (OWE) is a Wi-Fi standard which ensures that communication between a public hotspot and end devices is protected from other end devices. In contrast to conventional public hotspots, the data is transmitted in encrypted form. ''OWE'' was introduced by the Wi-Fi Alliance in 2018 as part of the Wi-Fi Certified Enhanced Open program. OWE is an extension to IEEE 802.11. it is an encryption technique similar to that of Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) and is specified by Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in RFC 8110 with devices certified as Wi-Fi Certified Enhanced Open by the Wi-Fi Alliance. With a network without a password, each WPA3 device that connects to it will still have its connection encrypted, OWE does encryption, not authentication, Evil twin (wireless networks) attack protection requires either WPA3-Personal or WPA3-Enterprise. Unlike conventional Wi-Fi, it provides "Individualized Data Protection" such that data traffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
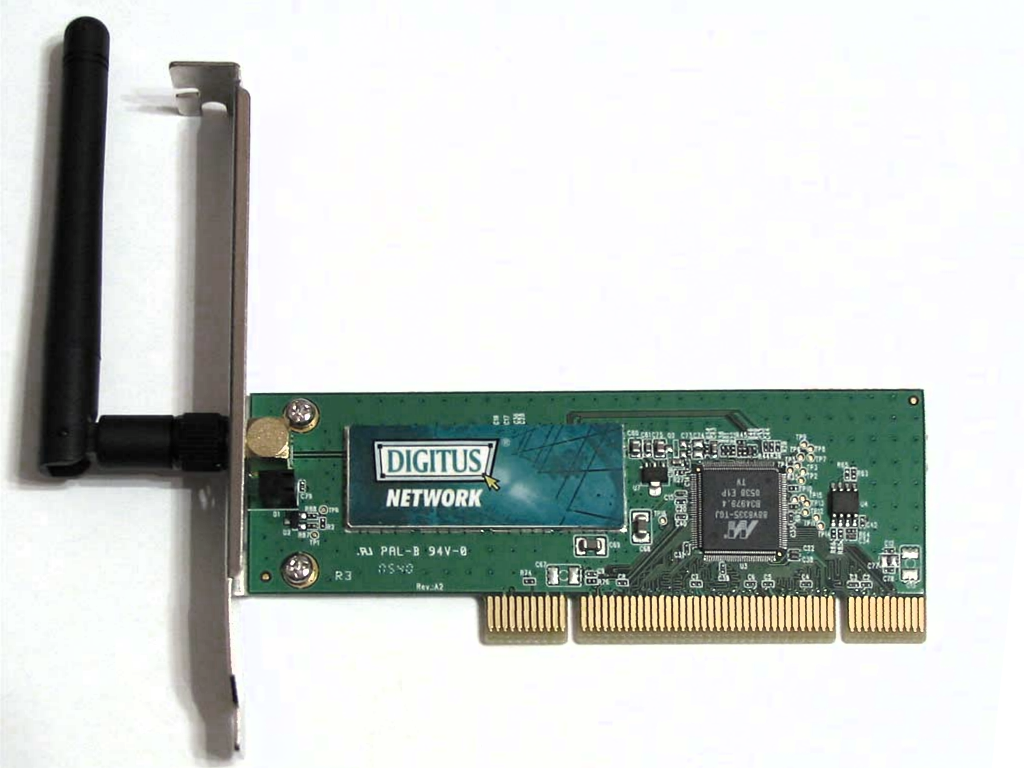
WLAN
A wireless LAN (WLAN) is a wireless computer network that links two or more devices using wireless communication to form a local area network (LAN) within a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, campus, or office building. This gives users the ability to move around within the area and remain connected to the network. Through a gateway, a WLAN can also provide a connection to the wider Internet. Wireless LANs based on the IEEE 802.11 standards are the most widely used computer networks in the world. These are commonly called Wi-Fi, which is a trademark belonging to the Wi-Fi Alliance. They are used for home and small office networks that link together laptop computers, printers, smartphones, Web TVs and gaming devices through a wireless network router, which in turn may link them to the Internet. Hotspots provided by routers at restaurants, coffee shops, hotels, libraries, and airports allow consumers to access the internet with portable wireless de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WPA-PSK
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) (Wireless Protected Access), Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2), and Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) are the three security certification programs developed after 2000 by the Wi-Fi Alliance to secure wireless computer networks. The Alliance defined these in response to serious weaknesses researchers had found in the previous system, Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP). WPA (sometimes referred to as the TKIP standard) became available in 2003. The Wi-Fi Alliance intended it as an intermediate measure in anticipation of the availability of the more secure and complex WPA2, which became available in 2004 and is a common shorthand for the full IEEE 802.11i (or IEEE 802.11i-2004) standard. In January 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance announced the release of WPA3, which has several security improvements over WPA2. As of 2023, most computers that connect to a wireless network have support for using WPA, WPA2, or WPA3. All versions thereof, at least as implemented throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packet Sniffer
A packet analyzer (also packet sniffer or network analyzer) is a computer program or computer hardware such as a packet capture appliance that can Traffic analysis, analyze and Logging (computing), log traffic that passes over a computer network or part of a network. Packet capture is the process of intercepting and logging traffic. As data streams flow across the network, the analyzer captures each Network packet, packet and, if needed, decodes the packet's raw data, showing the values of various fields in the packet, and analyzes its content according to the appropriate Request for Comments, RFC or other specifications. A packet analyzer used for intercepting traffic on wireless networks is known as a wireless analyzer - those designed specifically for Wi-Fi networks are Wi-Fi analyzers. While a packet analyzer can also be referred to as a Network analyzer (other), network analyzer or protocol analyzer these terms can also have other meanings. Protocol analyzer can t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authenticate
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an assertion, such as the identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicating a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of verifying that identity. Authentication is relevant to multiple fields. In art, antiques, and anthropology, a common problem is verifying that a given artifact was produced by a certain person, or in a certain place (i.e. to assert that it is not counterfeit), or in a given period of history (e.g. by determining the age via carbon dating). In computer science, verifying a user's identity is often required to allow access to confidential data or systems. It might involve validating personal identity documents. In art, antiques and anthropology Authentication can be considered to be of three types: The ''first'' type of authentication is accepting proof of identity given by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure Shell
The Secure Shell Protocol (SSH Protocol) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Its most notable applications are remote login and command-line execution. SSH was designed for Unix-like operating systems as a replacement for Telnet and unsecured remote Unix shell protocols, such as the Berkeley Remote Shell (rsh) and the related rlogin and rexec protocols, which all use insecure, plaintext methods of authentication, like passwords. Since mechanisms like Telnet and Remote Shell are designed to access and operate remote computers, sending the authentication tokens (e.g. username and password) for this access to these computers across a public network in an unsecured way poses a great risk of 3rd parties obtaining the password and achieving the same level of access to the remote system as the telnet user. Secure Shell mitigates this risk through the use of encryption mechanisms that are intended to hide th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTP Secure
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It uses encryption for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or, formerly, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). The protocol is therefore also referred to as HTTP over TLS, or HTTP over SSL. The principal motivations for HTTPS are authentication of the accessed website and protection of the privacy and integrity of the exchanged data while it is in transit. It protects against man-in-the-middle attacks, and the bidirectional block cipher encryption of communications between a client and server protects the communications against eavesdropping and tampering. The authentication aspect of HTTPS requires a trusted third party to sign server-side digital certificates. This was historically an expensive operation, which meant fully authenticated HTTPS connection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End-to-end Encryption
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a method of implementing a secure communication system where only communicating users can participate. No one else, including the system provider, telecom providers, Internet providers or malicious actors, can access the cryptographic keys needed to read or send messages. End-to-end encryption prevents data from being read or secretly modified, except by the true sender and intended recipients. Frequently, the messages are relayed from the sender to the recipients by a service provider. However, messages are encrypted by the sender and no third party, including the service provider, has the means to decrypt them. The recipients retrieve the encrypted messages and decrypt them independently. Since third parties cannot decrypt the data being communicated or stored, services that provide end-to-end encryption are better at protecting user data when they are affected by data breaches. Such services are also unable to share user data with governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |