|
Hitting The Wall
In endurance sports such as road cycling and long-distance running, hitting the wall or the bonk is a condition of sudden fatigue and loss of energy which is caused by the depletion of glycogen stores in the liver and muscles. Milder instances can be remedied by brief rest and the ingestion of food or drinks containing carbohydrates. Otherwise, it can be remedied by attaining second wind by either resting for approximately 10 minutes or by slowing down considerably and increasing speed slowly over a period of 10 minutes. Ten minutes is approximately the time that it takes for free fatty acids to sufficiently produce ATP in response to increased demand. During a marathon, for instance, runners typically hit the wall around kilometer 30 (mile 20). The condition can usually be avoided by ensuring that glycogen levels are high when the exercise begins, maintaining glucose levels during exercise by eating or drinking carbohydrate-rich substances, or by reducing exercise intensity. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statue Of The Tired Man
A statue is a free-standing sculpture in which the realistic, full-length figures of persons or animals are carved or cast in a durable material such as wood, metal or stone. Typical statues are life-sized or close to life-size. A sculpture that represents persons or animals in full figure, but that is small enough to lift and carry is a ''statuette'' or figurine, whilst those that are more than twice life-size are regarded as ''colossal statues''. Statues have been produced in many cultures from prehistory to the present; the oldest-known statue dating to about 30,000 years ago. Statues represent many different people and animals, real and mythical. Many statues are placed in public places as public art. The world's tallest statue, ''Statue of Unity'', is tall and is located near the Narmada dam in Gujarat, India. Colors Ancient statues often show the bare surface of the material of which they are made. For example, many people associate Greek classical art with white marb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shortness Of Breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of its distinct sensations, the degree of distress and discomfort involved, and its burden or impact on the patient's activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work to breathe, chest tightness or pain, and "air hunger" (the feeling of not enough oxygen). The tripod position is often assumed to be a sign. Dyspnea is a normal symptom of heavy physical exertion but becomes disease, pathological if it occurs in unexpected situations, when resting or during light exertion. In 85% of cases it is due to asthma, pneumonia, cardiac ischemia, reflux/LPR, cardiac ischemia, COVID-19, interstitial lung di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inborn Errors Of Carbohydrate Metabolism
Inborn errors of carbohydrate metabolism are inborn errors of metabolism that affect the catabolism and anabolism of carbohydrates. An example is lactose intolerance. Carbohydrates account for a major portion of the human diet. These carbohydrates are composed of three principal monosaccharides: glucose, fructose and galactose; in addition glycogen is the storage form of carbohydrates in humans. The failure to effectively use these molecules accounts for the majority of the inborn errors of human carbohydrates metabolism. By Carbohydrate Glycogen and Glucose Glycogen storage diseases are deficiencies of enzymes or transport proteins which impair glycogen synthesis, glycogen degradation or glycolysis. The two organs most commonly affected are the liver and the skeletal muscle. Glycogen storage diseases that affect the liver typically cause hepatomegaly and hypoglycemia; those that affect skeletal muscle cause exercise intolerance, progressive weakness and cramping. Gluco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen Storage Disease
A glycogen storage disease (GSD, also glycogenosis and dextrinosis) is a metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency of an enzyme or transport protein affecting glycogen synthesis, glycogen breakdown, or glycolysis, glucose breakdown, typically in muscles and/or liver cells. GSD has two classes of cause: genetic and environmental. Genetic GSD is caused by any Inborn errors of carbohydrate metabolism, inborn error of carbohydrate metabolism (genetically defective enzymes or transport proteins) involved in these processes. In livestock, environmental GSD is caused by Substance intoxication, intoxication with the alkaloid castanospermine. However, not every inborn error of carbohydrate metabolism has been assigned a GSD number, even if it is known to affect the muscles or liver. For example, phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency (gene PGK1) has a myopathic form. Also, Fanconi–Bickel syndrome, Fanconi-Bickel syndrome (gene SLC2A2) and Danon disease (gene LAMP2) were declassed as GSDs d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uric Acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the Chemical formula, formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. Hyperuricemia, High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones. Chemistry Uric acid was first isolated from kidney stones in 1776 by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. In 1882, the Ukrainian chemist Ivan Horbaczewski first synthesized uric acid by melting urea with glycine. Uric acid displays lactam–lactim tautomerism. Uric acid crystallizes in the lactam form, with computational chemistry also indicating that tautomer to be the most stable. Uric acid is a diprotic acid with pKa, p''K''a1 = 5.4 and p''K''a2 =&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoglobinuria
Myoglobinuria is the presence of myoglobin in the urine, which usually results from rhabdomyolysis or muscle injury. Myoglobin is present in muscle cells as a reserve of oxygen. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of myoglobinuria are usually nonspecific and needs some clinical prudence. Therefore, among the possible signs and symptoms to look for would be: *Swollen and painful muscles *Fever, nausea *Delirium (elderly individuals) *Myalgia *Dark urine * Calcium ion loss Causes Trauma, vascular problems, malignant hyperthermia, certain drugs and other situations can destroy or damage the muscle, releasing myoglobin to the circulation and thus to the kidneys. Under ideal situations myoglobin will be filtered and excreted with the urine, but if too much myoglobin is released into the circulation or in case of kidney problems, it can occlude the kidneys' filtration system leading to acute tubular necrosis and acute kidney injury. Other causes of myoglobinuria include: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis (shortened as rhabdo) is a condition in which damaged skeletal muscle breaks down rapidly. Symptoms may include muscle pains, weakness, vomiting, and confusion. There may be tea-colored urine or an irregular heartbeat. Some of the muscle breakdown products, such as the protein myoglobin, are harmful to the kidneys and can cause acute kidney injury. The muscle damage is most usually caused by a crush injury, strenuous exercise, medications, or a substance use disorder. Other causes include infections, electrical injury, heat stroke, prolonged immobilization, lack of blood flow to a limb, or snake bites as well as intense or prolonged exercise, particularly in hot conditions. Statins (prescription drugs to lower cholesterol) are considered a small risk. Some people have inherited muscle conditions that increase the risk of rhabdomyolysis. The diagnosis is supported by a urine test strip which is positive for "blood" but the urine contains no red blood c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purine Nucleotide Cycle
The Purine Nucleotide Cycle is a metabolic pathway in protein metabolism requiring the amino acids aspartate and glutamate. The cycle is used to regulate the levels of adenine nucleotides, in which ammonia and fumarate are generated. AMP converts into IMP and the byproduct ammonia. IMP converts to S-AMP ( adenylosuccinate), which then converts to AMP and the byproduct fumarate. The fumarate goes on to produce ATP (energy) via oxidative phosphorylation as it enters the Krebs cycle and then the electron transport chain. Lowenstein first described this pathway and outlined its importance in processes including amino acid catabolism and regulation of flux through glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. AMP is produced after strenuous muscle contraction when the ATP reservoir is low (ADP > ATP) by the adenylate kinase (myokinase) reaction. AMP is also produced from adenine and adenosine directly; however, AMP can be produced through less direct metabolic pathways, such as de novo synth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenylate Kinase
Adenylate kinase ( ECbr>2.7.4.3 (also known as ADK or myokinase) is a phosphotransferase enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of the various adenosine phosphates (ATP, ADP, and AMP). By constantly monitoring phosphate nucleotide levels inside the cell, ADK plays an important role in cellular energy homeostasis. Substrate and products The reaction catalyzed is: ATP + AMP ⇔ 2 ADP The equilibrium constant varies with condition, but it is close to 1. Thus, ΔGo for this reaction is close to zero. In muscle from a variety of species of vertebrates and invertebrates, the concentration of ATP is typically 7-10 times that of ADP, and usually greater than 100 times that of AMP. The rate of oxidative phosphorylation is controlled by the availability of ADP. Thus, the mitochondrion attempts to keep ATP levels high due to the combined action of adenylate kinase and the controls on oxidative phosphorylation. Isozymes To date there have been nine human ADK protein isoforms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyruvic Acid
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the keto acids, alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate acid, conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an metabolic intermediate, intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell. Pyruvic acid can be made from glucose through glycolysis, converted back to carbohydrates (such as glucose) via gluconeogenesis, or converted to fatty acids through a reaction with acetyl-CoA. It can also be used to construct the amino acid alanine and can be converted into ethanol or lactic acid via fermentation. Pyruvic acid supplies energy to cell (biology), cells through the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) when oxygen is present (aerobic respiration), and alternatively lactic acid fermentation, ferments to produce lactic acid, lactate when oxygen is lacking. Chemistry In 1834, Théophile-Jules Pelouze distilled tartaric acid and isolated glutaric acid and another unknown organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
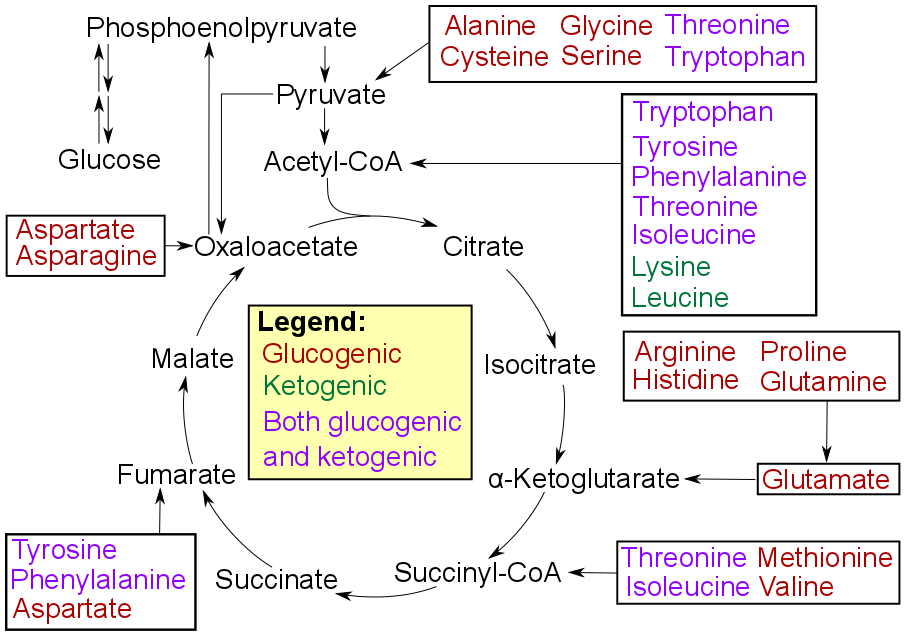
Protein Catabolism
In molecular biology, protein catabolism is the breakdown of proteins into smaller peptides and ultimately into amino acids. Protein catabolism is a key function of digestion process. Protein catabolism often begins with pepsin, which converts proteins into polypeptides. These polypeptides are then further degraded. In humans, the pancreatic proteases include trypsin, chymotrypsin, and other enzymes. In the intestine, the small peptides are broken down into amino acids that can be absorbed into the bloodstream. These absorbed amino acids can then undergo amino acid catabolism, where they are utilized as an energy source or as precursors to new proteins. The amino acids produced by catabolism may be directly recycled to form new proteins, converted into different amino acids, or can undergo amino acid catabolism to be converted to other compounds via the Krebs cycle. Interface with other metabolic and salvage pathways Protein catabolism produces amino acids that are used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |