|
History Of The Jews In Sofia
As per th2021 Bulgarian census the Jews in Sofia number around 901. Sofia had Jewish inhabitants before the ninth century; and in 811 the community was joined by coreligionists among the 30,000 prisoners whom the Bulgarian czar Krum brought with him on his return from an expedition against Thessaly, while a number of Jewish emigrants from the Byzantine Empire voluntarily settled in Sofia in 967. In 1360 some Jews from the south of Germany established themselves in the city, and their number was augmented seven years later by Jews driven from Hungary. When Murad I. seized Sofia, about 1389, he found four synagogues, belonging respectively to the Byzantine Jews, Byzantines ("ḳahal de los Gregos"), the Ashkenazim, the "Francos," or Italian Jews (especially those of Venice), and the native Jews. According to local statements, a Macedonian and a Maltese synagogue, founded at dates as yet unascertained, existed in Sofia up to the middle of the nineteenth century. Early in the fifteent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion, and community are highly interrelated, as Judaism is their ethnic religion, though it is not practiced by all ethnic Jews. Despite this, religious Jews regard Gerim, converts to Judaism as members of the Jewish nation, pursuant to the Conversion to Judaism, long-standing conversion process. The Israelites emerged from the pre-existing Canaanite peoples to establish Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Israel and Kingdom of Judah, Judah in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age.John Day (Old Testament scholar), John Day (2005), ''In Search of Pre-Exilic Israel'', Bloomsbury Publishing, pp. 47.5 [48] 'In this sense, the emergence of ancient Israel is viewed not as the cause of the demise of Canaanite culture but as its upshot'. Originally, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabbatai Zevi
Sabbatai Zevi (, August 1, 1626 – ) was an Ottoman Jewish mystic and ordained rabbi from Smyrna (now İzmir, Turkey). His family were Romaniote Jews from Patras. His two names, ''Shabbethay'' and ''Ṣebi'', mean Saturn and mountain gazelle, respectively. Active throughout the Ottoman Empire, Zevi claimed to be the long-awaited Jewish Messiah and founded the Sabbatean movement. Central to his teachings was the belief that during the Messianic Age, acts traditionally considered sinful would transform into righteous ones. This antinomian doctrine led Zevi and his followers to deliberately violate Jewish commandments, a controversial practice that later inspired movements like the Frankists. Upon arriving in Constantinople in February 1666, Sabbatai was imprisoned on the order of the grand vizier Köprülüzade Fazıl Ahmed Pasha. In September of that same year, after being moved from different prisons around the capital to the imperial courts' seat in Adrianople (now Edi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
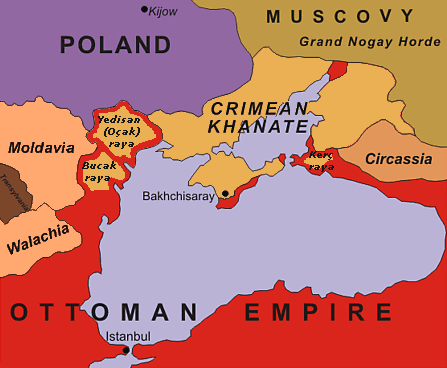
Turko-Russian War
The Russo-Turkish wars ( ), or the Russo-Ottoman wars (), began in 1568 and continued intermittently until 1918. They consisted of twelve conflicts in total, making them one of the longest series of wars in the history of Europe. All but four of these wars ended in losses for the Ottoman Empire, which was undergoing a period of stagnation and decline. Conversely, they showcased the ascendancy of the Russian Empire as a significant European power after Peter the Great oversaw extensive modernization efforts in the early 18th century. Ultimately, however, the end of the Russo-Turkish wars came about with the dissolution of the two belligerents' respective states as a consequence of World War I: the Russian Empire collapsed in 1917 and was ultimately succeeded by the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in 1922; while the Ottoman Empire was partitioned between 1918 and 1922 and succeeded by the Republic of Turkey in 1923. History Initial and intermediate phases (1568–1739) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
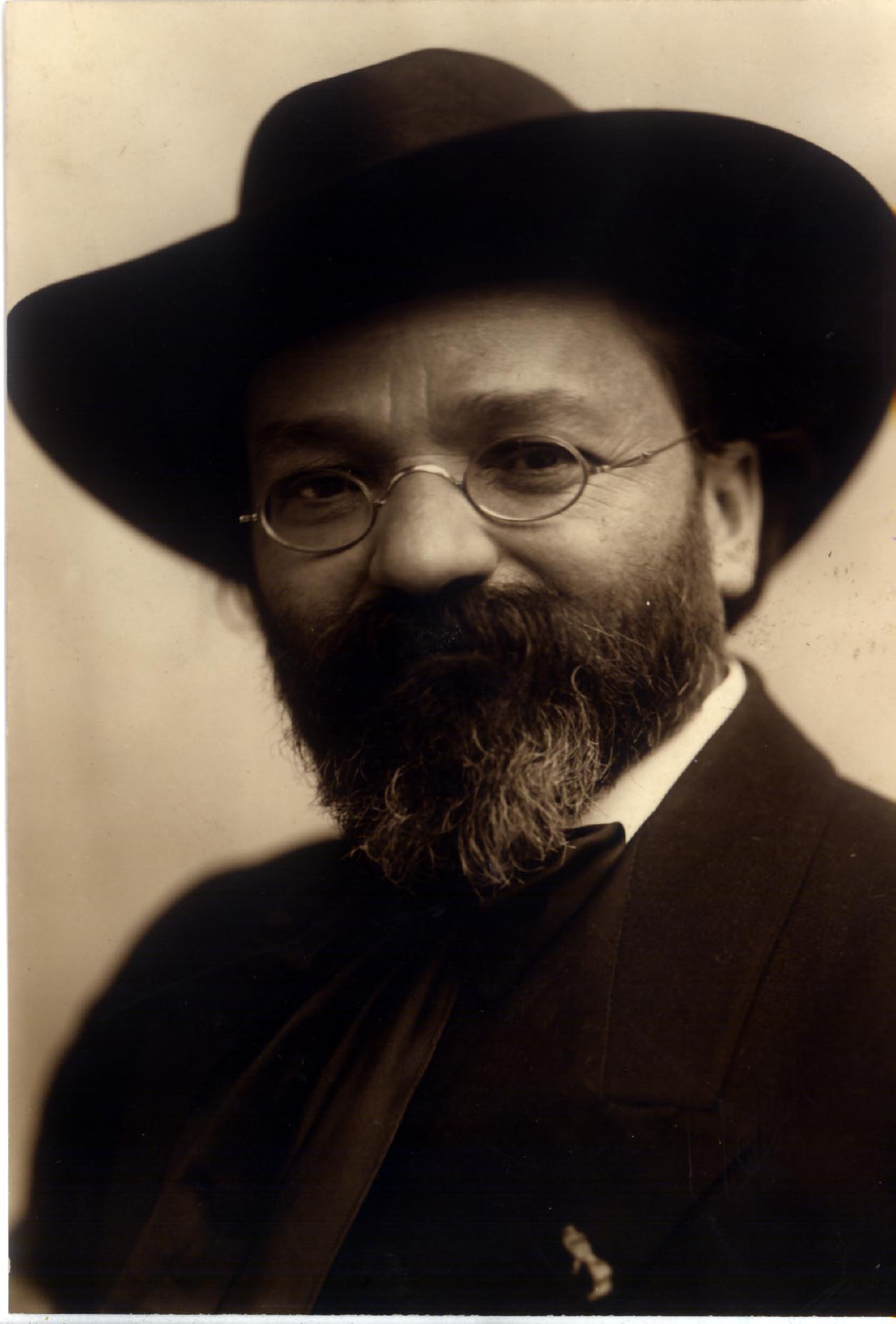
Moritz Grünwald
Moritz Grünwald (also spelled Greenwald; 20 March 1853 – 10 June 1895) was the Chief Rabbi in the cities of Bjelovar, Písek, and Mladá Boleslav, and later served as Chief Rabbi for the Principality of Bulgaria. Additionally, he was a writer and editor who wrote about the history of Jews and on linguistics of Jewish languages. Early life and education Grünwald was born in Uherské Hradiště in the Austrian Empire (now the Czech Republic). He attended both the University of Vienna and the Leipzig University, attaining degrees in philosophy and theology. In 1881, he was ordained as a rabbi by the Jewish Theological Seminary of Breslau, and appointed Chief Rabbi of Bjelovar in modern-day Croatia. From 1884 and 1893, he served as Chief Rabbi in the cities of Písek and Mladá Boleslav in Bohemia. Career In 1891, Dr. , the Chief Rabbi of Bulgaria, was forced to resign after a dispute with the Minister of Foreign Affairs and Religions, Dimitar Grekov, and 2 years later, Grü ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Conforte
Samuel is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the biblical judges to the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Kingdom of Israel under Saul, and again in the monarchy's transition from Saul to David. He is Veneration, venerated as a prophet in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In addition to his role in the Bible, Samuel is mentioned in Jewish rabbinic literature, rabbinical literature, in the Christian New Testament, and in the second chapter of the Quran (although the text does not mention him by name). He is also treated in the fifth through seventh books of ''Antiquities of the Jews'', written by the Jewish scholar Josephus in the first century. He is first called "the Seer" in Books of Samuel, 1 Samuel 9:9. Biblical account Family Samuel's mother was Hannah (biblical figure), Hannah and his father was Elkanah. Elkanah lived at Ramathaim-Zophim, Ramathaim in the district of Zuph. His genealogy is also found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |