|
History Of Mediaeval Arabic And Western European Domes
The early domes of the Middle Ages, particularly in those areas recently under Byzantine Empire, Byzantine control, were an extension of earlier Roman architecture. The domed church architecture of Italy from the sixth to the eighth centuries followed that of the Byzantine provinces and, although this influence diminishes under Charlemagne, it continued on in Venice, Southern Italy, and Sicily. Charlemagne's Palatine Chapel, Aachen, Palatine Chapel is a notable exception, being influenced by Byzantine models from Ravenna and Constantinople. The Dome of the Rock, an Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad Muslim religious shrine built in Jerusalem, was designed similarly to nearby Byzantine Martyrium (architecture), martyria and Christian churches. Domes were also built as part of Muslim palaces, throne halls, pavilions, and baths, and blended elements of both Byzantine and Iranian architecture, Persian architecture, using both pendentives and squinches. The origin of the Dome#Crossed-arch dome, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a matter of controversy and there are a wide variety of forms and specialized terms to describe them. A dome can rest directly upon a Rotunda (architecture), rotunda wall, a Tholobate, drum, or a system of squinches or pendentives used to accommodate the transition in shape from a rectangular or square space to the round or polygonal base of the dome. The dome's apex may be closed or may be open in the form of an Oculus (architecture), oculus, which may itself be covered with a roof lantern and cupola. Domes have a long architectural lineage that extends back into prehistory. Domes were built in ancient Mesopotamia, and they have been found in Persian architecture, Persian, Ancient Greek architecture, Hellenistic, Ancient Roman architecture, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquitaine
Aquitaine (, ; ; ; ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne (), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former Regions of France, administrative region. Since 1 January 2016 it has been part of the administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It is situated in the southwest corner of metropolitan France, along the Atlantic Ocean and the Pyrenees mountain range on the border with Spain; for most of its Recorded history, written history Bordeaux has been a vital port and administrative centre. It is composed of the five Departments of France, departments of Dordogne, Lot-et-Garonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Landes (department), Landes and Gironde. Gallia Aquitania was established by the Romans in ancient times and in the Middle Ages, Duchy of Aquitaine, Aquitaine was a kingdom and a duchy, whose boundaries fluctuated considerably. History Ancient history There are traces of human settlement by prehistoric peoples, especially in the Périgord, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of The Holy Apostles
The Church of the Holy Apostles (, ''Agioi Apostoloi''; ), also known as the Imperial Polyandrion (imperial cemetery), was a Byzantine Eastern Orthodox church in Constantinople, capital of the Eastern Roman Empire. The first structure dated to the 4th century, though future emperors would add to and improve upon it.Krautheimer (1992) It was second in size and importance only to the Hagia Sophia among the great churches of the capital. When Fall of Constantinople, Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in 1453, the Holy Apostles briefly became the seat of the Ecumenical Patriarch of the Eastern Orthodox Church. Three years later, the dilapidated edifice was abandoned, and the patriarchate moved to the Pammakaristos Church, Theotokos Pammakaristos Church. In 1461, the remains of the Church of the Holy Apostles were demolished by the Ottomans to make way for the Fatih Mosque, Istanbul, Fatih Mosque.Müller-Wiener (1977) p. 406 History The original Church of the Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mark's Basilica
The Patriarchal Cathedral Basilica of Saint Mark (), commonly known as St Mark's Basilica (; ), is the cathedral church of the Patriarchate of Venice; it became the episcopal seat of the Patriarch of Venice in 1807, replacing the earlier cathedral of San Pietro di Castello. It is dedicated to and holds the relics of Saint Mark the Evangelist, the patron saint of the city. The church is located on the eastern end of Saint Mark's Square, the former political and religious centre of the Republic of Venice, and is attached to the Doge's Palace. Prior to the fall of the republic in 1797, it was the chapel of the Doge and was subject to his jurisdiction, with the concurrence of the procurators of Saint Mark for administrative and financial affairs. The present structure is the third church, begun probably in 1063 to express Venice's growing civic consciousness and pride. Like the two earlier churches, its model was the sixth-century Church of the Holy Apostles in Constanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavia
Pavia ( , ; ; ; ; ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy, in Northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino (river), Ticino near its confluence with the Po (river), Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was a major political centre in the medieval period, being the capital of the Ostrogothic Kingdom from 540 to 553, of the Kingdom of the Lombards from 572 to 774, of the Kingdom of Italy (Holy Roman Empire), Kingdom of Italy from 774 to 1024 and seat of the Visconti of Milan, Visconti court from 1365 to 1413. Pavia is the capital of the fertile province of Pavia, which is known for a variety of agricultural products, including wine, rice, cereals, and dairy products. Although there are a number of industries located in the suburbs, these tend not to disturb the peaceful atmosphere of the town. It is home to the ancient University of Pavia (founded in 1361 and recognized in 2022 by the Times Higher Education World University Rankings, Times Higher Education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Michele Maggiore, Pavia
The Basilica of San Michele Maggiore is a Roman Catholic church in Pavia, region of Lombardy, Italy. The building, dating to the 11-12th centuries, is a well-preserved example of the Lombard- Romanesque style. History Archeological evidence, such as Ostrogoth silverware found at the site in 1968, suggests the site may have housed an early Christian basilica dating to the fifth century. The silverware is now preserved in the Pavia Civic Museums. Between 662 and 671, a church was built at the desire of King Grimoald. Dedicated to St Michael, it was built on the location of the Lombard Palace chapel. This church was destroyed by a fire in 1004, and only the lower part of the bell tower dates to the 7th-century church. The construction of the current crypt, choir and transept was begun in the late 11th century and was completed by 1130. The vaults of the nave, originally with two grossly squared groin-vaulted spans, were replaced in 1489 by the design of master architect Agostino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossing (architecture)
A crossing, in ecclesiastical architecture, is the junction of the four arms of a cruciform (cross-shaped) church. In a typically oriented church (especially of Romanesque and Gothic styles), the crossing gives access to the nave on the west, the transept arms on the north and south, and the choir, as the first part of the chancel, on the east. The crossing is sometimes surmounted by a tower or dome. A large crossing tower is particularly common on English Gothic cathedrals. With the Renaissance, building a dome above the crossing became popular. Because the crossing is open on four sides, the weight of the tower or dome rests heavily on the corners; a stable construction thus required great skill on the part of the builders. In centuries past, it was not uncommon for overambitious crossing towers to collapse. In other cases, the supports had to be reinforced with strainer arches. Sacrist Alan of Walsingham's octagon, built between 1322 and 1328 after the collapse of Ely's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. For most of its history the Empire comprised the entirety of the modern countries of Germany, Czechia, Austria, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Slovenia, and Luxembourg, most of north-central Italy, and large parts of modern-day east France and west Poland. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne Roman emperor, reviving the title more than three centuries after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476. The title lapsed in 924, but was revived in 962 when Otto I, OttoI was crowned emperor by Pope John XII, as Charlemagne's and the Carolingian Empire's successor. From 962 until the 12th century, the empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanesque Architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe that was predominant in the 11th and 12th centuries. The style eventually developed into the Gothic style with the shape of the arches providing a simple distinction: the Romanesque is characterized by semicircular arches, while the Gothic is marked by the pointed arches. The Romanesque emerged nearly simultaneously in multiple countries of Western Europe; its examples can be found across the continent, making it the first pan-European architectural style since Imperial Roman architecture. Similarly to Gothic, the name of the style was transferred onto the contemporary Romanesque art. Combining features of ancient Roman and Byzantine buildings and other local traditions, Romanesque architecture is known by its massive quality, thick walls, round arches, sturdy pillars, barrel vaults, large towers and decorative arcading. Each building has clearly defined forms, frequently of very regular, symmetrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, the east and southeast, Jordan to Jordan–Syria border, the south, and Israel and Lebanon to Lebanon–Syria border, the southwest. It is a republic under Syrian transitional government, a transitional government and comprises Governorates of Syria, 14 governorates. Damascus is the capital and largest city. With a population of 25 million across an area of , it is the List of countries and dependencies by population, 57th-most populous and List of countries and dependencies by area, 87th-largest country. The name "Syria" historically referred to a Syria (region), wider region. The modern state encompasses the sites of several ancient kingdoms and empires, including the Eblan civilization. Damascus was the seat of the Umayyad Caliphate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
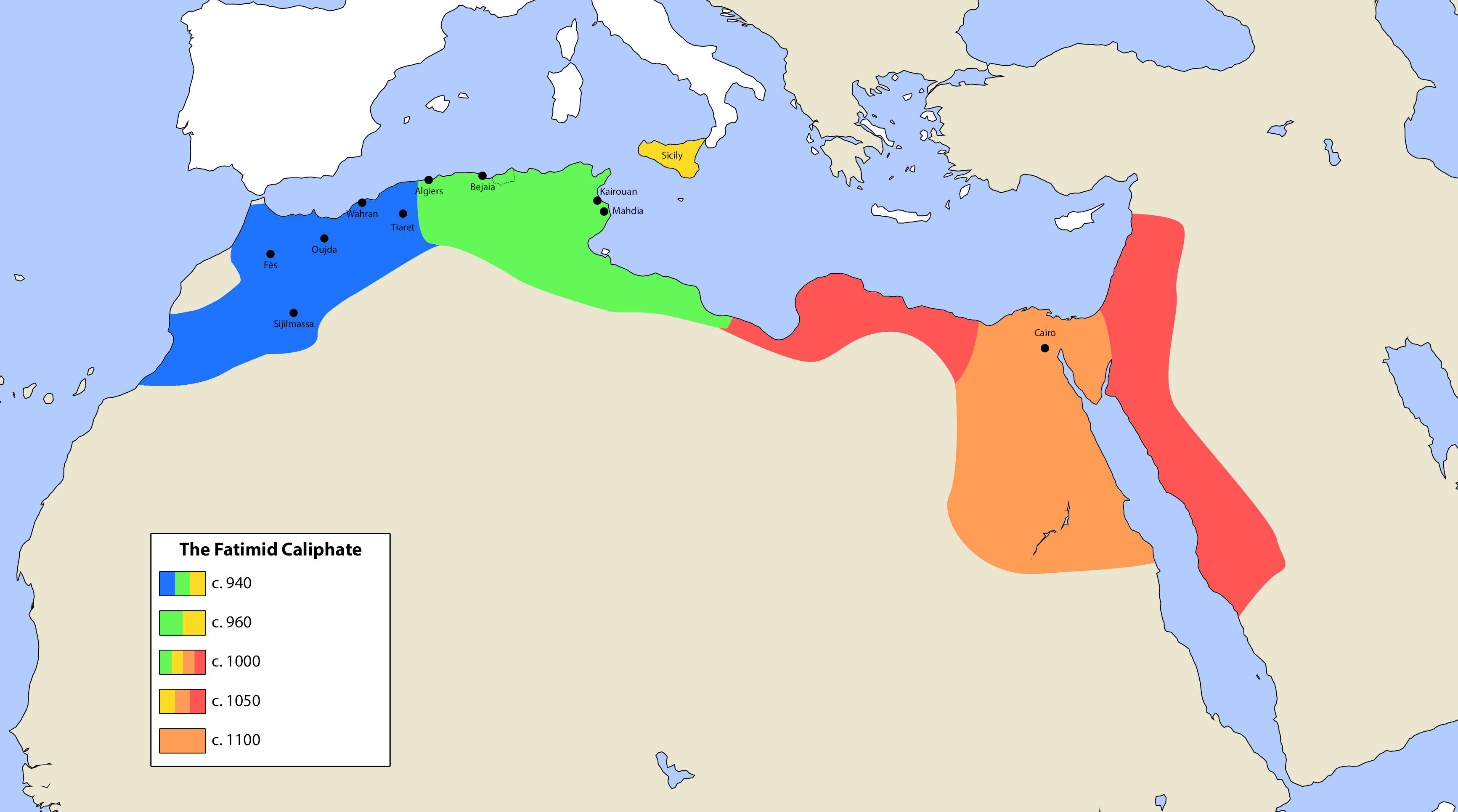
Fatimid Architecture
The Fatimid architecture that developed in the Fatimid Caliphate (909–1167 CE) of North Africa combined elements of eastern and western architecture, drawing on Abbasid architecture, Byzantine, Ancient Egyptian, Coptic architecture and North African traditions; it bridged early Islamic styles and the medieval architecture of the Mamluks of Egypt, introducing many innovations. The wealth of Fatimid architecture was found in the main cities of Mahdia (921–948), Al-Mansuriya (948–973) and Cairo (973–1169). The heartland of architectural activity and expression during Fatimid rule was at al-Qahira (Cairo), on the eastern side of the Nile, where many of the palaces, mosques and other buildings were built. Large-scale constructions were undertaken during the reigns of al-Mui'zz () Al-Aziz Billah () and al-Hakim (). The Fatimid caliphs competed with the rulers of the Abbasid and Byzantine empires and indulged in luxurious palace building. Their palaces, their greate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |