|
Heterotaxy Syndrome
Situs ambiguus (), or heterotaxy, is a rare congenital defect in which the major visceral Organ (anatomy), organs are distributed abnormally within the chest and abdomen. Clinically, heterotaxy spectrum generally refers to any defect of left-right asymmetry and arrangement of the visceral organs; however, classical heterotaxy requires multiple organs to be affected. This does not include the congenital defect situs inversus, which results when arrangement of all the organs in the abdomen and chest are mirrored, so the positions are opposite the normal placement. Situs inversus is the mirror image of situs solitus, which is normal asymmetric distribution of the abdominothoracic visceral organs. Situs ambiguus can also be subdivided into left-isomerism and right-isomerism based on the defects observed in the spleen, lungs and Atrium (heart), atria of the heart. Individuals with situs inversus or situs solitus do not experience fatal dysfunction of their organ systems, as general ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiology
Cardiology () is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease, and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a sub-specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery. Specializations All cardiologists in the branch of medicine study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult and child heart disorders each require different training pathways. Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric cardiologists are not trained to treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (biology), body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Some tissues such as cartilage, epithelium, and the lens (anatomy), lens and cornea of the eye are not supplied with blood vessels and are termed ''avascular''. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning ''vessel'', and is mostly used in relation to blood vessels. Etymology * artery – late Middle English; from Latin ''arteria'', from Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute (medicine)
In medicine, describing a disease as acute denotation, denotes that it is of recent wikt:onset#Noun, onset; it occasionally denotes a short wikt:duration#Noun, duration. The quantification (science), quantification of how much time constitutes "short" and "recent" varies by disease and by context, but the core denotation of "acute" is always qualitative property, qualitatively in contrast with "chronic condition, chronic", which denotes long-lasting disease (for example, in acute leukaemia and chronic leukaemia). In the context of the mass noun "acute disease", it refers to the acute phase (that is, a short course) of any disease entity. For example, in an article on ulcerative enteritis in poultry, the author says, "in acute disease there may be increased mortality rate, mortality without any obvious medical sign, signs", referring to the acute form or phase of ulcerative enteritis. Meaning variations A mild stubbed toe is an acute injury. Similarly, many acute upper respirator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
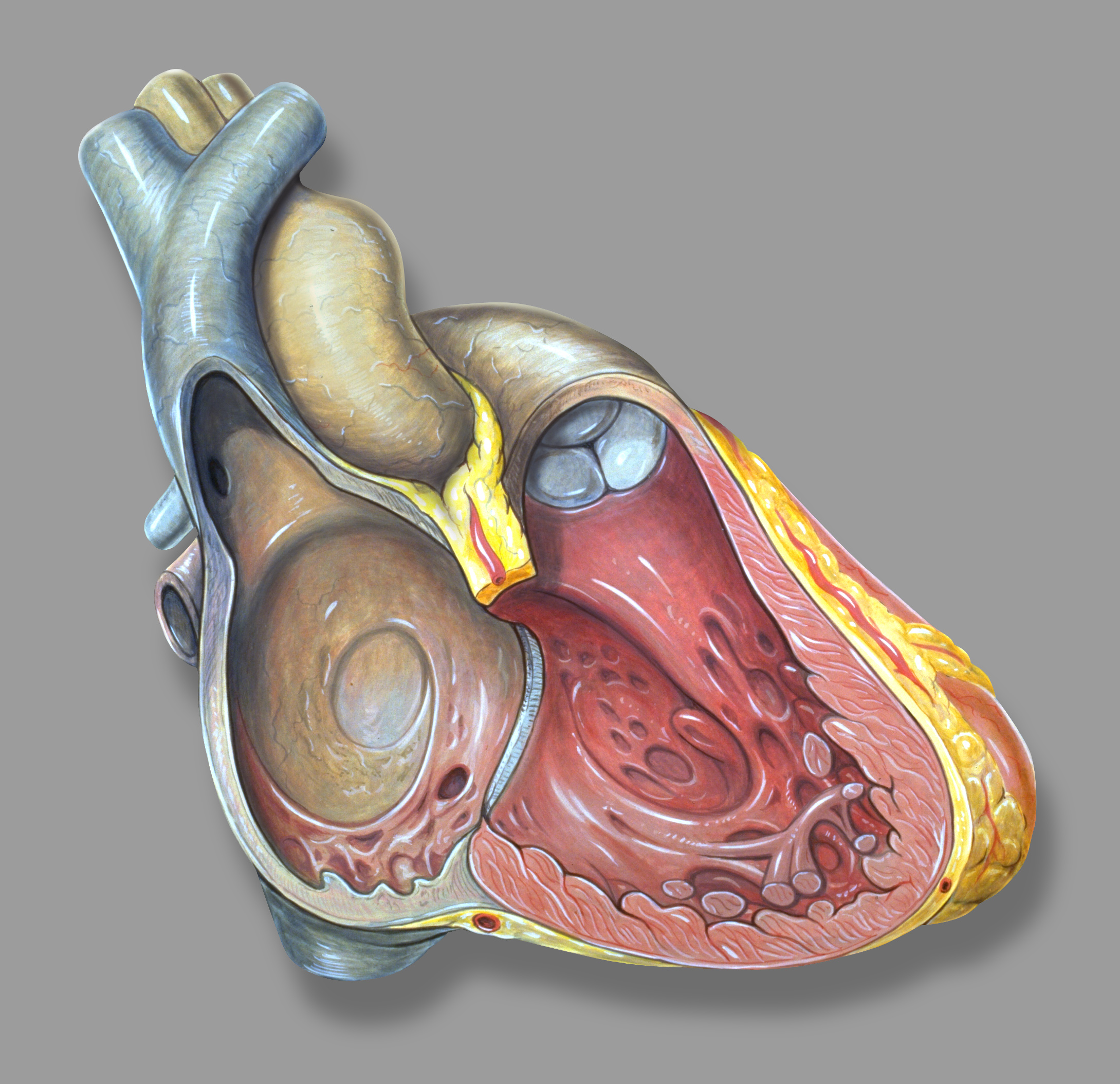
Right Atrial Isomerism
Asplenia with cardiovascular anomalies, also known as Ivemark syndrome and right atrial isomerism, is an example of a heterotaxy syndrome. These uncommon congenital disorders are characterized by defects in the heart, spleen and paired organs such as the lungs and kidneys. Another name is "asplenia-cardiovascular defect-heterotaxy". Right atrial isomerism is named for its discoverer, Swedish pathologist Biörn Ivemark. Presentation In right atrial isomerism, both atria of the heart are morphological right atria leading to associated abnormalities in the pulmonary venous system. In addition, individuals with right atrial isomerism develop asplenia, a midline liver, malrotation of the small intestine and the presence of two morphologic right lungs. Individuals with left atrial isomerism, by comparison, have two morphologic left atria, polysplenia, intestinal malrotation and two morphologic left lungs. Causes The cause of heterotaxy is unknown. The Ivemark Syndrome Association, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnose
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engineering and computer science, it is typically used to determine the causes of symptoms, mitigations, and solutions. Computer science and networking * Bayesian network * Complex event processing * Diagnosis (artificial intelligence) * Event correlation * Fault management * Fault tree analysis * Grey problem * RPR problem diagnosis * Remote diagnostics * Root cause analysis * Troubleshooting * Unified Diagnostic Services Mathematics and logic * Bayesian probability * Block Hackam's dictum * Occam's razor * Regression diagnostics * Sutton's law Medicine * Medical diagnosis * Molecular diagnostics Methods * CDR computerized assessment system * Computer-aided diagnosis * Differential diagnosis * Retrospective diagno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Heart Disease
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms are variable and may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure. Congenital heart defects are the most common birth defect. In 2015, they were present in 48.9 million people globally. They affect between 4 and 75 per 1,000 live births, depending upon how they are diagnosed. In about 6 to 19 per 1,000 they cause a moderate to severe degree of problems. Congenital heart defects are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomerism
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element (chemistry), element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. ''Isomerism'' refers to the existence or possibility of isomers. Isomers do not necessarily share similar chemical property, chemical or physical property, physical properties. Two main forms of isomerism are structural isomerism, structural (or constitutional) isomerism, in which ''chemical bond, bonds'' between the atoms differ; and stereoisomerism (or spatial isomerism), in which the bonds are the same but the ''relative positions'' of the atoms differ. Isomeric relationships form a hierarchy. Two chemicals might be the same constitutional isomer, but upon deeper analysis be stereoisomers of each other. Two molecules that are the same stereoisomer as each other might be in different conformational forms or be different Isotopologue, isotopologues. The depth of analy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial
The atrium (; : atria) is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle, the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, previously known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. Auricles in this modern terminology are distinguished by having thicker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinically Significant
In medicine and psychology, clinical significance is the practical importance of a treatment effect—whether it has a real genuine, palpable, noticeable effect on daily life. Types of significance Statistical significance Statistical significance is used in hypothesis testing, whereby the null hypothesis (that there is no relationship between variables) is tested. A level of significance is selected (most commonly ''α'' = 0.05 or 0.01), which signifies the probability of incorrectly rejecting a true null hypothesis. If there is a significant difference between two groups at ''α'' = 0.05, it means that there is only a 5% probability of obtaining the observed results under the assumption that the difference is entirely due to chance (i.e., the null hypothesis is true); it gives no indication of the magnitude or clinical importance of the difference. When statistically significant results are achieved, they favor rejection of the null hypothesis, but they do not prove that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There are two openings of the thoracic cavity, a superior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic inlet and a lower inferior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic outlet. The thoracic cavity includes the tendons as well as the cardiovascular system which could be damaged from injury to the back, spine or the neck. Structure Structures within the thoracic cavity include: * structures of the cardiovascular system, including the heart and great vessels, which include the thoracic aorta, the pulmonary artery and all its branches, the superior and inferior vena cava, the pulmonary veins, and the azygos vein * structures of the respiratory system, including the diaphragm, trachea, bronchi and lungs * structures of the digestive system, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contain Organ (anatomy), organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet, opening into the pelvis. Structure Organs Organs of the abdominal cavity include the stomach, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, small intestine, kidneys, large intestine, and adrenal glands. Peritoneum The abdominal cavity is lined with a protective membrane termed the peritoneum. The inside wall is covered by the parietal peritoneum. The kidneys are located behind the peritoneum, in the retroperitoneum, outside the abdominal cavity. The viscera are also covered by visceral peritoneum. Between the visceral and parietal peritoneum is the peritoneal cavity, which is a potential space. It contains a serous fluid called peritoneal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry In Biology
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, the face of a human being has a plane of symmetry down its centre, or a pine cone displays a clear symmetrical spiral pattern. Internal features can also show symmetry, for example the tubes in the human body (responsible for transporting gases, nutrients, and waste products) which are cylindrical and have several planes of symmetry. Biological symmetry can be thought of as a balanced distribution of duplicate body parts or shapes within the body of an organism. Importantly, unlike in mathematics, symmetry in biology is always approximate. For example, plant leaves – while considered symmetrical – rarely match up exactly when folded in half. Symmetry is one class of patterns in nature whereby there is near-repetition of the pattern element, either by reflection or rotation. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |