|
Hermann Of Carinthia
Herman of Carinthia (1105/1110 – after 1154), also called Hermanus Dalmata or Sclavus Dalmata, Secundus, by his own words born in the "heart of Istria", was a philosopher, astronomer, astrologer, mathematician and translator of Arabic works into Latin. Alongside Adelard of Bath, John of Seville, Gerard of Cremona and Plato of Tivoli, Herman is the most important translator of Arabic astronomical works in 12th century. The influence of his translations on the development of medieval European astronomy was especially large. Name Herman (also spelled Hermann) is known by several bynames in English and Latin referring to his land of origin or his ethnicity: Hermann of Carinthia (''Hermannus de Carinthia''); Hermann of Dalmatia or Hermann the Dalmatian (''Hermannus Dalmata''; ; .); or Hermann the Slav (''Hermannus Sclavus''). Herman always refers to his homeland as Carinthia or Istria. His own preferred nickname was ''Hermannus Secundus'', that is, the "second Hermann", by way of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew Of Paris
Matthew Paris, also known as Matthew of Paris (; 1200 – 1259), was an English Benedictine monk, chronicler, artist in illuminated manuscripts, and cartographer who was based at St Albans Abbey in Hertfordshire. He authored a number of historical works, many of which he scribed and illuminated himself, typically in drawings partly coloured with watercolour washes, sometimes called "tinted drawings". Some were written in Latin, others in Anglo-Norman or French verse. He is sometimes confused with the nonexistent Matthew of Westminster. His is a renowned Medieval work, in many cases being a key source for mid-13th century Europe, partially due to his verbose insertion of personal opinions into his narrative and his use of sources such as records, letters, and conversations with witnesses to events including the English king Henry III, earl Richard of Cornwall, the Norwegian king Haakon IV, a number of English bishops, and many others. Modern historians recognise Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. For most of its history the Empire comprised the entirety of the modern countries of Germany, Czechia, Austria, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Slovenia, and Luxembourg, most of north-central Italy, and large parts of modern-day east France and west Poland. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne Roman emperor, reviving the title more than three centuries after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476. The title lapsed in 924, but was revived in 962 when Otto I, OttoI was crowned emperor by Pope John XII, as Charlemagne's and the Carolingian Empire's successor. From 962 until the 12th century, the empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathedral School Of Chartres
During the High Middle Ages, the Chartres Cathedral established the cathedral School of Chartres, an important center of French scholarship located in Chartres. It developed and reached its apex during the transitional period of the 11th and 12th centuries, at the start of the Latin translation movement. This period was also right before the spread of medieval universities, which eventually superseded cathedral schools and monastic schools as the most important institutions of higher learning in the Latin West.Natural Philosophy at School and University, (Lecture 18), in Lawrence M. Principe (2002) ''History of Science: Antiquity to 1700''. Teaching Company, Course No. 1200 In the early 11th century (c. 1020), Bishop Fulbert established Chartres as one of the leading schools in Europe. Although the role of Fulbert himself as a scholar and teacher has been questioned, his administrative ability established the conditions in which the school could flourish. Great scholars were at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Paris
The University of Paris (), known Metonymy, metonymically as the Sorbonne (), was the leading university in Paris, France, from 1150 to 1970, except for 1793–1806 during the French Revolution. Emerging around 1150 as a corporation associated with the cathedral school of Paris, it was considered the List of medieval universities, second-oldest university in Europe.Charles Homer Haskins: ''The Rise of Universities'', Henry Holt and Company, 1923, p. 292. Officially chartered in 1200 by Philip II of France, King Philip II and recognised in 1215 by Pope Innocent III, it was nicknamed after its theological College of Sorbonne, founded by Robert de Sorbon and chartered by King Louis IX around 1257. Highly reputed internationally for its academic performance in the humanities ever since the Middle Ages – particularly in theology and philosophy – it introduced academic standards and traditions that have endured and spread, such as Doctor (title), doctoral degrees and student nations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thierry Of Chartres
Thierry of Chartres (''Theodoricus Chartrensis'') or Theodoric the Breton (''Theodericus Brito'') (died before 1155, probably 1150) was a twelfth-century philosopher working at Chartres and Paris, France. The cathedral school at Chartres promoted scholarship before the first university was founded in France. Thierry was a major figure in twelfth-century philosophy and learning, and, like many twelfth-century scholars, is notable for his embrace of Plato's '' Timaeus'' and his application of philosophy to theological issues. Some modern scholars believed Thierry to have been a brother of Bernard of Chartres who had founded the school of Chartres, but later research has shown that this is unlikely. Thierry became chancellor of Chartres after his predecessor, Gilbert of Poitiers, returned to his native city in 1141. John of Salisbury, Herman of Carinthia, and Clarembald of Arras were among Thierry's students. Works ''Hexaemeron'' The ''Hexaemeron'' interprets the Genesis with r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedictine
The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict (, abbreviated as O.S.B. or OSB), are a mainly contemplative monastic order of the Catholic Church for men and for women who follow the Rule of Saint Benedict. Initiated in 529, they are the oldest of all the religious orders in the Latin Church. The male religious are also sometimes called the Black Monks, especially in English speaking countries, after the colour of their habits, although some, like the Olivetans, wear white. They were founded by Benedict of Nursia, a 6th-century Italian monk who laid the foundations of Benedictine monasticism through the formulation of his Rule. Benedict's sister, Scholastica, possibly his twin, also became a religious from an early age, but chose to live as a hermit. They retained a close relationship until her death. Despite being called an order, the Benedictines do not operate under a single hierarchy. They are instead organized as a collection of autonomous monasteries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
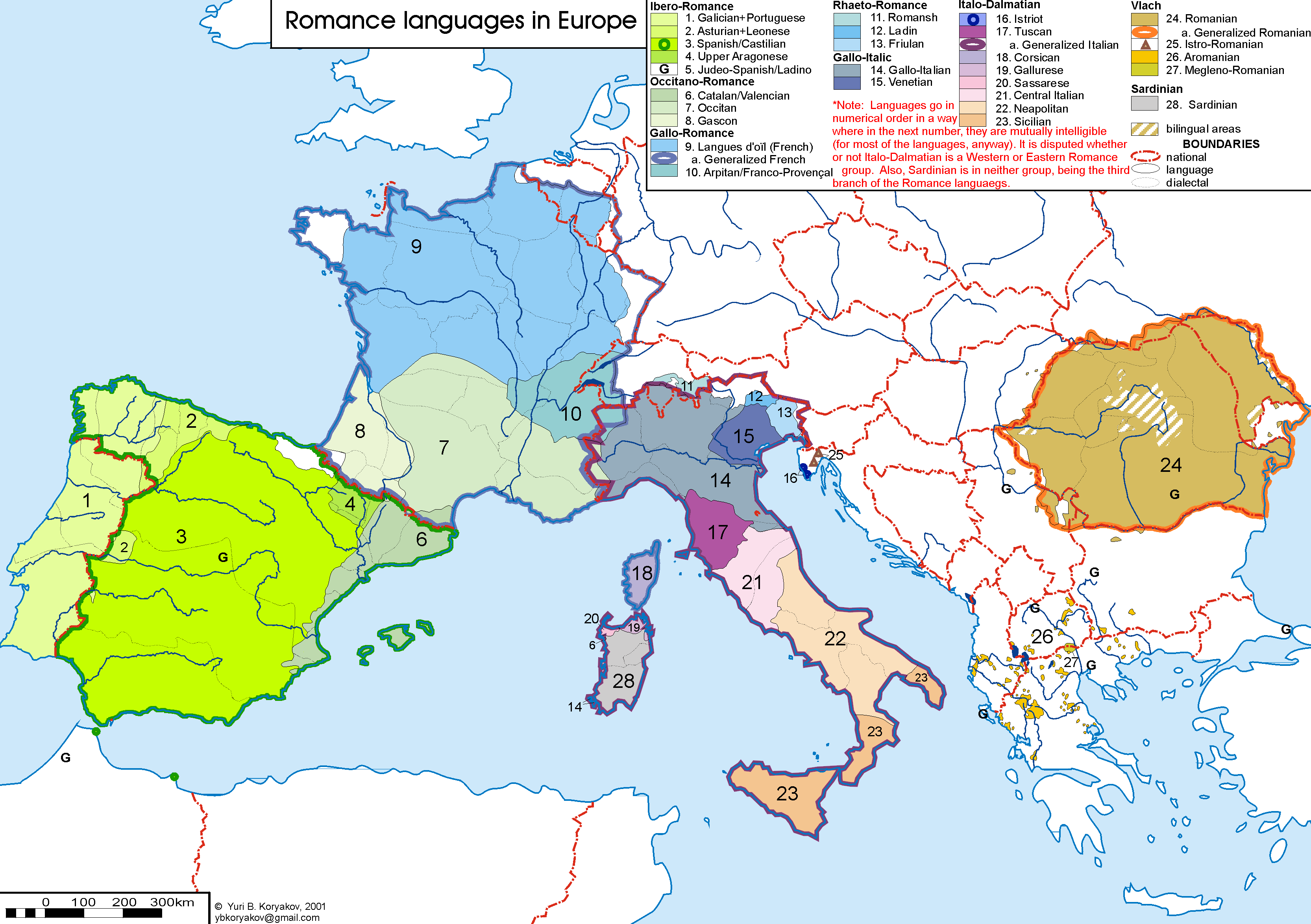
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Slavic Languages
The South Slavic languages are one of three branches of the Slavic languages. There are approximately 30 million speakers, mainly in the Balkans. These are separated geographically from speakers of the other two Slavic branches (West Slavic languages, West and East Slavic languages, East) by a belt of German language, German, Hungarian language, Hungarian and Romanian language, Romanian speakers. History The first South Slavic language to be written (also the first attested Slavic language) was the variety of the Eastern South Slavic spoken in Thessaloniki, now called Old Church Slavonic, in the ninth century. It is retained as a liturgical language in Slavic Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox churches in the form of various local Church Slavonic language, Church Slavonic traditions. Classification The South Slavic languages constitute a Dialect continuum#South Slavic continuum, dialect continuum. Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin constitute a single dialect wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vipava Valley
The Vipava Valley (; , , ) is a valley in the Slovenian Littoral, roughly between the village of Podnanos to the east and the border with Italy to the west. The main towns are Ajdovščina and Vipava. Geography The narrow valley of the Vipava River serves as the main passage between the Friulian lowland and central Slovenia, and is thus also an important corridor connecting Northern Italy to Central Europe. It is closed to the north by the high Trnovo Forest Plateau (), and to the south by the Karst Plateau and the narrow Branica Valley, a geographical sub-unit of the Vipava Valley. It is named after the Vipava River. Its main urban center is Ajdovščina. Administratively, it is subdivided into the municipalities of Ajdovščina, Vipava, Nova Gorica, Renče-Vogrsko, and Miren-Kostanjevica. The municipality of Savogna d'Isonzo in the Province of Gorizia (Italy) is also located in the valley. The Vipava Valley comprises five microregions: # The Lower Vipava Valley wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Carniola
Inner Carniola ( ; ) is a traditional region of Slovenia, the southwestern part of the larger Carniola region. It comprises the Hrušica (plateau), Hrušica karst plateau up to Postojna Gate, bordering the Slovenian Littoral (the Goriška, Gorizia region) in the west. Its administrative and economic center of the region is Postojna, and other minor centers include Vrhnika, Logatec, Cerknica, Pivka, and Ilirska Bistrica. Name The English name ''Inner Carniola'', like the Slovene name ''Notranjska'', is a translation of German ''Innerkrain'', referring to the southwest part of Carniola. The name was created by analogy with ''Inner Austria'' (), referring to the southwestern Habsburg hereditary lands. History Inner Carniola was a ''Circle (administrative division), kreis'' of the Duchy of Carniola, ruled by the archducal House of Habsburg within the Inner Austrian lands starting in the 14th century. The territorial arrangement was described by the scholar Johann Weikhard von Val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duino
Duino (, ) is today a seaside resort on the northern Adriatic Sea, Adriatic coast. It is a ''hamlet (place), hamlet'' of Duino-Aurisina, a municipality (''comune'') of the Friuli–Venezia Giulia region of northeastern Italy. The settlement, picturesquely situated on the steep Karst cliffs of the Gulf of Trieste, is known for Duino Castle, immortalized by the poet Rainer Maria Rilke in his ''Duino Elegies''. Name Duino was attested in historical sources as ''Duino'' in 1139, ''Dewin'' in the 13th century, and ''Tybein'' 1370, among various other forms of the name. Equivalents of the Slovene name appear in various Slavic languages (cf. Slovak language, Slovak ''Devín'', Polish language, Polish ''Dziewin, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Dziewin'', etc., all ultimately derived from Slavic ''*děva'' 'girl'). However, another possibility is that the name of this settlement may derive from Romance languages, Romance ''tubīnum'' < Latin ''tubus'' '(water) pipe'. History |
Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, regional decentralization entity of Trieste. Trieste is located at the head of the Gulf of Trieste, on a narrow strip of Italian territory lying between the Adriatic Sea and Slovenia; Slovenia lies close, at approximately east and southeast of the city, while Croatia is about to the south of the city. The city has a long coastline and is surrounded by grassland, forest, and karstic areas. As of 2025, it has a population of 198,668. Trieste belonged, as Triest, to the Habsburg monarchy from 1382 until 1918. In the 19th century, the monarchy was one of the Great Powers of Europe and Trieste was its most important seaport. As a prosperous trading hub in the Mediterranean region, Trieste grew to become the fourth largest city of the Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |