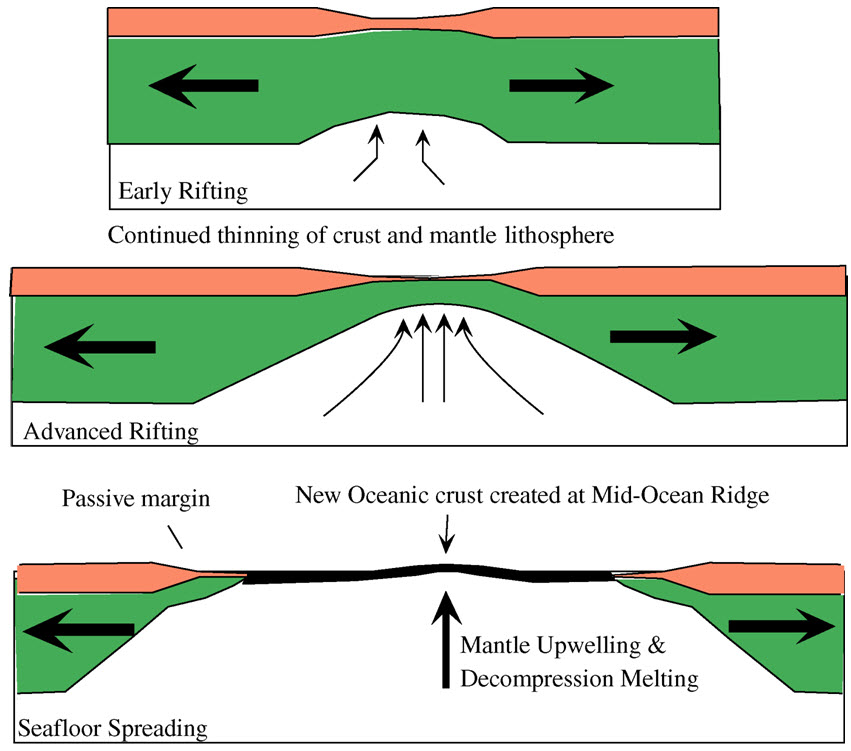
|
Helgrindur
Helgrindur (, also known as Lýsuskarð, Lysuhóll or Lysukard) is a volcanic mountain range or massif in the middle of the Snæfellsnes peninsula that provides a backdrop to the port of Grundarfjörður. The volcano can be regarded as potentially active, with a risk of lava flows and much more rarely explosive tephra eruptions. The range with its prominent peaks, of Tröllkerling at in its south-east, Böðvarskúla at and Kaldnasaborgir (Kaldnasi) in its north-west at is popular with hikers or mountaineers. Geography The wide range, is in the middle of the Snæfellsnes peninsula and thus divides the northern large bay of Breiðafjörður from the southern bay of Faxaflói. Reykjavík is about to the range's south across Faxaflói. The weather systems in the two large bays are often quite different and the stormy winds across the range are quite notorious and can be heard sometimes at sea level. Geology The range is part of the Snæfellsnes volcanic belt that extends f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Iceland
There are too many presumed extinct or now inactive volcanic features to list all of these below, so most monogenetic volcanoes can not be mentioned individually. This list of volcanoes in Iceland only includes major active and dormant volcano, volcanic mountains, of which at least 18 vents have erupted since human settlement of Iceland began around 900 AD. Subsequent to the main list a list is presented that classifies the volcanoes into zones, systems and types. This is in the context that there are several classification systems and many of the volcanoes may have separate shallow magma chambers and a deeper common magma source. Where a major vent is part of a larger volcano this is indicated in the list comment. Since some of these vent eruptions have been very large, disruptive or been regarded in popular culture as a separate volcano they have been included in the list but where this is not the case it is not appropriate to duplicate or create entries. So for minor vent eru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Deformation Of Iceland
The geological deformation of Iceland is the way that the rocks of the island of Iceland are changing due to tectonic forces. The geological deformation help to explain the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, fissures, and the shape of the island. Iceland is the largest landmass () situated on an oceanic ridge. It is an elevated plateau of the sea floor, situated at the crossing of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the Greenland-Iceland-Scotland ridge. It lies along an oceanic divergent plate boundary: the western part of Iceland sits on the North American Plate and the eastern part sits on the Eurasian Plate. The Reykjanes Ridge of the Mid-Atlantic ridge system in this region crosses the island from southwest and connects to the Kolbeinsey Ridge in the northeast. Iceland is geologically young: all rocks there were formed within the last 25 million years. It started forming in the Early Miocene sub-epoch, but the oldest rocks found at the surface of Iceland are from the Middle Miocene sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ljósufjöll
Ljósufjöll () is a fissure vent system and central volcano on the Snæfellsnes Peninsula in Iceland. The name derives from the central volcano and translates into English as "Mountains of the Light". Geography The volcanic system has a length of about and a maximum width at its eastern end of about . The north-western part of the Ljósufjöll volcanic system has hyaloclastite hills and lava flows about wide. This progresses into the ridge like central volcano with its highest peak of . The fissure swarm widens to the south-east and extends towards the Haffjarðará river and the town of Bifröst at the eastern base of the peninsula. Geology The volcanic system is part of the Snæfellsnes volcanic belt (zone). This is an intra-plate volcanic zone less than 3.3 million years old, erupting through of crust at Ljósufjöll. The belt has relatively low geothermal gradients for Iceland at about and erupts alkalic to transitional basalts, with the Ljósufjöll system tendi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snæfellsjökull
Snæfellsjökull (, ''snow-fell glacier'') is a 700,000-year-old glacier-capped stratovolcano in western Iceland. It is situated on the westernmost part of the Snæfellsnes peninsula. Sometimes it may be seen from the city of Reykjavík over Faxa Bay, at a distance of . The mountain is one of the most famous sites of Iceland, primarily due to the novel ''Journey to the Center of the Earth'' (1864 in literature, 1864) by Jules Verne, in which the protagonists find the entrance to a passage leading to the center of the Earth on Snæfellsjökull. The mountain is part of Snæfellsjökull National Park (Icelandic: ''Þjóðgarðurinn Snæfellsjökull''). Snæfellsjökull was visible from an extreme distance due to an Fata Morgana (mirage), arctic mirage on 17 July 1939. Captain Robert Bartlett (explorer), Robert Bartlett of the ''Effie M. Morrissey'' sighted Snæfellsjökull from a position some distant. In August 2012, the summit was ice-free for the first time in recorded history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snæfellsnes
The Snæfellsnes () is a peninsula situated to the west of Borgarfjörður, in western Iceland. The peninsula has a volcanic origin having the Snæfellsnes volcanic belt down its centre, and the Snæfellsjökull volcano A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most oft ..., regarded as one of the symbols of Iceland, at its western tip. With its height of , it is the highest mountain on the peninsula and has a glacier at its peak (''jökull'' means "glacier" in Icelandic language, Icelandic). The volcano can be seen on clear days from Reykjavík, a distance of about . The mountain is also known as the setting of the novel ''Journey to the Center of the Earth'' by the French author Jules Verne. The area surrounding Snæfellsjökull has been designated one of the four national parks b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subglacial Volcanoes Of Iceland
Subglacial means "formed, or occurring beneath a glacier or other body of ice". It may refer to: * Subglacial eruption * Subglacial lake A subglacial lake is a lake that is found under a glacier, typically beneath an ice cap or ice sheet. Subglacial lakes form at the boundary between ice and the underlying bedrock, where liquid water can exist above the lower melting point of ic ... * Subglacial stream * Subglacial volcano {{Disambiguation Glaciology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Iceland
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism Of Iceland
:''The volcano system in Iceland that started activity on August 17, 2014, and ended on February 27, 2015, is Bárðarbunga.'' :''The volcano in Iceland that erupted in May 2011 is Grímsvötn.'' Iceland experiences frequent volcanic activity, due to its location both on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary, and being over a hotspot. Nearly thirty volcanoes are known to have erupted in the Holocene epoch; these include Eldgjá, source of the largest lava eruption in human history. Some of the various eruptions of lava, gas and ash have been both destructive of property and deadly to life over the years, as well as disruptive to local and European air travel. Volcanic systems and volcanic zones of Iceland Holocene volcanism in Iceland is mostly to be found in the ''Neovolcanic Zone'', comprising the Reykjanes volcanic belt (RVB), the West volcanic zone (WVZ), the Mid-Iceland belt (MIB), the East volcanic zone (EVZ) and the North volcanic zone (NVZ). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Iceland
The geology of Iceland is unique and of particular interest to geologists. Iceland lies on the divergent boundary between the Eurasian plate and the North American plate. It also lies above a hotspot, the Iceland plume. The plume is believed to have caused the formation of Iceland itself, the island first appearing over the ocean surface about 16 to 18 million years ago. The result is an island characterized by repeated volcanism and geothermal phenomena such as geysers. The eruption of Laki in 1783 caused much devastation and loss of life, leading to a famine that killed about 25% of the island's population and resulted in a drop in global temperatures, as sulfur dioxide was spewed into the Northern Hemisphere. This caused crop failures in Europe and may have caused droughts in India. The eruption has been estimated to have killed over six million people globally. Between 1963 and 1967, the new island of Surtsey was created off the southwest coast by a volcanic eruption. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture (geology), texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained matrix (geology), groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent of granite. Its high silica content makes rhyolitic magma extremely viscosity, viscous. This favors explosive eruptions over effusive eruptions, so this type of magma is more often erupted as pyroclastic rock than as lava flows. Rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs are among the most voluminous of continental igneous rock formations. Rhyolitic tuff has been used extensively for construction. Obsidian, which is rhyolitic volcanic glass, has been used for tools from prehistoric times to the present day because it can be shaped to an extremely sharp edge. Rhyolitic pumice finds use as an abrasive, in concrete, and as a soil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picrite Basalt
Picrite basalt or picrobasalt is a variety of high-magnesium olivine basalt that is very rich in the mineral olivine. It is dark with yellow-green olivine phenocrysts (20-50%) and black to dark brown pyroxene, mostly augite. The olivine-rich picrite basalts that occur with the more common tholeiitic basalts of Kīlauea and other volcanoes of the Hawaiian Islands are the result of accumulation of olivine crystals either in a portion of the magma chamber or in a caldera lava lake. The compositions of these rocks are well represented by mixes of olivine and more typical tholeiitic basalt. The name "picrite" can also be applied to an olivine-rich alkali basalt: such picrite consists largely of phenocrysts of olivine and titanium-rich augite pyroxene with minor plagioclase set in a groundmass of augite and more sodic plagioclase and perhaps analcite and biotite. More generally the classification of fine grained rocks recognises a group known as 'picritic rocks' that are char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |