|
Hawaiite
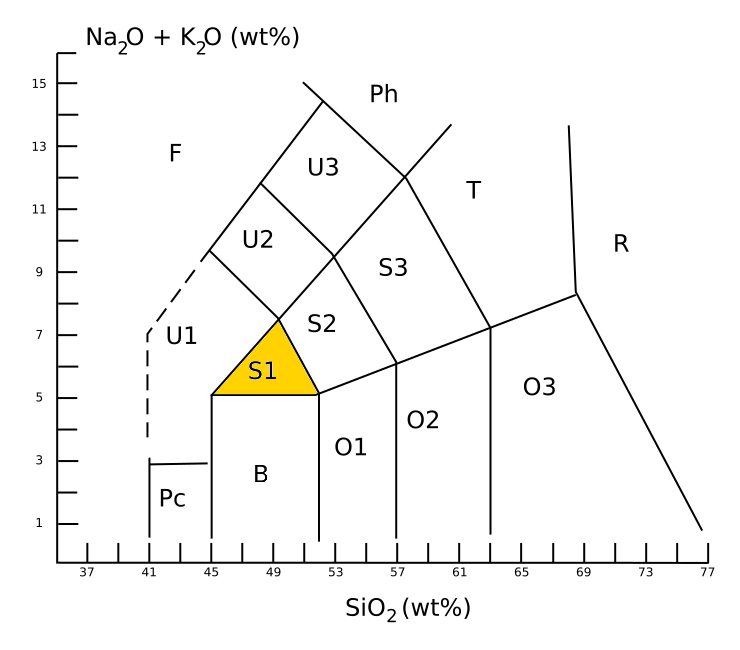
Hawaiite is an olivine basalt with a composition between alkali basalt and mugearite. It was first used as a name for some lavas found on the island of Hawaii. It occurs during the later stages of volcanic activity on oceanic islands such as Hawaii, which happens to be when the alkali metals are most present. In gemology, hawaiite is a colloquial term for Hawaii-originated peridot, which is a gem-quality form of the mineral olivine. Description Hawaiite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) volcanic rock produced by rapid cooling of lava moderately poor in silica and enriched in alkali metal oxides (potassium oxide plus sodium oxide). It is often impractical to determine the mineral composition of such a fine-grained rock, and so hawaiite is defined chemically. Under the TAS classification, hawaiite is sodic trachybasalt, with a silica content close to 49 wt%, a total alkali metal oxide content close to 6%, and wt% > wt% + 2. This places hawaiite in the S1 field of the TAS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachybasalt
Trachybasalt is a volcanic rock with a composition between trachyte and basalt. It resembles basalt but has a high content of alkali metal oxides. Minerals in trachybasalt include alkali feldspar, calcic plagioclase, olivine, clinopyroxene and likely very small amounts of leucite or analcime. Description An aphanitic (fine-grained) igneous rock is classified as trachybasalt when it has a silica content of about 49% and a total alkali metal oxide content of about 6%. This places trachybasalt in the S1 field of the TAS classification, TAS diagram. Trachybasalt is further divided into sodium-rich ''hawaiite'' and potassium-rich ''potassic trachybasalt'', with wt% > + 2 for hawaiite. The intrusive equivalent of trachybasalt is monzonite. Trachybasalt is not defined on the QAPF diagram, which classifies crystalline igneous rock by its relative content of feldspars and quartz. However, the U.S. Geological Survey defines trachybasalt as a mafic volcanic rock (composed of over 35% ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Magma Series
The alkaline magma series is a chemically distinct range of magma compositions that describes the evolution of an Alkaline volcanic rock, alkaline mafic magma into a more evolved, silica-rich end member. Geochemical characterization Rocks in the alkaline magma series are distinguished from rocks in the subalkaline tholeiitic and calc-alkaline magma series by their high content of alkali metal oxides (K2O plus Na2O) relative to silica (SiO2). They are distinct from the rare peralkaline volcanic rock, peralkaline magmas, which have excess alkali oxides relative to alumina (Na2O + K2O > Al2O3). Alkaline magmas tend to show high titanium oxide (TiO2) content, typically in excess of 3% by weight. Other incompatible elements, such as phosphorus and LREE, light rare earth elements, are also elevated. This is attributed to a very low degree of partial melting of the source rock, with only 5% or less of the source rock going into the magma melt. Petrography All alkaline series magmas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mugearite
Mugearite () is a type of oligoclase-bearing basalt, comprising olivine, apatite, and opaque oxides. The main feldspar in mugearite is oligoclase. Mugearite is a sodium-rich member of the alkaline magma series. In the TAS classification of volcanic rock, mugearite is classified as sodium-rich basaltic trachyandesite. Examples Western Scotland Mugearite was first identified at Mugeary on the island of Skye, Scotland by Alfred Harker in 1904. Outcrops of mugearite also occur on the island of Mull. These examples of mugearite were formed during a period of continental flood basalt volcanic activity that happened in western Scotland during the Paleogene period of the Earth's geological history, when the North Atlantic Ocean opened between Europe and North America. Oceanic islands Mugearite has been erupted by the volcanoes of some oceanic islands at hotspots. Examples are Hawaii, Ascension Island, Saint Helena, Réunion, Mauritius and Tahiti. Mars Analysis of a Martian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron Silicate minerals, silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of Nesosilicates, nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickly on the surface. Olivine has many uses, such as the gemstone peridot (or chrysolite), as well as industrial applications like metalworking processes. The ratio of magnesium to iron varies between the two endmember (mineralogy), endmembers of the solid solution series: forsterite (Mg-endmember: ) and fayalite (Fe-endmember: ). Compositions of olivine are commonly expressed as Mole (unit), molar percentages of forsterite (Fo) and/or fayalite (Fa) (''e.g.'', Fo70Fa30, or just Fo70 with Fa30 implied). Forsterite's melting temperature is unusually high at atmospheric pressure, almost , while fayalite's is much lower – about . Melting temperature varies smoothly between the two end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The Geology, geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock (geology), rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral or may be an aggregate (geology), aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankaramite
Ankaramite is volcanic rock type of mafic composition. It is a dark porphyritic variety of basanite containing abundant pyroxene and olivine phenocrysts.https://dialnet.unirioja.es/descarga/articulo/281059.pdf Luis Enrique Ortiz Hernández, ''An Arc Ankaramite Occurrence in Central Mexico,'' Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Geológicas, volumen 17, número 1 2000, p. 34-44 It contains minor amounts of plagioclase and accessory biotite, apatite, and iron oxides. Its type locality is Ankaramy in Madagascar. It was first described in 1916. It is also found in the Sierra de Guanajuato of Central Mexico, the South Pacific on islands such as Tahiti, Rarotonga, Samoa and in the Zealandia Zealandia (pronounced ), also known as (Māori language, Māori) or Tasmantis (from Tasman Sea), is an almost entirely submerged continent, submerged mass of continental crust in Oceania that subsided after breaking away from Gondwana 83� ..., Alexandra Volcanic Group. References Porphyrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andesite
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende. Andesite is the extrusive equivalent of plutonic diorite. Characteristic of subduction zones, andesite represents the dominant rock type in island arcs. The average composition of the continental crust is andesitic. Along with basalts, andesites are a component of the Geology of Mars, Martian crust. The name ''andesite'' is derived from the Andes mountain range, where this rock type is found in abundance. It was first applied by Christian Leopold von Buch in 1826. Description Andesite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) to porphyritic (coarse-grained) igneous rock that is intermediate in its content of silica and low in alkali metals. It has less than 20% quartz and 10% feldspa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated Px) are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents ions of calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe(II)) or magnesium (Mg) and more rarely zinc, manganese or lithium, and Y represents ions of smaller size, such as chromium (Cr), aluminium (Al), magnesium (Mg), cobalt (Co), manganese (Mn), scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V) or even iron (Fe(II) or Fe(III)). Although aluminium substitutes extensively for silicon in silicates such as feldspars and amphiboles, the substitution occurs only to a limited extent in most pyroxenes. They share a common structure consisting of single chains of silica tetrahedra. Pyroxenes that crystallize in the monoclinic system are known as clinopyroxenes and those that crystallize in the orthorhombic system are known as orthopyroxenes. The name ''pyroxene'' is derived from the Ancient Greek w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albite
Albite is a plagioclase feldspar mineral. It is the sodium endmember of the plagioclase solid solution series. It represents a plagioclase with less than 10% anorthite content. The pure albite endmember has the formula . It is a tectosilicate. Its color is usually pure white, hence its name from Latin, . It is a common constituent in felsic rocks. Properties Albite crystallizes with triclinic pinacoidal forms. Its specific gravity is about 2.62 and it has a Mohs hardness of 6 to 6.5. Albite almost always exhibits crystal twinning often as minute parallel striations on the crystal face. Albite often occurs as fine parallel segregations alternating with pink microcline in perthite as a result of exolution on cooling. There are two variants of albite, which are referred to as 'low albite' and 'high albite'; the latter is also known as 'analbite'. Although both variants are triclinic, they differ in the volume of their unit cell, which is slightly larger for the 'high' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andesine
Andesine is a silicate mineral, a member of the plagioclase feldspar solid solution series. Its chemical formula is ( Ca, Na)( Al, Si)4 O8, where Ca/(Ca + Na) (% anorthite) is between 30 and 50%. The formula may be written as Na0.7-0.5Ca0.3-0.5Al1.3-1.5Si2.7-2.5O8. The plagioclase feldspars are a continuous solid solution series and as such the accurate identification of individual members requires detailed optical study, chemical analysis or density measurements. Refractive indices and specific gravity increase directly with calcium content.Klein, Cornelis, and Cornelius S. Hurlbut, Jr., ''Manual of Mineralogy,'' Wiley, 20th ed. 1985, p. 455 It is sometimes used as a gemstone. Name and discovery Andesine was first described in 1841 for an occurrence in the Marmato mine, Marmato, Cauca, Chocó Department, Colombia. The name is for the Andes due to its abundance in the andesite lavas in those mountains. In the early 2000s, red and green gemstones began to be marketed under th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plagioclase
Plagioclase ( ) is a series of Silicate minerals#Tectosilicates, tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more properly known as the plagioclase feldspar series. This was first shown by the German mineralogist Johann F. C. Hessel, Johann Friedrich Christian Hessel (1796–1872) in 1826. The series ranges from albite to anorthite endmembers (with respective compositions NaAlSi3O8 to CaAl2Si2O8), where sodium and calcium atoms can substitute for each other in the mineral's crystallography, crystal lattice structure. Plagioclase in hand samples is often identified by its polysynthetic crystal twinning or "phonograph record, record-groove" effect. Plagioclase is a major constituent mineral in Earth's crust and is consequently an important diagnostic tool in petrology for identifying the composition, origin and evolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali Feldspar
Feldspar ( ; sometimes spelled felspar) is a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldspars and the ''alkali'' (potassium-sodium) feldspars. Feldspars make up about 60% of the Earth's crust and 41% of the Earth's continental crust by weight. Feldspars crystallize from magma as both intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks and are also present in many types of metamorphic rock. Rock formed almost entirely of calcic plagioclase feldspar is known as anorthosite. Feldspars are also found in many types of sedimentary rocks. Etymology The name ''feldspar'' derives from the German , a compound of the words ' ("field") and ("flake"). had long been used as the word for "a rock easily cleaved into flakes"; was introduced in the 18th century as a more specific term, referring perhaps to its common occurre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |