|
Haselton Glacier
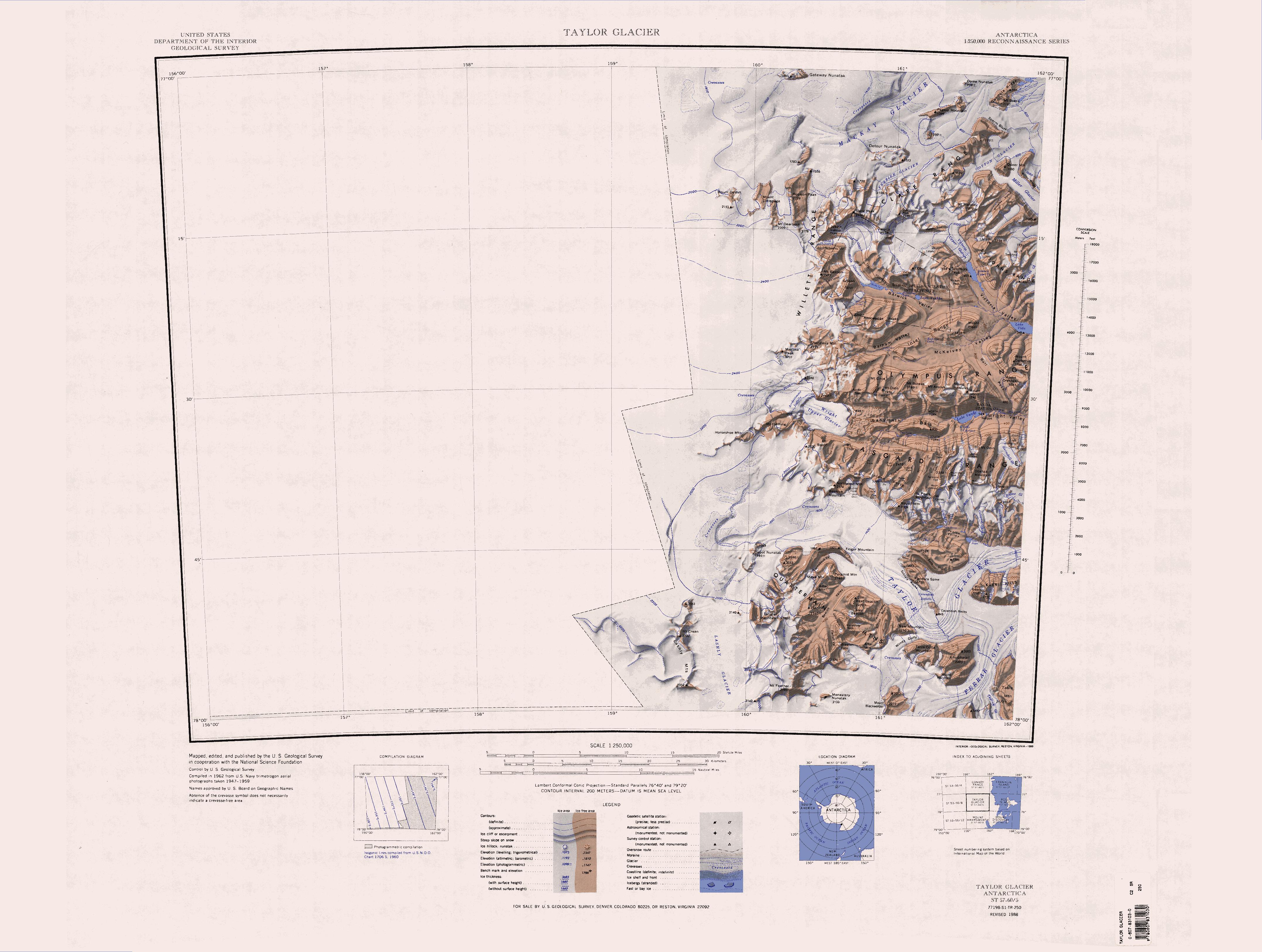
Barwick Valley () is an ice-free valley north of Apocalypse Peaks, extending from Webb Glacier to Victoria Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. A large part of the valley has been designated an Antarctic Specially Protected Area because of its pristine condition. Naming Barwick Valley was named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (VUWAE) (1958–59) for Richard Essex Barwick (1929-2012), summer biologist with the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) who worked in this area in 1957–58 and as a member of the VUWAE, 1958–59. Location The Barwick Valley is one of the McMurdo Dry Valleys. It runs southeast from the Webb Icefall to the Insel Range, where it is joined from the southwest by Balham Valley. The combined valley continues east to Victoria Valley. To the north the valley is bounded by The Fortress and other features of the Cruzen Range (formerly part of the Clare Range). To the west and southwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willett Range
The Willett Range () is the range extending north from Mistake Peak and running for as a high shelf along the edge of the continental ice to the Mackay Glacier, in Victoria Land. The range is breached by several glaciers flowing east from the plateau. Name The Willett Range was named by the New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE; 1956–58) for R.W. Willett, Director of the New Zealand Geological Survey, who gave valuable assistance throughout the expedition and in the compilation stages after its return. Location The Willet Range runs from south to north along the eastern side of the Antarctic Plateau. It is north of Wright Upper Glacier and the Olympus Range, and west of Balham Valley, the Apocalypse Peaks, Barwick Valley, the Cruzen Range, and Clare Range. The head of the Mackay Glacier is to the north. Head Mountains . A group of mountains to the south of Gateway Nunatak and the head of Mackay Glacier Mackay Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peterson Terrace
The Cruzen Range () is a mountain range that rises to in Vashka Crag and extends west to east for between Salyer Ledge and Nickell Peak in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Victoria Land, Antarctica. The range is bounded to north, east, south and west by the Clare Range, Victoria Valley, Barwick Valley, and the Webb Glacier. Name The Cruzen Range was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAP) in 2005 after Rear Admiral Richard H. Cruzen, commander of Task Force 68 during the U.S. Navy Antarctic Developments Project, 1946-47 (Operation Highjump). Location The Cruzen Range was formerly the southern part of the Clare Range, to the north. It is separated from the Clare Range by Webb Cirque which holds the névé at the head of the Webb Glacier to the northwest, and Victoria Upper Névé that feeds Victoria Upper Glacier to the northeast. The two are separated by a ridge leading south from Parker Mesa to The Fortress. To the south the range is bounde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Besson Spur
The Apocalypse Peaks () are a group of peaks with a highest point of , standing east of Willett Range and between Barwick Valley and Balham Valley, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. Name The Apocalypse Peaks were so named by the Victoria University of Wellington Antarctic Expedition (1958–59) because the peaks are cut by talus slopes which gives them the appearance of the " Riders of the Apocalypse." Location The Apocalypse Peaks are bounded by the Barwick Valley to the northeast and the Balham Valley to the southeast. The Willett Range lies to the west, the Cruzen Range (formerly part of the Clare Range) to the north, the Insel Range to the southeast and the Olympus Range to the south. Southern features Features of the south of the peaks include, from west to east, Edbrooke Hill . A hill, high, at the extreme west end of the Apocalypse Peaks. The hill rises high above the adjacent plateau ice, which diverges at the hill to the east-northeast-flowing Haselton Glacier an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Névé
Névé is a young, granular type of snow which has been partially melted, refrozen and compacted, yet precedes the form of ice. This type of snow can contribute to glacier formation through the process of ''nivation''. Névé that survives a full season of ablation turns into firn, which is both older and slightly denser. Firn eventually becomes glacial ice – the long-lived, compacted ice that glaciers are composed of. Glacier formation can take years to hundreds of years, depending on freeze-thaw factors and snow-compaction rates. Névé is annually observed in skiing slopes, and is generally disliked as an icy falling zone. Névé has a minimum density of 500 kg/m3, which is Density#Water, roughly half of the density of liquid water at 1 Atmosphere (unit), atm. Névé can also refer to the Alpine climate, alpine region in which snowfall accumulates, becomes névé, and feeds a glacier. See also * Suncup (snow), Suncup Notes External links * Névés, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parker Mesa
The Clare Range () is the range extending west-southwest from Sperm Bluff to the Willett Range on the south side of Mackay Glacier, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It is south of the Convoy Range and north of the Olympus Range. Exploration and name The Clare Range was circumnavigated in 1957 by the New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE; 1956–58), and named by them after Clare College, Cambridge, England. Location The Clare Range runs in an east-northeast direction to the south of the Frazier Glacier and Mackay Glacier. The Willett Range is to its east. The head of the Webb Glacier and Victoria Upper Névé separate it from the Cruzen Range to the south. The eastern part of the range is north of the Saint Johns Range and Cotton Glacier Wilson Piedmont Glacier () is a large piedmont glacier extending from Granite Harbour to Marble Point on the coast of Victoria Land. Discovery and name The Wilson Piedmont Glacier was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal Environmental factor, factors. External factors—including climate—control the ecosystem's structure, but are not influenced by it. By contrast, internal factors control and are controlled by ecosystem processes; these include decomposition, the types of species present, root competition, shading, disturbance, and succession. While external factors generally determine which Resource (biology), resource inputs an ecosystem has, their availability within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors. Ecosystems are wikt:dynamic, dynamic, subject to periodic disturbances and always in the process of recovering from past disturbances. The tendency of an ecosystem to remain clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |