|
Haplogroup R2 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup R2, or R-M479, is a Y-chromosome haplogroup characterized by genetic marker M479. It is one of two primary descendants of Haplogroup R (R-M207), the other being R1 (R-M173). It has two primary branches: R2a (M124) and R2b (R-FGC21706) R-M479, especially its downstream R2a (R-M124), has been concentrated geographically in South Asia, Central Asia and parts Middle East since prehistory. R2(xR2a) appears to reach its highest levels among the Burusho people in North Pakistan. Structure * R (M207/Page37/UTY2) ** R1 (M173/P241/Page29) ** R2 (M479/PF6107, L266/PF6108, L722, L726) *** R2a (M124, F820/Page4, L381, P249) **** R2a1 (L263) **** R2a2 (P267/PF6109) *** R2b (FGC21706, FGC50198, FGC50325, FGC50333, SK2163, SK2164, SK2165, SK2166) **** R2b1 (FGC50339) ''Source: ISOGG 2017.'' Geographical distribution Most research has tested only for the presence of R-M479 (R2) and R-M124 (R2a) – or SNPs downstream from M124 like P249, P267, L266, PAGES000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Before Present
Before Present (BP) or "years before present (YBP)" is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use 1January 1950 as the commencement date (epoch) of the age scale, with 1950 being labelled as the "standard year". The abbreviation "BP" has been interpreted retrospectively as "Before Physics", which refers to the time before nuclear weapons testing artificially altered the proportion of the carbon isotopes in the atmosphere, which scientists must account for when using radiocarbon dating for dates of origin that may fall after this year. In a convention that is not always observed, many sources restrict the use of BP dates to those produced with radiocarbon dating; the alternative notation "RCYBP" stands for the explicit "radio carbon years before present". Usage The BP scale is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Jews
Iranian Jews, (; ) also Persian Jews ( ) or Parsim, constitute one of the oldest communities of the Jewish diaspora. Dating back to the History of ancient Israel and Judah, biblical era, they originate from the Jews who relocated to Iran (historically known as Name of Iran, Persia) during the time of the Achaemenid Empire. Books of the Hebrew Bible (i.e., Book of Esther, Esther, Book of Isaiah, Isaiah, Book of Daniel, Daniel, Book of Ezra, Ezra, and Book of Nehemiah, Nehemiah) bring together an extensive narrative shedding light on contemporary Jewish life experiences in History of Iran, ancient Iran; there has been a continuous History of the Jews in Iran, Jewish presence in Iran since at least the time of Cyrus the Great, who led Immortals (Achaemenid Empire), Achaemenid army's conquest of the Neo-Babylonian Empire and subsequently freed the Kingdom of Judah, Judahites from the Babylonian captivity. After 1979, Jewish emigration from Iran increased dramatically in light of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
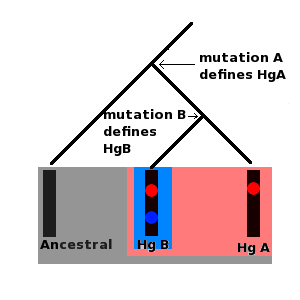
Human Y-DNA Haplogroups
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are great apes characterized by their hairlessness, bipedalism, and high intelligence. Humans have large brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, languages, and traditions (collectively termed institutions), each of which bolsters human society. Humans are also highly curious: the desire to understand and influence phenomena has motivated humanity's development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup R
Haplogroup R may refer to: * Haplogroup R (mtDNA) Haplogroup R is a widely distributed Human mitochondrial DNA haplogroup, human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. Haplogroup R is associated with the peopling of Eurasia after about 70,000 years ago, and is distributed in modern populations ..., a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup * Haplogroup R (Y-DNA), a human Y-chromosome (Y-DNA) haplogroup {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup R-U106 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the , ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and ) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplotype is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (haplogroup) is also a subset of a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup R-M420 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup R1a (R-M420), is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup which is distributed in a large region in Eurasia, extending from Scandinavia and Central Europe to Central Asia, southern Siberia and South Asia. The R1a (R-M420) subclade diverged from R1 (R-M173) 15-25,000 years ago, its subclade M417 (R1a1a1) diversified c. 3,400-5,800 years ago. The place of origin of the subclade plays a role in the debate about the origins of Proto-Indo-Europeans. The SNP mutation R-M420 was discovered after R-M17 (R1a1a), which resulted in a reorganization of the lineage in particular establishing a new paragroup (designated R-M420*) for the relatively rare lineages which are not in the R-SRY10831.2 (R1a1) branch leading to R-M17. Origins R1a origins The genetic divergence of R1a (M420) is estimated to have occurred 25,000 years ago, which is the time of the last glacial maximum. A 2014 study by Peter A. Underhill et al., using 16,244 individuals from over 126 populations from across Eura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup R-M342 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the , ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and ) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplotype is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (haplogroup) is also a subset of a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup R-M17 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup R1a (R-M420), is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup which is distributed in a large region in Eurasia, extending from Scandinavia and Central Europe to Central Asia, southern Siberia and South Asia. The R1a (R-M420) subclade diverged from R1 (R-M173) 15-25,000 years ago, its subclade M417 (R1a1a1) diversified c. 3,400-5,800 years ago. The place of origin of the subclade plays a role in the debate about the origins of Proto-Indo-Europeans. The SNP mutation R-M420 was discovered after R-M17 (R1a1a), which resulted in a reorganization of the lineage in particular establishing a new paragroup (designated R-M420*) for the relatively rare lineages which are not in the R-SRY10831.2 (R1a1) branch leading to R-M17. Origins R1a origins The genetic divergence of R1a (M420) is estimated to have occurred 25,000 years ago, which is the time of the last glacial maximum. A 2014 study by Peter A. Underhill et al., using 16,244 individuals from over 126 populations from across Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup R-M167 (Y-DNA)
In human genetics, Haplogroup R-M167 (R1b1a1a2a1a2a1b1a1) is a Y-chromosome haplogroup which is a subdivision of Haplogroup R-DF27 and the wider haplogroup R-M269 (more specifically, its subclade R-) defined by the presence of the marker M167 (also known as SRY2627).ISOGG tree as of 2017isogg.org It arose comparatively recently, after the beginning of the European Bronze Age, and is mostly prevalent in the population of the Pyrenees region. Distribution The first author to test for this marker (long before current haplogroup nomenclature existed) was Hurles in 1999, who tested 1158 men in various populations. He found it relatively common among Basques (13/117: 11%) and Catalans (7/32: 22%). Other occurrences were found among other Spanish, Béarnais, other French, British and Germans. In 2000 Rosser et al., in a study which tested 3616 men in various populations also tested for that same marker, naming the haplogroup Hg22, and again it was found mainly among Basques (19%), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup R-L295 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup R-L295 also known as R2a1 is a Y-chromosome haplogroup characterized by genetic marker L295, which has been found in South Asia, Anatolia, Arabian Peninsula, Europe and Central Asia. Subclades Paragroup R-L295* Paragroup is a term used in population genetics to describe lineages within a haplogroup that are not defined by any additional unique markers. They are typically represented by an asterisk (*) placed after the main haplogroup. Y-chromosomes which are positive to the L295 SNP and negative to the L294 SNP, are categorized as belonging to Paragroup R-L295*. It is found in South Asia, Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Europe, & Central Asia so far.R2-M124-WTY (Walk Through the Y) Project,R2-M124-WTY (Walk Through the Y) Project" Haplogroup R-L294 Haplogroup R-L294 is represented by the L294 SNP and found in Armenia Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup R-L21 (Y-DNA)
R-L21 or R1b1a2a1a2c, also known as R-M529 or R-S145, is a Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is often linked to the Insular Celts. One subclade, R-DF13 comprises over 99% of bearers. It is dominant among males in Ireland, Scotland, Wales and Brittany, present in high frequencies in England and western France and present also to a lesser extent in Iberia, Scandinavia and the Low Countries. History This haplogroup first emerges in the Early Bronze Age in Britain and Ireland, where the earliest samples begin to appear. Its introduction was part of a large genetic transformation associated with the Bell Beaker culture, wherein steppe descended peoples largely replaced Britain's earlier Neolithic population. The lineage reached a frequency of 90% in early Bronze Age Britain (being nearly absent in contemporary samples from the continent), it gradually declined through the Middle Bronze Age to 70% by the Iron Age (due to continental migrations which also increased the levels of EEF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |