|
Haplogroup I-Z63
Haplogroup I-Z63, also known as I1a3 per the International Society of Genetic Genealogy ('ISOGG), is a Y chromosome haplogroup. It is correlated with a DYS456 value inferior to 15, but there are exceptions. I-Z63 is most common in England, Scotland, Germany, Fennoscandia and Poland. Its progenitor is assumed to have lived in Jutland at around 2500 BCE. The earliest archeological sample for I-Z63 is indeed connected to an individual from near Hjørring in Jutland, present Denmark. Within Fennoscandia, I-Z63 has a particularly strong association with Finland. To date, ancient I-Z63 has been found archeologically in historic Jutland (present Denmark and Germany) along with Poland, Hungary, Turkey and Italy. Origins On the basis of analysing samples of volunteers in Next-gen sequencing, YDNA sequencing, the YDNA analysis companYFullestimated that I-Z63 formed 4,600 years ago (26th century BC, 2600 BC) (95% Confidence interval, CI 5,100 4,000 ybp) with a TMRCA (Time to Most Recent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
26th Century BC
The 26th century BC was a century that lasted from the year 2600 BC to 2501 BC. Events Crete * c. 2600–2400 BC: Minoan civilization, Early Minoan I period in Crete. Egypt * c. 2551–2526 BC: Reign of Khufu, second pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth Dynasty. The height of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom under the reigns of Khufu, Khafre and Menkaure. Khufu leads an expedition in Sinai Peninsula, Sinai and has the Great Pyramid of Giza built. During his reign, the solar cult of Ra prevails, as evidenced by the Khufu ship. His successor, Djedefre, is the first pharaoh to refer to himself by the epithet "Son of Ra". The pharaoh's divine filiation asserts itself in the second part of the Fourth Dynasty: the Ancient Egyptian royal titulary, royal title is definitively fixed with the appearance of a Nomen (Ancient Egypt), fifth royal name preceded by the title "Son of Ra". * c. 2520–2493 BC: Reign of Khafre. the Pyramid of Khafre is built, along with the Great Sph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
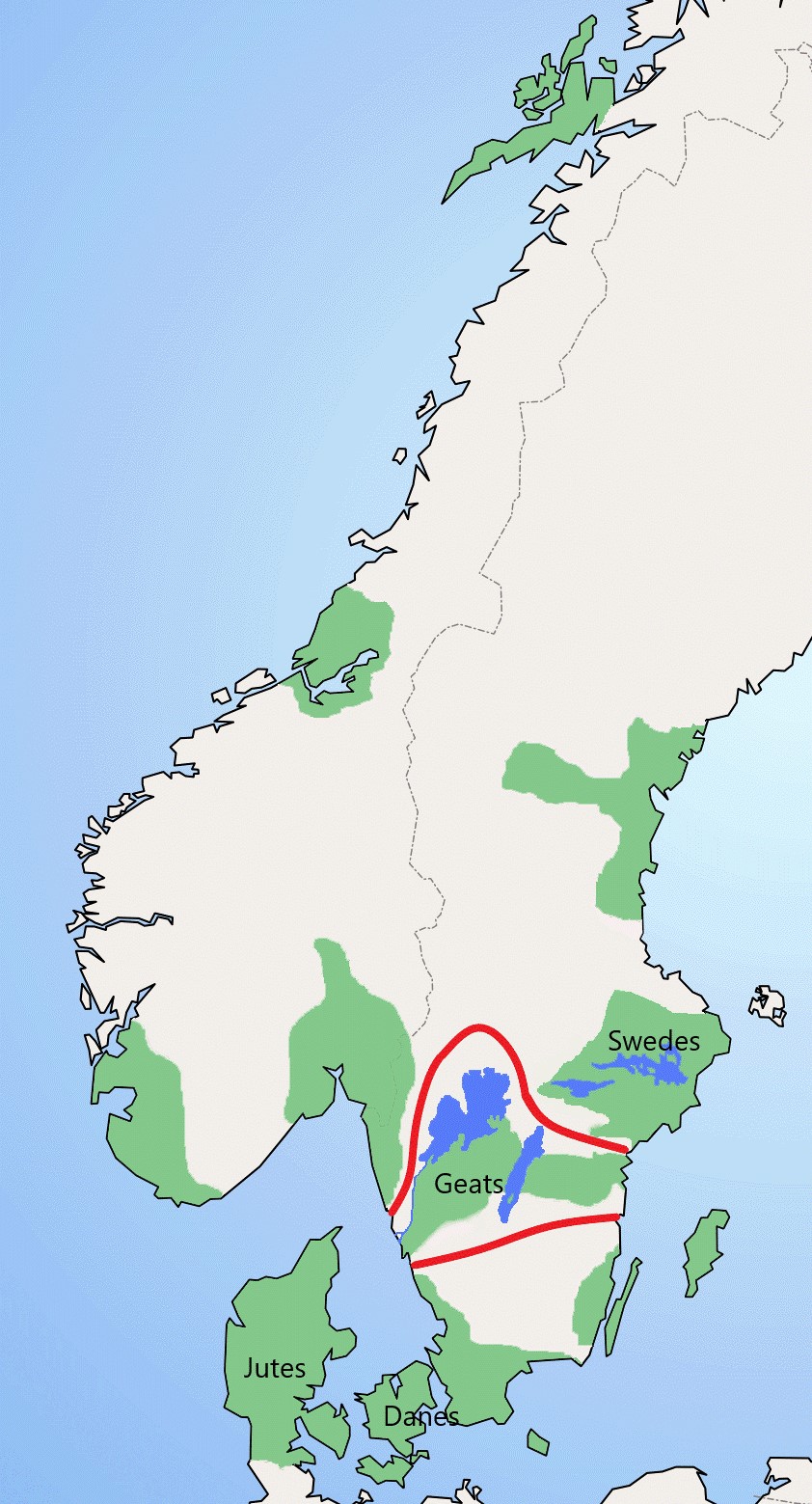
Geats
The Geats ( ; ; ; ), sometimes called ''Geats#Goths, Goths'', were a large North Germanic peoples, North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the Late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with the tribes of Swedes (tribe), Swedes and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Provinces of Sweden, Swedish provinces of and , the western and eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms. The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, ''Götamål''. Etymology The etymology of the name ''Geat'' (Old English ', from a Proto-Germanic *''Gautaz'', plural *''Gautōz'') is similar to that of ''Goths'' and ''Gutes'' (*''Gutô'', plural *''Gutaniz''). The names derive from Indo-European ablaut, ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *''geutaną'', meaning "to pour". They have the literal meaning "they who pour their se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th Century AD
The 4th century was the time period from 301 CE (represented by the Roman numerals CCCI) to 400 CE (CD) in accordance with the Julian calendar. In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two-emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, largest European island, and the List of islands by area, ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The island of Ireland, with an area 40 per cent that of Great Britain, is to the west – these islands, along with over List of islands of the British Isles, 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, comprise the British Isles archipelago. Connected to mainland Europe until 9,000 years ago by a land bridge now known as Doggerland, Great Britain has been inhabited by modern humans for around 30,000 years. In 2011, it had a population of about , making it the world's List of islands by population, third-most-populous islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wielbark, Pomeranian Voivodeship
Wielbark is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Malbork, within Malbork County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It lies approximately south-west of Malbork (on the road towards Sztum), and is south-east of the regional capital Gdańsk. Between the end of the 13th century and the 15th, the village lay in the territory of the Teutonic Knights. In 1454, King Casimir IV Jagiellon incorporated the region to the Kingdom of Poland. In 1466, the Teutonic Knights renounced claims, and it was confirmed as part of Poland,Górski, p. 91 within which it was a royal village, administratively located in the Malbork Voivodeship in the province of Royal Prussia in the Greater Poland Province. After the First Partition of Poland, it was annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia and from 1871 it was also part of Germany. After Germany's defeat in World War II World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, globa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gepids
The Gepids (; ) were an East Germanic tribes, East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary, and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava, and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion and language of the Goths and Vandals. They are first mentioned by Roman sources in the third century. In the fourth century, they were among the peoples incorporated into the Huns, Hunnic Empire, within which they formed an important part. After the death of Attila, the Gepids under their leader Ardaric, led an alliance of other peoples who had been in the empire, and defeated the sons of Attila and their remaining allies at the Battle of Nedao in 454. The Gepids and their allies subsequently founded kingdoms on the Middle Danube, bordering on the Roman Empire. The Gepid Kingdom was one of the most important and long-lasting of these, centered on Sirmium, and sometimes referred to as Gepidia. It covered a large part of the Roman Dacia, former Roman province o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous mainland of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by some, simply as the Continent. When Eurasia is regarded as a single continent, Europe is treated both as a continent and Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent. Usage The continental territory of the historical Carolingian Empire was one of the many old cultural concepts used for mainland Europe. This was consciously invoked in the 1950s as one of the basis for the prospective European integration (see also multi-speed Europe) The most common definition of mainland Europe excludes these Island#Continental islands, continental islands: the list of islands of Greece, Greek islands, Cyprus, Malta, Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica, the Balearic Islands, Great Britain and Ireland and surrounding islands, Novaya Zemlya and the Nordic archipelago, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotland
Gotland (; ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a Provinces of Sweden, province/Counties of Sweden, county (Swedish län), Municipalities of Sweden, municipality, and List of dioceses, deaneries and parishes of the Church of Sweden, diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the north, as well as the Karlsö Islands (Lilla Karlsö, Lilla and Stora Karlsö, Stora) to the west. The population is 61,023 (2024) of which about 23,600 live in Visby, the main town. Outside Visby, there are minor settlements and a mainly rural population. The island of Gotland and the other areas of the province of Gotland make up less than one percent of Sweden's total land area. The county formed by the archipelago is the second smallest by area and is the least populated in Sweden. In spite of the small size due to its narrow width, the driving distance between the furthermost points of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gutasaga
Gutasaga (''Gutasagan'') is a saga regarding the history of Gotland before its Christianization. It was recorded in the 13th century and survives in only a single manuscript, the Codex Holm. B 64, dating to , kept at the National Library of Sweden in Stockholm together with the Gutalagen, Gutalag, the legal code of Gotland. It was written in the Old Gutnish language, a variety of Old Norse. Contents A local creation myth The saga begins with Gotland being discovered by a man named Þieluar (Swedish language, Swedish: Tjälvar, Gutnish: ''Tjelvar''). Gotland is under a spell and under water during the day and out of water only during the night, a spell that is broken by Þieluar lighting a fire on the island. Þieluar had a son named Hafþi (Swedish: Hafþi), who married a woman named Hwitastierna (Swedish: Vitastjärna; English: White-star). After Hafþi's and Hwitastierna's first night together, she has a dream about three snakes entwined in her bosom. Hafþi interprets her dream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wihtwara
Wihtwara ( or ) were the Early Medieval inhabitants of the Isle of Wight, a island off the south coast of England. Writers such as Bede attribute their origin to Jutes who migrated to the island during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. They formed an independent kingdom at points in the Early Middle Ages, with their last king Arwald dying as the last heathen Anglo-Saxon king. After this point, the island was controlled from Great Britain. Name The term translates from Old English as "the people of the Isle of Wight", with the suffix denoting a people group, as in ("the people of Kent"). In the Old English translation of Bede's work, the term is used instead, possibly as it was the more common name by which the group was known at the time of writing. It has been suggested that the suffixes and may have had a slight semantic difference, with the latter being used more for political purposes and in reference to groups with a fixed location. Consequently, the loss of po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osburga
Osburh or Osburga (also Osburga Oslacsdotter) was the first wife of King Æthelwulf of Wessex and mother of King Alfred the Great. Alfred's biographer, Asser, described her as "a most religious woman, noble in character and noble by birth". Sources Osburh's existence is known only from Asser's ''Life of King Alfred''. She is not named as witness to any charters, nor is her death reported in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle''. So far as is known, she was the mother of all Æthelwulf's children, his five sons Æthelstan, Æthelbald, Æthelberht, Æthelred and Alfred, and his daughter Æthelswith, wife of King Burgred of Mercia. Osburh is best known from Asser's story about a book of Saxon songs which she showed to her sons, offering to give the book to whoever could first memorise it, a challenge which Alfred took up and won. This exhibits high-status ninth-century women's interest in books and their role in educating their children. Osburh was the daughter of Oslac (who is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred The Great
Alfred the Great ( ; – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfred was young. Three of Alfred's brothers, Æthelbald, King of Wessex, Æthelbald, Æthelberht, King of Wessex, Æthelberht and Æthelred I of Wessex, Æthelred, reigned in turn before him. Under Alfred's rule, considerable administrative and military reforms were introduced, prompting lasting change in England. After ascending the throne, Alfred spent several years fighting Viking invasions. He won a decisive victory in the Battle of Edington in 878 and made an agreement with the Vikings, dividing England between Anglo-Saxon territory and the Viking-ruled Danelaw, composed of Scandinavian York, the north-east Midlands and East Anglia. Alfred also oversaw the conversion of Viking leader Guthrum to Christianity. He defended his kingdom again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |