|
Hans-Arwed Weidenmüller
Hans-Arwed Weidenmüller (born 26 July 1933 in Dresden) is a German theoretical physicist, who works primarily in the field of nuclear physics. Life and work Weidenmüller studied in Bonn and from 1956 to 1957 in Heidelberg under J. Hans D. Jensen, who was his doctoral thesis advisor for his thesis on stripping reactions (Zeitschrift für Physik Bd.150, 1958, 389), in which the nuclei used as projectiles lose nucleons to the nuclei used as targets. He was from 1963 professor for theoretical physics at the University of Heidelberg. From 1968 he worked at the Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics and was director there from 1972 until his 2001 retirement. Weidenmüller is known above all for his work in the theory of nuclear reactions. He examined nuclear reactions in the shell model under inclusion of continuum states and developed a microscopic statistical theory of nuclear reactions; this statistical theory (now known as transport theory) had applications to the interpretati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg, and Cologne), and the third-most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Saxony, Coswig, Radeberg, and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Dresden Basin, Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated, area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Matrix
In probability theory and mathematical physics, a random matrix is a matrix-valued random variable—that is, a matrix in which some or all of its entries are sampled randomly from a probability distribution. Random matrix theory (RMT) is the study of properties of random matrices, often as they become large. RMT provides techniques like mean-field theory, diagrammatic methods, the cavity method, or the replica method to compute quantities like traces, spectral densities, or scalar products between eigenvectors. Many physical phenomena, such as the spectrum of nuclei of heavy atoms, the thermal conductivity of a lattice, or the emergence of quantum chaos, can be modeled mathematically as problems concerning large, random matrices. Applications Physics In nuclear physics, random matrices were introduced by Eugene Wigner to model the nuclei of heavy atoms. Wigner postulated that the spacings between the lines in the spectrum of a heavy atom nucleus should resemble the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Purpose: Because living persons may suffer personal harm from inappropriate information, we should watch their articles carefully. By adding an article to this category, it marks them with a notice about sources whenever someone tries to edit them, to remind them of WP:BLP (biographies of living persons) policy that these articles must maintain a neutral point of view, maintain factual accuracy, and be properly sourced. Recent changes to these articles are listed on Special:RecentChangesLinked/Living people. Organization: This category should not be sub-categorized. Entries are generally sorted by family name In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several give .... Maintenance: Individuals of advanced age (over 90), for whom there has been no new documentation in the last ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1933 Births
Events January * January 11 – Australian aviator Sir Charles Kingsford Smith makes the first commercial flight between Australia and New Zealand. * January 17 – The United States Congress votes in favour of Philippines independence, against the wishes of U.S. President Herbert Hoover. * January 28 – "Pakistan Declaration": Choudhry Rahmat Ali publishes (in Cambridge, UK) a pamphlet entitled ''Now or Never; Are We to Live or Perish Forever?'', in which he calls for the creation of a Muslim state in northwest India that he calls "Pakistan, Pakstan"; this influences the Pakistan Movement. * January 30 ** Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler is appointed Chancellor of Germany (German Reich), Chancellor of Germany by President of Germany Paul von Hindenburg. ** Édouard Daladier forms a government in France in succession to Joseph Paul-Boncour. He is succeeded on October 26 by Albert Sarraut and on November 26 by Camille Chautemps. February * February 1 – Adolf Hitle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Johannesburg
The University of Johannesburg, colloquially known as UJ, is a public university A public university, state university, or public college is a university or college that is State ownership, owned by the state or receives significant funding from a government. Whether a national university is considered public varies from o ... located in Johannesburg, South Africa. The University of Johannesburg was established on 1 January 2005 as the result of a merger between the Rand Afrikaans University (RAU), the Technikon Witwatersrand (TWR) and the Soweto and East Rand campuses of Vista University. Prior to the merger, the Daveyton, Gauteng, Daveyton and Soweto campuses of the former Vista University had been incorporated into RAU. As a result of the merger of Rand Afrikaans University (RAU), it is common for alumni to refer to the university as RAU. The institution is one of the largest comprehensive university, comprehensive contact universities in South Africa from the 26 public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck Medal
The Max Planck Medal is the highest award of the German Physical Society , the world's largest organization of physicists, for extraordinary achievements in theoretical physics. The prize has been awarded annually since 1929, with few exceptions, and usually to a single person. The winner is awarded with a gold medal and hand-written parchment. In 1943 it was not possible to manufacture the gold medal because the Berlin foundry was hit by a bomb. The board of directors of the German Physical Society decided to manufacture the medals in a substitute metal and to deliver the gold medals later. The highest award of the German Physical Society for outstanding results in experimental physics is the Stern–Gerlach Medal. List of recipients *2025 Reinhard F. Werner *2024 Erwin Frey *2023 Rashid A. Sunyaev *2022 Annette Zippelius *2021 Alexander Markovich Polyakov *2020 Andrzej Buras *2019 Detlef Lohse *2018 Juan Ignacio Cirac *2017 Herbert Spohn *2016 Herbert Wagner *2015 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Academy Of Sciences Leopoldina
The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina (), in short Leopoldina, is the national academy of Germany, and is located in Halle (Saale). Founded on 1 January 1652, based on academic models in Italy, it was originally named the ''Academia Naturae Curiosorum'' until 1687 when Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Leopold I raised it to an academy and named it after himself. It was since known under the German name ''Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher Leopoldina'' until 2007, when it was declared to be Germany's National Academy of Sciences. It is the oldest continuously operating academy of natural sciences worldwide. History ' The Leopoldina was founded in the imperial city of Schweinfurt on 1 January 1652 under the Latin name sometimes translated into English as "Academy of the Curious as to Nature." It was founded by four local physicians – Johann Laurentius Bausch, the first president of the society, Johann Michael Fehr, Georg Balthasar Metzger, and Georg Baltha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weizmann Institute
The Weizmann Institute of Science ( ''Machon Weizmann LeMada'') is a Public university, public research university in Rehovot, Israel, established in 1934, fourteen years before the State of Israel was founded. Unlike other List of Israeli universities and colleges, Israeli universities it exclusively offers postgraduate-only degrees in the natural science, natural and exact sciences. The institute is a multidisciplinary research center, employing around 3,800 scientists, Postdoctoral researcher, postdoctoral fellows, Ph.D. and M.Sc. students, and scientific, technical, and administrative staff working at the institute. As of 2019, the Weizmann Institute of Science has been associated with six Nobel laureates and three Turing Award winners. The Weizmann Institute of Science and Elbit Systems have collaborated on various projects, notably including the development and supply of the space telescope for Israel's Ultraviolet Transient Astronomy Satellite (ULTRASAT) program and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
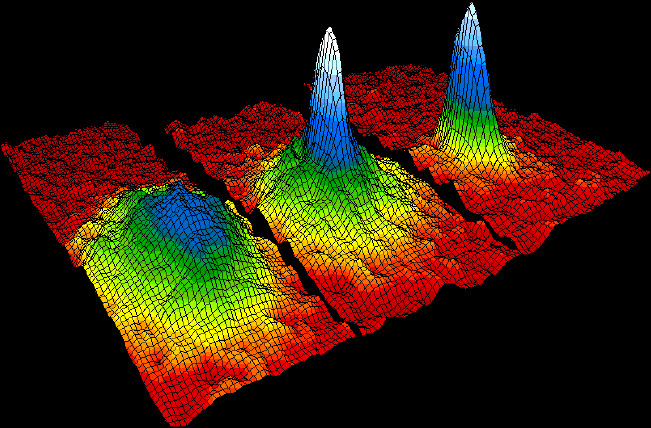
Bose–Einstein Condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low Density, densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero#Relation with Bose–Einstein condensate, absolute zero, i.e. . Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which microscopic Quantum mechanics, quantum-mechanical phenomena, particularly wave interference#Quantum interference, wavefunction interference, become apparent Macroscopic quantum phenomena, macroscopically. More generally, condensation refers to the appearance of macroscopic occupation of one or several states: for example, in BCS theory, a superconductor is a condensate of Cooper pairs. As such, condensation can be associated with phase transition, and the macroscopic occupation of the state is the order parameter. Bose–Einstein condensate was first predicted, generally, in 1924–1925 by Albert Einstein, credit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonn
Bonn () is a federal city in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, located on the banks of the Rhine. With a population exceeding 300,000, it lies about south-southeast of Cologne, in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr region. This metropolitan area, Germany's largest, is also the second largest in the European Union by GDP, with over 11 million residents. Bonn served as the capital of West Germany from 1949 until 1990 and was the seat of government for reunified Germany until 1999, when the government relocated to Berlin. The city holds historical significance as the birthplace of Germany's current constitution, the Basic Law. Founded in the 1st century BC as a settlement of the Ubii and later part of the Roman province Germania Inferior, Bonn is among Germany's oldest cities. It was the capital city of the Electorate of Cologne from 1597 to 1794 and served as the residence of the Archbishops and Prince-electors of Cologne. The period during which Bonn was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, including particle therapy for oncology, oncological purposes, Isotopes in medicine, radioisotope production for medical diagnostics, Ion implantation, ion implanters for the manufacturing of Semiconductor, semiconductors, and Accelerator mass spectrometry, accelerator mass spectrometers for measurements of rare isotopes such as radiocarbon. Large accelerators include the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York, and the largest accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider near Geneva, Switzerland, operated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |