|
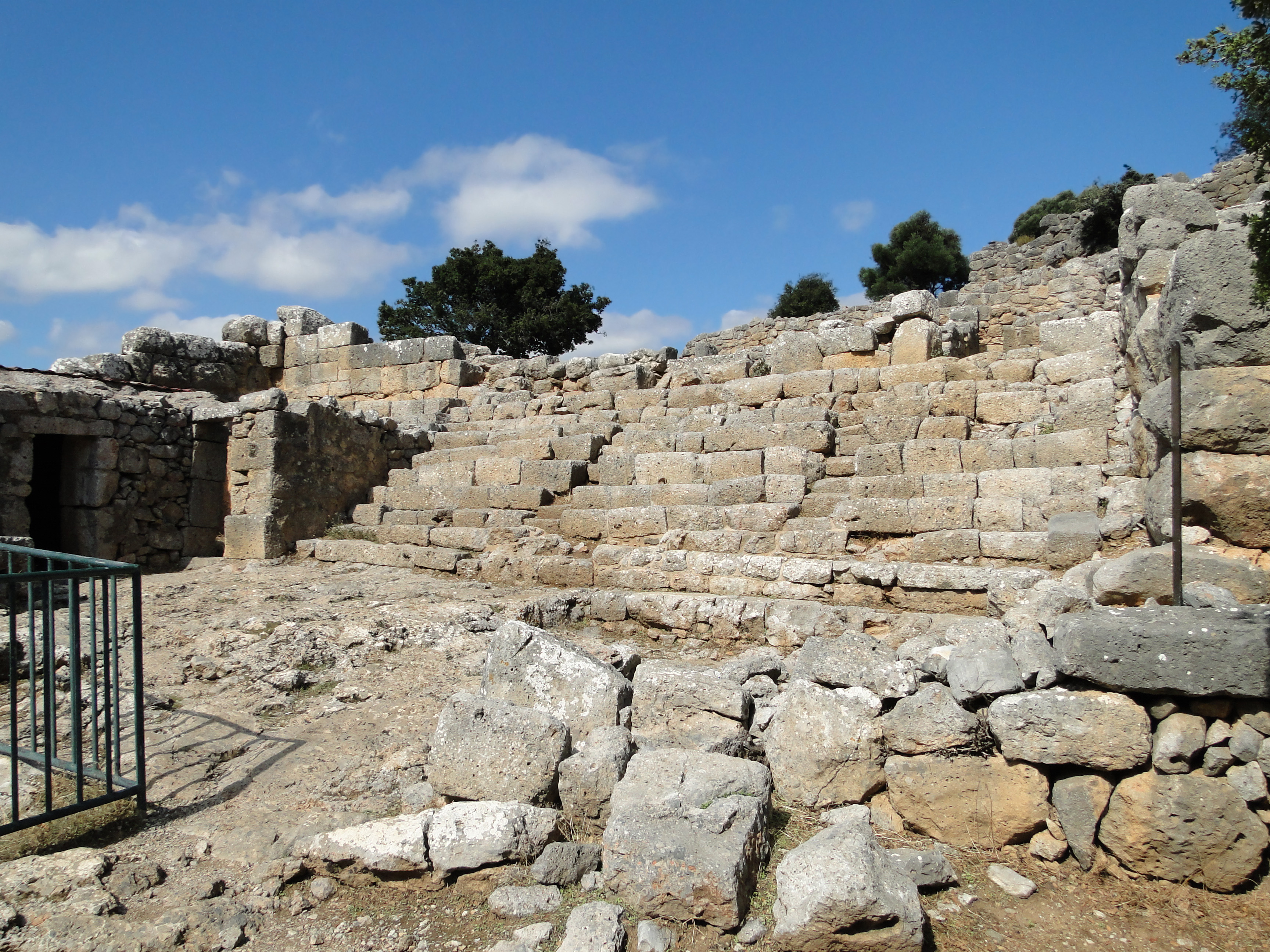
Halikarnassos
Halicarnassus ( ; Latin: ''Halicarnassus'' or ''Halicarnāsus''; ''Halikarnāssós''; ; Carian: 𐊠𐊣𐊫𐊰 𐊴𐊠𐊥𐊵𐊫𐊰 ''alos k̂arnos'') was an ancient Greek city in Caria, in Anatolia.Livius.org Halicarnassus/Bodrum "Usually, Greek settlers first occupied an island near a native settlement; later, they settled on the mainland. We may assume that the first Greeks built their houses on the island that was later known as the Royal Island. Today, it is no longer an island, but an impressive castle built in the age of the Crusades. The native settlement probably was at the Salmacis hill, which was crowned by a sanctuary of Hermaphroditus.", "Later, the Greeks settled on the mainland. To the northeast of the island, they founded a marketplace to trade with the natives. The new G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum At Halicarnassus
The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus or Tomb of Mausolus (; ) was a tomb built between 353 and 351 BC in Halicarnassus (present Bodrum, Turkey) for Mausolus, an Anatolian from Caria and a satrap in the Achaemenid Persian Empire, and his sister-wife Artemisia II of Caria. The structure was designed by the Greek architects Satyros and Pythius of Priene. Its elevated tomb structure is derived from the tombs of neighbouring Lycia, a territory Mausolus had invaded and annexed , such as the Nereid Monument. The Mausoleum was approximately in height, and the four sides were adorned with sculptural reliefs, each created by one of four Greek sculptors: Leochares, Bryaxis, Scopas of Paros, and Timotheus. The Mausoleum contained 400 freestanding sculptures. The mausoleum was considered to be such an aesthetic triumph that Antipater of Sidon identified it as one of his Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It was destroyed by successive earthquakes from the 12th to the 15th century; it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausolus
Mausolus ( or , ''Mauśoλ'') was a ruler of Caria (377–353 Common Era, BCE) and a satrap of the Achaemenid Empire. He enjoyed the status of king or dynast by virtue of the powerful position created by his father Hecatomnus ( ), who was the first satrap of Caria from the hereditary Hecatomnid dynasty. Alongside Caria, Mausolus also ruled Lycia and parts of Ionia and the Dodecanese islands. He is best known for his monumental tomb and one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, the construction of which has traditionally been ascribed to his wife and sister Artemisia II of Caria, Artemisia. Name Mausolus' name is only known directly in Greek ( or ). It is clearly of Carian language, Carian origin, though, and would have been written as *𐊪𐊠𐊲𐊸𐊫𐊦 (''*Mauśoλ'') or similar. This is a compound name perhaps meaning "much blessed". The first part, ''*Ma-'', may mean "much", similar to the same word in Hieroglyphic Luwian. The sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
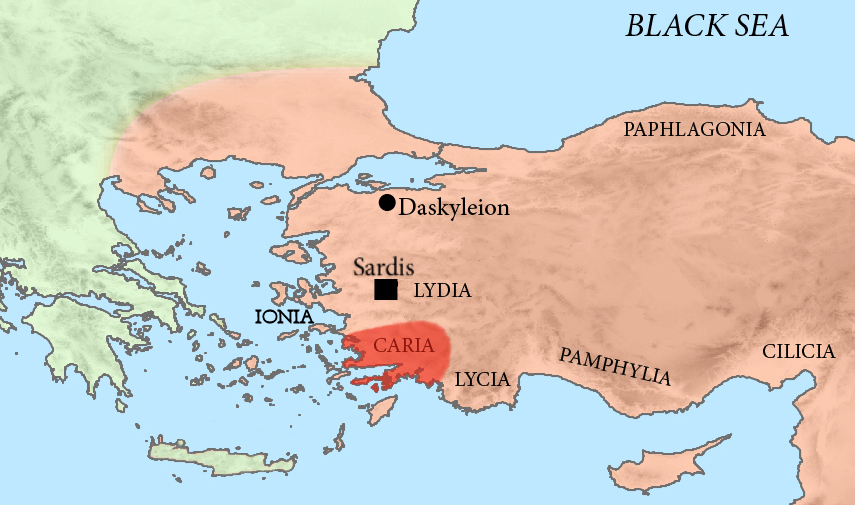
Caria
Caria (; from Greek language, Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; ) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Carians were described by Herodotus as being Anatolian mainlanders and they called themselves Caria because of the name of their king.''The Histories'', Book I Section 171. He reports the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians. The Carians spoke Carian language, Carian, a native Anatolian language closely related to Luwian language, Luwian. Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians. Municipalities of Caria Cramer's detailed catalog of Carian towns is based entirely on ancient sources. The multiple names of towns and geomorphic features, such as bays and headlands, reveal an ethnic layering consistent with the known colonization. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorians
The Dorians (; , , singular , ) were one of the four major ethnic groups into which the Greeks, Hellenes (or Greeks) of Classical Greece divided themselves (along with the Aeolians, Achaeans (tribe), Achaeans, and Ionians). They are almost always referred to as just "the Dorians", as they are called in the earliest literary mention of them in the ''Odyssey'', where they already can be found inhabiting the island of Crete. They were diverse in way of life and social organization, varying from the populous trade center of the city of Ancient Corinth, Corinth, known for its ornate style in art and architecture, to the isolationist, military state of Sparta; and yet, all Hellenes knew which localities were Dorian and which were not. Dorian states at war could more likely, but not always, count on the assistance of other Dorian states. Dorians were distinguished by the Doric Greek dialect and by characteristic social and historical traditions. In the 5th century BC, Dorians and Ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmacis (Caria)
Salmacis or Salmakis () was a town of ancient Caria. While the famed fountain appears in Strabo, the town is only mentioned in inscriptions. It was a ''polis'' (city-state) and a member of the Delian League The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian .... Its site is unlocated. References Populated places in ancient Caria Former populated places in Turkey Greek city-states Members of the Delian League Lost ancient cities and towns {{AncientCaria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
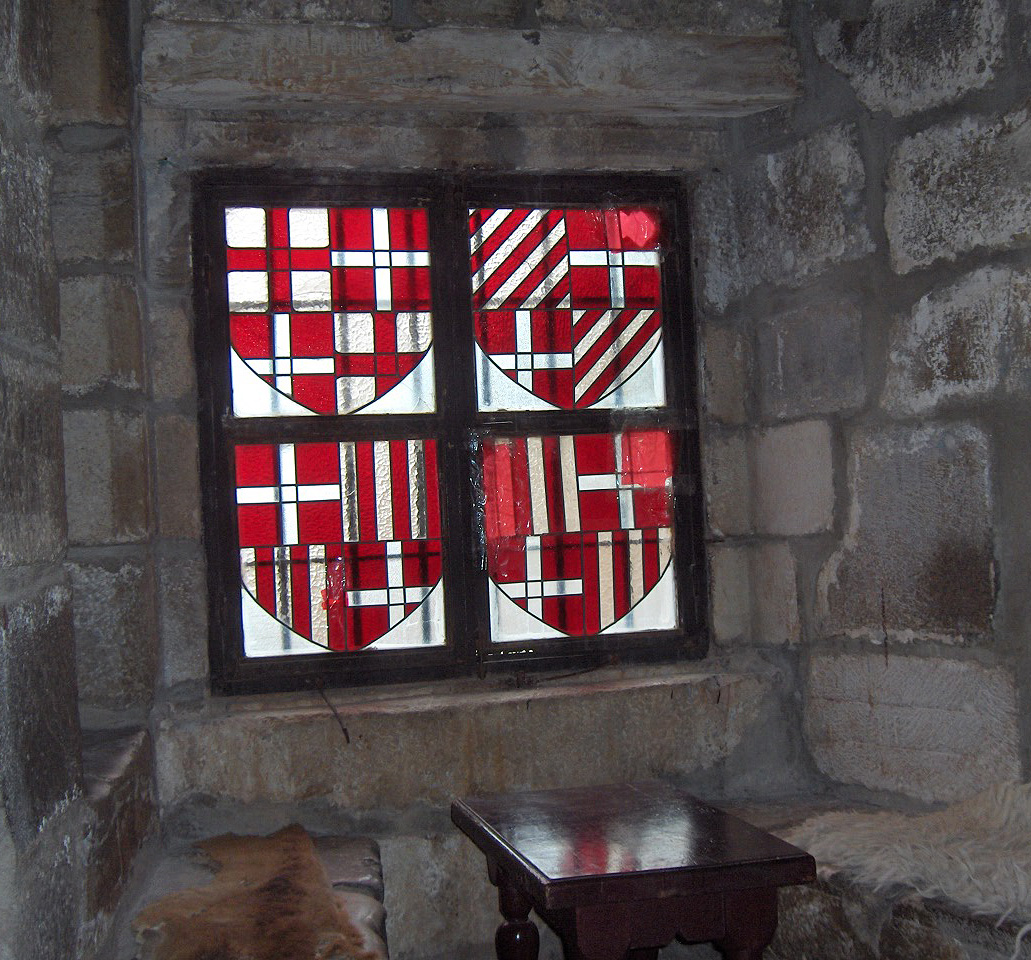
Bodrum Castle
Bodrum Castle () is a historical fortification located in southwest Turkey in the port city of Bodrum, built from 1402 onwards, by the Knights of St John (Knights Hospitaller) as the ''Castle of St. Peter'' or ''Petronium''. A transnational effort, it has four towers known as the English, French, German, and Italian towers, bearing the names of the nations responsible for their construction. The chapel was built around 1407 and the first walls completed in 1437. The castle started reconstruction in the late 15th century, only to be taken over by the Islamic Ottoman Empire in 1523. The chapel was converted to a mosque, and a minaret was added. The castle remained under the empire for almost 400 years. After remaining empty following World War I, in the early 1960s, the castle became the home for the Bodrum Museum of Underwater Archaeology. In 2016 it was inscribed in the UNESCO Tentative list of World Heritage Sites in Turkey. History Confronted by the now firmly established Ott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knights Of Rhodes
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), is a Catholic military order. It was founded in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century and had headquarters there until 1291, thereafter being based in Kolossi Castle in Cyprus (1302–1310), the island of Rhodes (1310–1522), Malta (1530–1798), and Saint Petersburg (1799–1801). The Hospitallers arose in the early 12th century at the height of the Cluniac movement, a reformist movement within the Benedictine monastic order that sought to strengthen religious devotion and charity for the poor. Earlier in the 11th century, merchants from Amalfi founded a hospital in Jerusalem dedicated to John the Baptist where Benedictine monks cared for sick, poor, or injured Christian pilgrims to the Holy Land. Blessed Gerard, a lay brother of the Benedictine order, became its head when it was established. After the Christian conquest of Jerusalem in 1099 du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carians
The Carians (; , ''Kares'', plural of , ''Kar'') were the ancient inhabitants of Caria in southwest Anatolia, who spoke the Carian language. Historical accounts Karkisa It is not clear when the Carians enter into history. The definition is dependent on corresponding Caria and the Carians to the "Karkiya" or "Karkisa" mentioned in the Hittites, Hittite records. Bronze Age Karkisa are first mentioned as having aided the Assuwa League against the Hittite King Tudhaliya I. Later in 1323 BC, King Arnuwandas II was able to write to Karkiya for them to provide asylum for the deposed Manapa-Tarhunta of "the land of the Seha River", one of the principalities within the Luwians, Luwian Arzawa complex in western Anatolia. This they did, allowing Manapa-Tarhunta to take back his kingdom. In 1274 BC, Karkisa are also mentioned among those who fought on the History of the Hittites, Hittite Empire side against the Egyptians in the Battle of Kadesh. Taken as a whole, Hittite records seem to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leleges
The Leleges (; ) were an aboriginal people of the Aegean Sea, Aegean region, before the Greek people, Greeks arrived. They were distinct from another pre-Hellenic people of the region, the Pelasgians. The exact areas to which they were native are uncertain, since they were apparently pre-literate and the only references to them are in ancient Greek sources. These references are casual and (it is alleged) sometimes fictitious. Likewise, little is known about the language of the ''Leleges''. Many Greek authors link the Leleges to the Carians of south-west Anatolia. Homer names the Leleges among the Trojan Battle Order, Trojan allies alongside the Carians, Pelasgians, Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonians and Paphlagonia, Gaucones. Etymology It is thought that the name ''Leleges'' is an exonym, in a long-extinct language, rather than an endonym (or autonym). That is, during the Bronze Age the word ''lulahi'' apparently meaning "strangers" was used in the Luwian language and in other Anatolian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20 and spent most of his ruling years conducting Wars of Alexander the Great, a lengthy military campaign throughout West Asia, Western Asia, Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of 30, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from History of Greece, Greece to northwestern History of India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-Greek Substrate
The pre-Greek substrate (or substratum) consists of the unknown pre-Greek language or languages (either Pre-Indo-European languages, Pre-Indo-European or other Indo-European languages) spoken in prehistoric Greece prior to the emergence of the Proto-Greek language in the region , during the Early Helladic period. About 1,000 words of Greek vocabulary cannot be adequately explained as derivatives from Proto-Greek or Proto-Indo-European, leading to the Stratum (linguistics), substratum hypothesis. According to scholars, Ancient Greek was likely influenced by two types of substrates: one Indo-European, probably an unknown Anatolian language that has been called "Parnassian", and one or several non-Indo-European languages that pre-date the coming of Greeks to the region. Overview Linguistic situation Based upon toponymic and lexical evidence, it is generally assumed that one or several languages were once spoken in both the Greek peninsula and western Asia Minor before Mycenaean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |