|
H-IIB
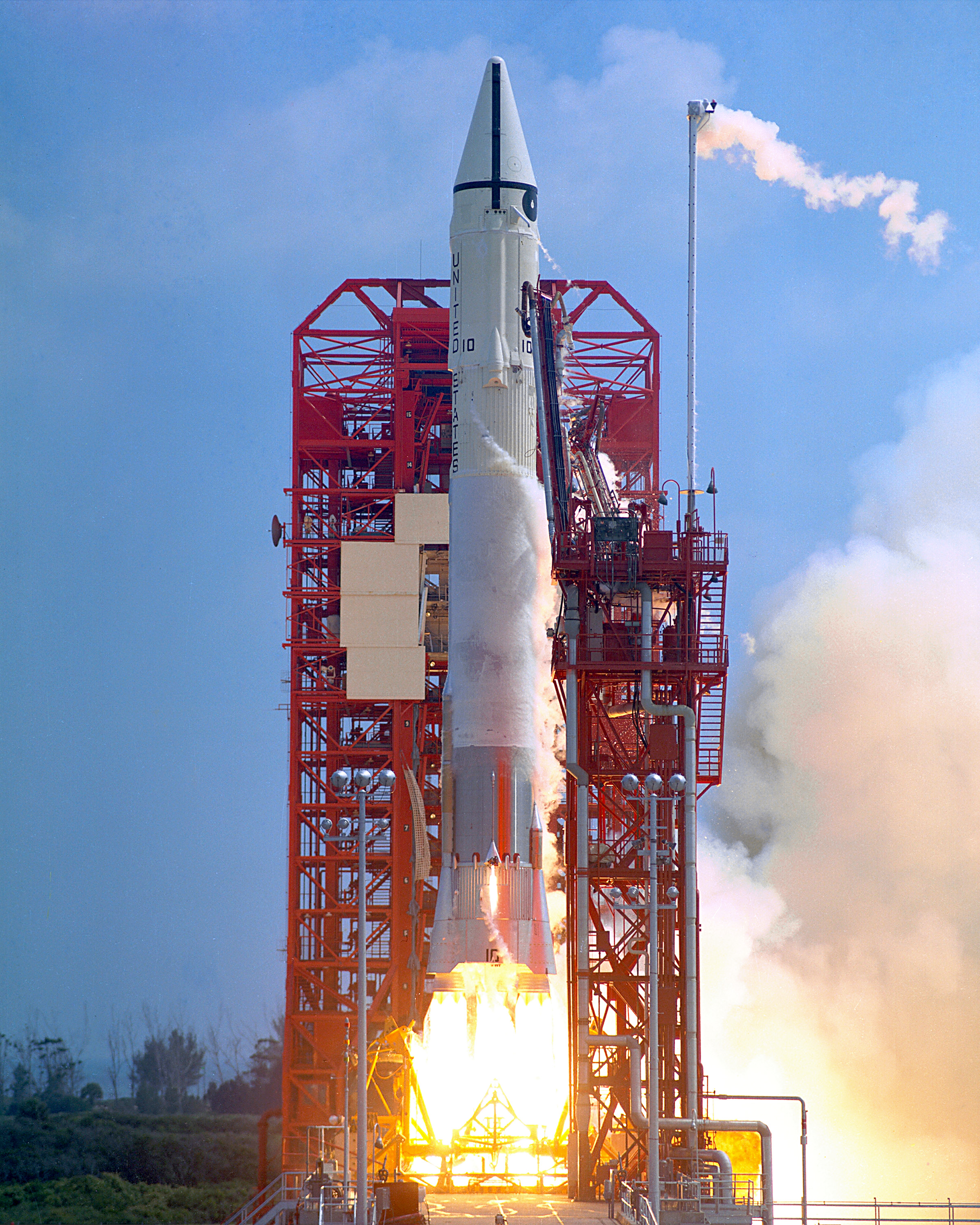
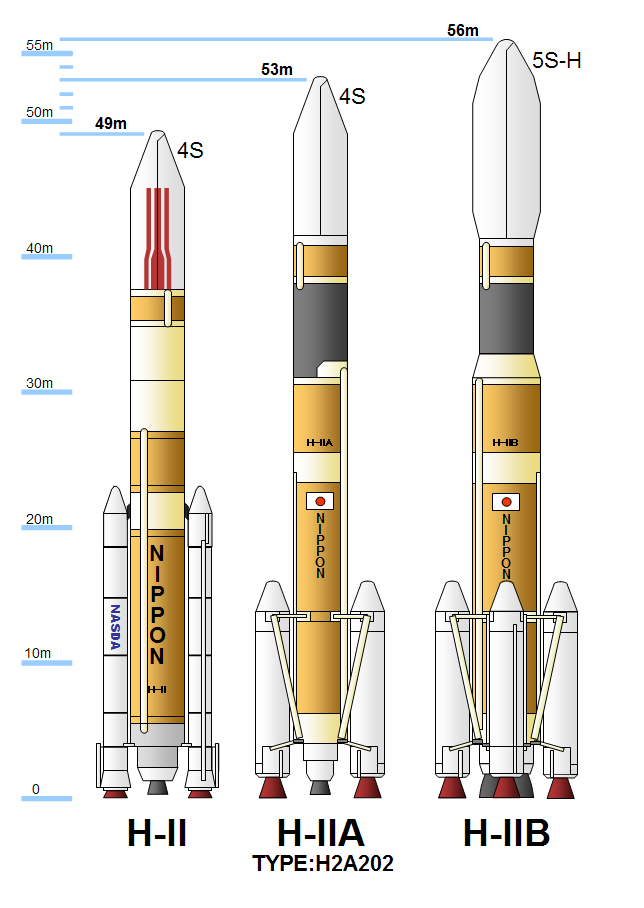
H-IIB (H2B) was an expendable space launch system jointly developed by the Japanese government's space agency JAXA and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. It was used to launch the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV, or ''Kōnotori'') cargo spacecraft for the International Space Station. The H-IIB was a liquid-fueled rocket, with solid-fuel strap-on boosters and was launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan. H-IIB made its first flight in 2009, and had made a total of nine flights through 2020 with no failures. H-IIB was able to carry a payload of up to to Geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), compared with the payload of 4000–6000 kg for the H-IIA, a predecessor design. Its performance to low Earth orbit (LEO) was sufficient for the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV). The first H-IIB was launched in September 2009 and the last H-IIB was launched in May 2020. Development The H-IIB was a space launch vehicle jointly designed, manufactured and operated by JAXA and Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-II Transfer Vehicle
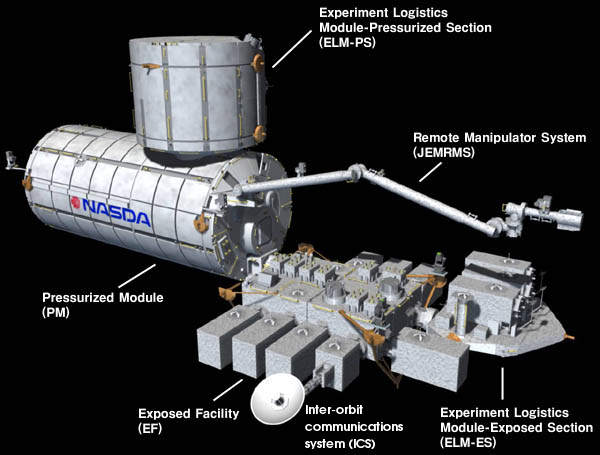
The H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV), also called , is an Expendable launch system, expendable Japanese Cargo spacecraft, automated cargo spacecraft designed for International Space Station (ISS) resupply missions, particularly the Kibo (ISS module), ''Kibō'' Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). Development of the spacecraft began in the early 1990s and the HTV's first mission, HTV-1, was launched on 10September 2009 on an H-IIB launch vehicle. The name ''Kounotori'' was chosen because "a white stork carries an image of conveying an important thing (a baby, happiness, and other joyful things), therefore, it precisely expresses the HTV's mission to transport essential materials to the ISS". The HTV is crucial for ISS resupply, especially after the retirement of the Space Shuttle, as it's the only vehicle capable of transporting large International Standard Payload Racks (ISPR) and disposing of old ones within the ISS's US Orbital Segment. The final HTV mission, Kounotori 9, was laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-II (rocket Family)
This is a list of launches made by JAXA using H-II, H-IIA, H-IIB H-IIB (H2B) was an expendable space launch system jointly developed by the Japanese government's space agency JAXA and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. It was used to launch the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV, or ''Kōnotori'') cargo spacecraft for ... and H3 rockets. Launch statistics Rocket configurations Launch sites Launch outcomes Launch history Planned launches Sources: Gunter's Space Page and Cabinet Office of Japan References {{Space exploration lists and timelines H-II seriesand H3 Lists of events in Japan Mitsubishi Heavy Industries space launch vehicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). Before the mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-IIA
H-IIA (H-2A) is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. These liquid fuel rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit; lunar orbiting spacecraft; '' Akatsuki'', which studied the planet Venus; and the Emirates Mars Mission, which was launched to Mars in July 2020. Launches occur at the Tanegashima Space Center. The H-IIA first flew in 2001. , H-IIA rockets were launched 49 times, including 43 consecutive missions without a failure, dating back to 29 November 2003. Production and management of the H-IIA shifted from JAXA to MHI on 1 April 2007. Flight 13, which launched the lunar orbiter SELENE, was the first H-IIA launched after this privatization. The H-IIA is a derivative of the earlier H-II rocket, substantially redesigned to improve reliability and minimize costs. There have been four variants, with two in active service (as of 2020) for various purposes. A d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational engineering, electrical equipment and electronics corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. MHI is one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group and its automobile division is the predecessor of Mitsubishi Motors. MHI's products include aerospace and Automotive industry, automotive components, Air conditioning, air conditioners, elevators, Forklift, forklift trucks, Hydraulic machinery, hydraulic equipment, Printing, printing machines, missiles, tanks, Electric power system, power systems, ships, aircraft, Rail transport, railway systems, and space launch vehicles. Through its defense-related activities, it is the world's 23rd-largest defense contractor measured by 2011 defense revenues and the largest based in Japan. History In 1857, at the request of the Tokugawa Shogunate, a group of Dutch people, Dutch engineers were invited, including Dutch naval engineer Hendrik Hardes, and began work on the ''Nagasaki Yotetsu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LE-7A
The LE-7 and its succeeding upgrade model the LE-7A are staged combustion cycle LH/ LOX liquid rocket engines produced in Japan for the H-II series of launch vehicles. Design and production work was all done domestically in Japan, the first major ( main/first-stage) liquid rocket engine with that claim, in a collaborative effort from the National Space Development Agency (NASDA), Aerospace Engineering Laboratory (NAL), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and Ishikawajima-Harima. NASDA and NAL have since been integrated into JAXA. However, a large part of the work was contracted to Mitsubishi, with Ishikawajima-Harima providing turbomachinery, and the engine is often referred to as the Mitsubishi LE-7(A). The original LE-7 was an expendable, high efficiency, medium-sized motor with sufficient thrust for use on the H-II. H-II Flight 8, only operational LE-7 failure The fuel turbopump had an issue using the originally designed inducer (a propeller-like axial pump used to raise the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoshinobu Launch Complex
Yoshinobu Launch Complex (abbreviated as LA-Y) is a List of rocket launch sites, rocket launch site at the Tanegashima Space Center on Tanegashima. The site and its collection of facilities were originally built for the H-II launch vehicle and later used for H-IIA, H-IIB and H3 (rocket), H3 launches. It is the most Northern launch complex at Tanegashima, and along with the now inactive Osaki Launch Complex used for orbital launches. The Yoshinobu Launch Complex consists of two launch pads. The complex also contains a Engine test stand, test stand for firing the LE-7 engines used in the first stage of the H-II and its derivatives. Prior to launch, rockets are processed vertically in the complex's vehicle assembly building. The rocket is rolled out to the launch pad on a mobile launcher platform about twelve hours before it is scheduled to launch. It takes around thirty minutes to transport the rocket from the assembly building to Pad 1. See also * References Space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SRB-A
SRB-A is a series of Japanese solid-fueled rocket booster manufactured by IHI Corporation for use on the H-IIA, H-IIB, and Epsilon rockets. Design SRB-A is 2.5 meters in diameter, and 15.1 meters in length. Its casing is a carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer filament-wound composite. Two-axis attitude control is provided by electrically-actuated thrust vectoring. IHI led the development and production of the SRB-A, and various companies also participated in its development and production. For example, the composite fuel is BP-208, developed and manufactured by NOF Corporation ( ja), and the carbon fiber, one of the components of the motor case, is T1000GB, developed and manufactured by Toray. On the other hand, in order to shorten the development time of the SRB-A, foreign technology was used for the molding process of the motor case. The composite motor case design is based on technology used on the Castor 120 motor by Alliant Techsystems, itself based on the first stage motor for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H-II
The H-II (H2) rocket was a Japanese satellite launch system, which flew seven times between 1994 and 1999, with five successes. It was developed by NASDA in order to give Japan a capability to launch larger satellites in the 1990s. It was the first two-stage liquid-fuelled rocket Japan made using only technologies developed domestically. It was superseded by the H-IIA rocket following reliability and cost issues. Background Prior to H-II, NASDA had to use components licensed by the United States in its rockets. In particular, crucial technologies of H-I and its predecessors were from the Delta rockets (the manufacturer of the Delta rockets, McDonnell Douglas, later Boeing and the United Launch Alliance, would later use the H-IIA's technologies (the rocket itself is the successor to the H-II) to create the Delta III, albeit short lived). Although the H-I did have some domestically produced components, such as LE-5 engine on the second stage and inertial guidance system, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium-lift Launch Vehicle
A medium-lift launch vehicle (MLV) is a rocket launch vehicle that is capable of lifting between by NASA classification or between by Russian classification of payload into low Earth orbit (LEO).50t payloads" An MLV is between a small-lift launch vehicle and a heavy-lift launch vehicle. Medium-lift vehicles comprise the majority of orbital launches , with both the Soyuz and Falcon 9 having launched several hundred times. History Soviet Union and Russia The Soviet R-7 family was based on the world's first intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). Sputnik was a small-lift derivative that carried the first satellite into orbit, and the R-7 design quickly grew in capacity, with Luna launching in 1958. The 1960s saw the R-7 series continue to develop, with Vostok 1 carrying the first human into space, Voskhod carrying multiple crew members, and the first Soyuz. , Soyuz variants are still operational and have launched over 1,100 times. The R-7 family has launched more times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H3 (rocket)
The H3 rocket is a Japanese expendable launch system. H3 launch vehicles are liquid-propellant rockets with strap-on solid rocket boosters and are launched from Tanegashima Space Center in Japan. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) and JAXA are responsible for the design, manufacture, and operation of the H3. The H3 is the world's first rocket to use an Expander cycle, expander bleed cycle for the first stage engine. , the minimum configuration is to carry a payload of up to into Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO) for about 5 billion Japanese yen, yen, and the maximum configuration is to carry more than into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO). The H324 variant will deliver more than of payload to Trans-lunar injection, lunar transfer orbit (TLI) and of payload to geostationary transfer orbit (GTO)(∆V=1830 m/s). Development Mitsubishi Heavy Industries supervised the development and manufacture of the H3 rocket's airframe and liquid-fuel engines, while IHI Corporation develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |