|
Gülüstan, Nakhchivan
Gülüstan () is a village and municipality in the Julfa District of Nakhchivan, Azerbaijan. It is located 5 km in the north-west from the district center, on the right bank of the Aras River. The modern site of Gülüstan was originally the location of a district of the city of Julfa. The village was called Cuğa until 1999, derived from the Armenian name of the city. During the First Nagorno-Karabakh War, the Armenian population of the village was ethnically cleansed. Its current population is busy with farming and animal husbandry. There is a secondary school, a cultural house, two libraries, a communication center, and a medical center in the village. It has a population of 482. Armenian presence Prior to population removals started under Shah Abbas in 1604, Julfa had been an Armenian city of around 40,000 people. The city was a center of Armenian culture, housing a fortress, a massive bridge, and the largest medieval Armenian cemetery. After the population removal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
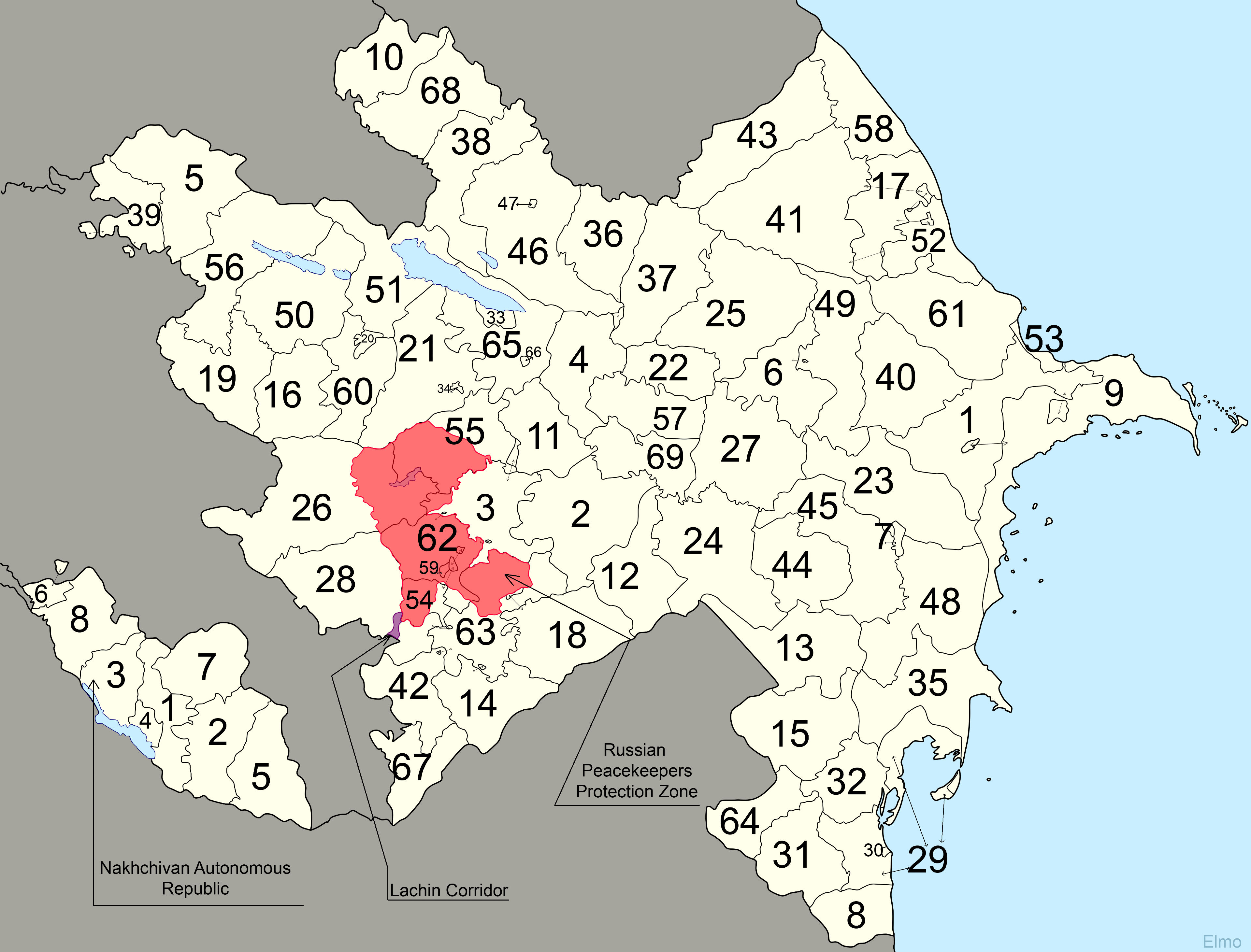
Administrative Divisions Of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 66 districts () and 11 cities () that are subordinate to the Republic. Out of these, 7 districts and 1 city is located within the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The districts are further divided into municipalities (). Additionally, the districts of Azerbaijan are grouped into 14 Economic Regions (). On July 7, 2021, the President of Azerbaijan Ilham Aliyev signed Decree "On the new division of economic regions in the Republic of Azerbaijan". Administrative divisions Contiguous Azerbaijan The territory of former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast presently consists of the districts of Khojavend, Shusha, Khojaly, the eastern portion of Kalbajar and the western portion of Tartar. The Autonomous Oblast was abolished on 26 November 1991, by the Supreme Soviet of the Azerbaijan SSR. Since then, the territory of the autonomous oblast has been administratively split between the aforementioned districts. As a result of the First Nag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora of around five million people of full or partial Armenian ancestry living outside modern Armenia. The largest Armenian populations today exist in Russia, the United States, France, Georgia, Iran, Germany, Ukraine, Lebanon, Brazil, and Syria. With the exceptions of Iran and the former Soviet states, the present-day Armenian diaspora was formed mainly as a result of the Armenian genocide. Richard G. Hovannisian, ''The Armenian people from ancient to modern times: the fifteenth century to the twentieth century'', Volume 2, p. 421, Palgrave Macmillan, 1997. Armenian is an Indo-European language. It has two mutually intelligible spoken and written forms: Eastern Armenian, today spoken mainly in Armenia, Artsakh, Iran, and the former S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajami Nakhchivani
Ajami ibn Abubakr Nakhchivani ( az, Əcəmi ibn Əbubəkr Naxçıvani) was a 12th and 13th-century Muslim architect who contributed greatly to the architecture of Nakhchivan. He was the founder of the Nakhchivan school of architecture and is the architect of buildings such as Yusif ibn Kuseyir Mausoleum, Momine Khatun Mausoleum and Juma Mosque. Architecture Yusif ibn Kuseyir Mausoleum One of the ancient monuments created by Ajami is the mausoleum of Yusif ibn Kuseyir, known as "Atababa". The ayahs (verses) from Koran are inscribed on the walls of the monument. Date of construction of this mausoleum (1161-1162 AD) was defined from its traditional built-in plate or ''katiba''. This eight-sided mausoleum consists of the underground plinth burial place (sardaba, fa, سردابه or cellar) and its on-ground top. Each side of this construction is decorated with various ornaments. Momine Khatun Mausoleum The masterpiece of Ajami is the Momina-Khatun's mausoleum, also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Momine Khatun Mausoleum
Momine Khatun Mausoleum (or Mu'mine Khatun) is a 12th century mausoleum located in the city of Nakchivan in Azerbaijan. The mausoleums of Nakhchivan were nominated for the UNESCO List of World Heritage Sites in 1998 by Gulnara Mehmandarova, the president of the Azerbaijan Committee of ICOMOS. History Momine Khatun Mausoleum, a monument of the Azerbaijani architecture (monuments of the architectural school of Nakhichevan – Maragha) was built in the west part of Nakhchivan city (within the Atabek Complex of Architecture in Nakhchivan city’s historical centre) in 1186. The mausoleum is the only monument that has reached our era from that complex. Shamsaddin Eldaniz, the founder of the Azerbaijan Atabaylar state (Eldiguzids) initiated to erect a mausoleum on the grave of his wife Momine Khatun. However, its construction was finished by Mahammad Jahan Pahlavan, the son of Shamsaddin Eldeniz, in A.H. 582, in the Maharram month (April 1186). According to some investigators, Shams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhas Of Bamiyan
The Buddhas of Bamiyan (or Bamyan) were two 6th-century monumental statues carved into the side of a cliff in the Bamyan valley of Hazarajat region in central Afghanistan, northwest of Kabul at an elevation of . Carbon dating of the structural components of the Buddhas has determined that the smaller "Eastern Buddha" was built around 570 CE, and the larger "Western Buddha" was built around 618 CE, which would date both to the time when the Hephthalites ruled the region. The statues represented a later evolution of the classic blended style of ancient art in Afghanistan. Present-day inhabitants of the area, who follow Islam and speak the Hazaragi dialect of Dari Persian, call the larger statue Salsal ("the light shines through the universe") and identify it as male. The shorter statue is called Shamama ("Queen Mother") identifying it as a female figure. Technically both were reliefs, as at their backs they merged into the cliff wall. The main bodies were hewn directly from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Genocide
Cultural genocide or cultural cleansing is a concept which was proposed by lawyer Raphael Lemkin in 1944 as a component of genocide. Though the precise definition of ''cultural genocide'' remains contested, the Armenian Genocide Museum defines it as "acts and measures undertaken to destroy nations' or ethnic groups' culture through spiritual, national, and cultural destruction." Some ethnologists, such as Robert Jaulin, use the term '' ethnocide'' as a substitute for ''cultural genocide'', although this usage has been criticized as risking the confusion between ethnicity and culture. Juxtaposed next to ''ethnocide'', ''cultural genocide'' was considered in the 2007 United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples; however, it was removed in the final document and simply replaced with "genocide". Definition The legal definition of ''genocide'' is unspecific about the exact way in which genocide is committed, only stating that it is destruction with the intent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Cemetery In Julfa
The Armenian cemetery in Julfa ( hy, Ջուղայի գերեզմանատուն, ''Jughayi gerezmanatun'') was a cemetery near the town of Julfa (known as Jugha in Armenian), in the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan that originally housed around 10,000 funerary monuments. The tombstones consisted mainly of thousands of ''khachkars—''uniquely decorated cross-stones characteristic of medieval Christian Armenian art. The cemetery was still standing in the late 1990s, when the government of Azerbaijan began a systematic campaign to destroy the monuments. Several appeals were filed by both Armenian and international organizations, condemning the Azerbaijani government and calling on it to desist from such activity. In 2006, Azerbaijan barred European Parliament members from investigating the claims, charging them with a "biased and hysterical approach" to the issue and stating that it would only accept a delegation if it visited Armenian-occupied territory as well. In the spring of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbas The Great
Abbas I ( fa, ; 27 January 157119 January 1629), commonly known as Abbas the Great (), was the 5th Safavid Shah (king) of Iran, and is generally considered one of the greatest rulers of Iranian history and the Safavid dynasty. He was the third son of Shah Mohammad Khodabanda. Although Abbas would preside over the apex of Safavid Iran's military, political and economic power, he came to the throne during a troubled time for the country. Under the ineffective rule of his father, the country was riven with discord between the different factions of the Qizilbash army, who killed Abbas' mother and elder brother. Meanwhile, Iran's enemies, the Ottoman Empire (its archrival) and the Uzbeks, exploited this political chaos to seize territory for themselves. In 1588, one of the Qizilbash leaders, Murshid Qoli Khan, overthrew Shah Mohammed in a coup and placed the 16-year-old Abbas on the throne. However, Abbas soon seized power for himself. Under his leadership, Iran developed the ghilman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic
The Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic ( az, Naxçıvan Muxtar Respublikası, ), is a landlocked exclave of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The region covers Official portal of Nakhchivan Autonomous RepublicNakhchivan Autonomous Republic with a population of 459,600 bordered by Armenia to the east and north, Iran to the southwest, and Turkey to the west. The republic, especially the capital city of Nakhchivan, has a long history dating back to about 1500 BCE. ''Nakhijevan'' was one the cantons of the historical Armenian province of Vaspurakan in the Kingdom of Armenia. Historically though, the Persians, Armenians, Mongols, and Turks all competed for the region. The area that is now Nakhchivan became part of Safavid Iran in the 16th century. In 1828, after the last Russo-Persian War and the Treaty of Turkmenchay, the Nakhchivan Khanate passed from Iranian into Imperial Russian possession. After the 1917 February Revolution, Nakhchivan and its surrounding region were under the autho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer, it also includes indirect methods aimed at forced migration by coercing the victim group to flee and preventing its return, such as murder, rape, and property destruction. It constitutes a crime against humanity and may also fall under the Genocide Convention, even as ''ethnic cleansing'' has no legal definition under international criminal law. Many instances of ethnic cleansing have occurred throughout history; the term was first used by the perpetrators as a euphemism during the Yugoslav Wars in the 1990s. Since then, the term has gained widespread acceptance due to journalism and the media's heightened use of the term in its generic meaning. Etymology An antecedent to the term is the Greek word (; lit. "enslavement"), which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |