|
Guneus
In Greek mythology, the name Guneus (; Ancient Greek: Γουνεὐς derived from ''gounos'' "fruitful land") may refer to: *Guneus, a man from Pheneus and father of Laonome, wife of Alcaeus. Through his daughter, he was the grandfather of Amphitryon, Anaxo and Perimede. *Guneus, leader of the Aenianes and Perrhaebians during the Trojan War. According to Homer, "Guneus brought two and twenty ships from Cyphus, and he was followed by the Enienes and the valiant Peraebi, who dwelt about wintry Dodona." Guneus survived the war, and went to Libya where he settled near the Cinyps River. Guneus was an obscure character, though his tribal followers (Aenienians and Perrhaebians) are usually placed in northwestern Greece. Homer does not record his pedigree, but elsewhere his parents were said to be Ocytus and Aurophyte, otherwise unknown. Yet another source gives his mother's name as either Tauropoleia or Hippodameia.Tzetzes, ''Allegories of the Iliad'' Prologue 629–630 Notes Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinyps, Libya
Ka'am, Wadi Caam or Wadi Ka'am (Cinyps) is a small river in Tripolitana, site of a failed Greek attempt to build a city under the leadership of Spartan Dorieus. Sources The source of the river are in the 80 km long Wadi Taraglat but they are all located at the coastal end of the Wadi in a part of the Wadi called Wadi Caam, whereas Herodotus had erroneously claimed that the source was near the Hill of Graces some 260 km inland. History The springs in Wadi Caam were the source of the water used in the Hadrianic baths of Leptis Magna with the water diversion scheme using the aqueduct built by Quintus Servillius Candidus in 119-120A.D. The Greeks under Dorieus of Sparta who was said to be angry because Cleomenes was chosen to be king of Sparta ahead of him left the Peloponnese to found his own colony He chose to found his colony at the mouth of the Cinyps. After three years, around 515B.C. they were expelled by the Carthaginians from Leptis Magna, in alliance with local Lib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perimede (mythology)
In Greek mythology, the name Perimede (; Ancient Greek: Περιμήδη "very cunning" or "cunning all round", derived from ''peri'' "round" and ''medea'', "cunning" or "craft') refers to: *Perimede, an Argive queen as the wife of Phoroneus, king of Argos and possible mother of his children. *Perimede, a Thessalian princess as the daughter of King Aeolus of Aeolia and Enarete, daughter of Deimachus. She was the sister of Salmoneus, Athamas, Sisyphus, Cretheus, Perieres, Deioneus, Magnes, Calyce, Canace, Alcyone and Pisidice. Perimede was the mother of Hippodamas and Orestes by the river god Achelous. *Perimede, a Calydonian princess as the daughter of King Oeneus, mother of Astypalaea and Europe by Phoenix (son of Agenor). *Perimede, other name for Polymede, mother of Jason by Aeson. *Perimede, daughter of Alcaeus and granddaughter of Perseus and Andromeda. Her mother was named either Astydameia, the daughter of Pelops and Hippodamia, or Laonome, daughter of Guneu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
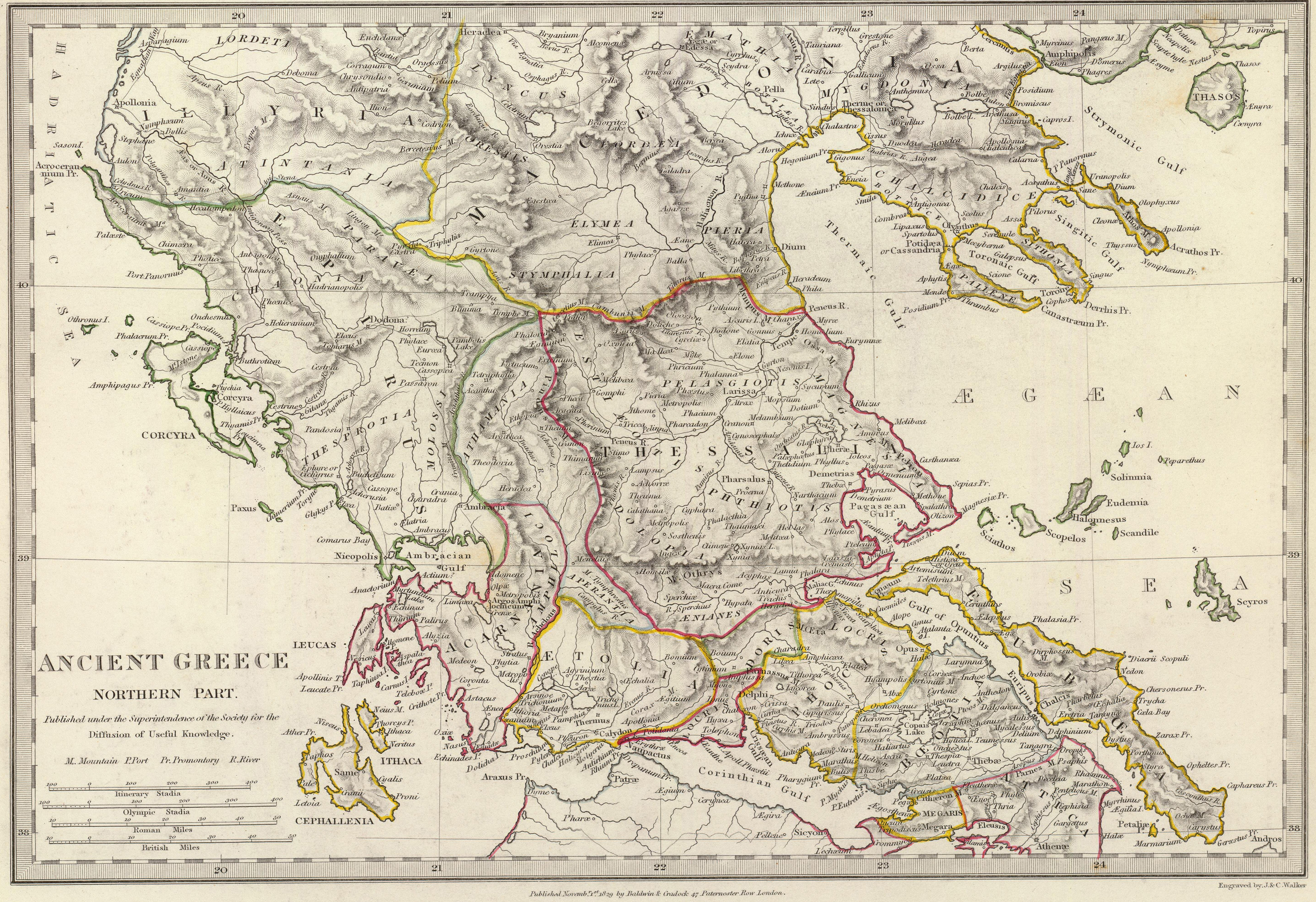
Perrhaebi
The Perrhaebi () were an ancient Greek people who lived on the western slopes of Olympus, on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia. They took part in the Trojan War under Guneus and also fought in the Battle of Thermopylae. History Still independent at the time of the ''Iliad'', they were tributary ''períoikoi'' to the neighbouring Thessali in the 5th century BC, with a special dependence upon the city of Larisa. They could, however, enjoy some degree of autonomy whenever the Thessalian League was weaker, and they had retained from their independence two votes in the Delphic Amphictyonic League (''Amphiktyonía''), until Philip II of Macedon took one vote from them. They were part of the Macedonian Kingdom until the Roman conquest by Titus Quinctius Flamininus in 196 BC. They were listed in Xerxes' vast army by Herodotus. A coin of the Perrhaebi depicted a man restraining a bull on one side and a horse on the other. The inscription was "Περραιβών".Handbook of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laonome
In Greek mythology, the name Laonome (Ancient Greek: 'law of the people' derived from ''laos "''people" and ''nomos'', "law") may refer to: *Laonome, daughter of Guneus, possible spouse of Alcaeus and mother of Amphitryon, Anaxo and Perimede. She was a woman of Pheneus where Heracles migrated first and lived with her after he was expelled by Eurystheus. This happened before the hero went to Thebes and later on settled there. *Laonome, daughter of Amphitryon and Alcmene (thus granddaughter of the precedent), sister of Iphicles and half-sister of Heracles. She married an Argonaut, either Euphemus or Polyphemus. *Laonome, mother by Hodoedocus of Kalliaros, eponym of the city Kalliaros in Locris. Stephanus of Byzantium, s.v. ''Kalliaros'' Notes References * Pausanias, ''Description of Greece'' with an English Translation by W.H.S. Jones, Litt.D., and H.A. Ormerod, M.A., in 4 Volumes. Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1918Online version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcaeus (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Alcaeus or Alkaios (Ancient Greek: Ἀλκαῖος derived from ''alke'' "strength") was the name of a number of different people: *Alcaeus, was a Mycenaean prince. He was a son of Perseus and Andromeda and thus the brother of Perses, Heleus, Mestor, Sthenelus, Electryon, Cynurus, Gorgophone and Autochthe. Alcaeus was married either to Astydameia, the daughter of Pelops and Hippodamia, or Laonome, daughter of Guneus, or else Hipponome, daughter of Menoeceus, by whom he became the father of Amphitryon, Anaxo and Perimede. *Alcaeus, the original name of Heracles (according to Diodorus Siculus), which was given to him on account of his descent from Alcaeus, the son of Perseus mentioned above. *Alcaeus, a son of Heracles by a female slave of Iardanus, from whom the dynasty of the Heraclids in Lydia were believed to be descended. Diodorus Siculus writes that this son of Heracles is named " Cleolaus". *Alcaeus, a Cretan general of Rhadamanthus, accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphitryon
Amphitryon (; Ancient Greek: Ἀμφιτρύων, ''gen''.: Ἀμφιτρύωνος; usually interpreted as "harassing either side", Latin: Amphitruo), in Greek mythology, was a son of Alcaeus, king of Tiryns in Argolis. His mother was named either Astydameia, the daughter of Pelops and Hippodamia, or Laonome, daughter of Guneus, or else Hipponome, daughter of Menoeceus. Amphitryon was the brother of Anaxo (wife of Electryon), and Perimede, wife of Licymnius. He was a husband of Alcmene, Electryon's daughter, and stepfather of the Greek hero Heracles.Roman, L., & Roman, M. (2010). Mythology Amphitryon, a Theban general, was originally from Tiryns in the eastern part of the Peloponnese, and was a friend of Panopeus. Having accidentally killed his father-in-law Electryon, king of Mycenae, Amphitryon was driven out by Electryon's brother, Sthenelus. He fled with Alcmene to Thebes, where he was cleansed from the guilt of blood by Creon, king of Thebes. Alcmene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaxo (daughter Of Alcaeus)
In Greek mythology, Anaxo ( or ; Ancient Greek: Ἀναξώ) was the daughter of Alcaeus (son of Perseus and Andromeda) and Astydameia (daughter of Pelops and Hippodamia). Her mother was also named as Laonome, daughter of Guneus, otherwise she was Hipponome, daughter of Menoeceus. Anaxo was the sister of Amphitryon and Perimede, wife of Licymnius. She married Electryon, king of Mycenae, and her father's brother, being the son of Perseus and Andromeda. Her children were Alcmena, Stratobates, Gorgophonus, Phylonomus, Celaeneus, Amphimachus, Lysinomus, Cheirimachus, Anactor, and Archelaus.Pseudo-Apollodorus, ''Bibliotheca'' 2.4.5 Note References * Patricia Turner, Charles Russell Coulter, "Dictionary of ancient deities", Oxford University Press, 2001, {{ISBN, 0-19-514504-6 *Pseudo-Apollodorus The ''Bibliotheca'' (Ancient Greek: grc, Βιβλιοθήκη, lit=Library, translit=Bibliothēkē, label=none), also known as the ''Bibliotheca'' of Pseudo-Apollodorus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzetzes
John Tzetzes ( grc-gre, Ἰωάννης Τζέτζης, Iōánnēs Tzétzēs; c. 1110, Constantinople – 1180, Constantinople) was a Byzantine poet and grammarian who is known to have lived at Constantinople in the 12th century. He was able to preserve much valuable information from ancient Greek literature and scholarship. Biography Tzetzes described himself as pure Greek on his father's side and part Iberian ( Georgian) on his mother's side. In his works, Tzetzes states that his grandmother was a relative of the Georgian Bagratid princess Maria of Alania who came to Constantinople with her and later became the second wife of the ''sebastos'' Constantine Keroularios, '' megas droungarios'' and nephew of the patriarch Michael Keroularios. He worked as a secretary to a provincial governor for a time and later began to earn a living by teaching and writing. He was described as vain, seems to have resented any attempt at rivalry, and violently attacked his fellow grammarians. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycophron
Lycophron (; grc-gre, Λυκόφρων ὁ Χαλκιδεύς; born about 330–325 BC) was a Hellenistic Greek tragic poet, grammarian, sophist, and commentator on comedy, to whom the poem ''Alexandra'' is attributed (perhaps falsely). Life and miscellaneous works He was born at Chalcis in Euboea, and flourished at Alexandria in the time of Ptolemy Philadelphus (285–247 BC). According to the ''Suda'', the massive tenth century Byzantine Greek historical encyclopaedia, he was the son of Socles, but was adopted by Lycus of Rhegium. He was entrusted by Ptolemy with the task of arranging the comedies in the Library of Alexandria; as the result of his labours he composed a treatise ''On Comedy''. Lycophron is also said to have been a skilful writer of anagrams. Tragedies The poetic compositions of Lycophron chiefly consisted of tragedies, which secured him a place in the Pleiad of Alexandrian tragedians. The ''Suda'' gives the titles of twenty tragedies, of which a very few f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring thousands of islands. The country consists of nine traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western civilization, being the birthplace of democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major scientific and mathematica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyginus
Gaius Julius Hyginus (; 64 BC – AD 17) was a Latin author, a pupil of the scholar Alexander Polyhistor, and a freedman of Caesar Augustus. He was elected superintendent of the Palatine library by Augustus according to Suetonius' ''De Grammaticis'', 20. It is not clear whether Hyginus was a native of the Iberian Peninsula or of Alexandria. Suetonius remarks that Hyginus fell into great poverty in his old age and was supported by the historian Clodius Licinus. Hyginus was a voluminous author: his works included topographical and biographical treatises, commentaries on Helvius Cinna and the poems of Virgil, and disquisitions on agriculture and bee-keeping. All these are lost. Under the name of Hyginus there are extant what are probably two sets of school notes abbreviating his treatises on mythology; one is a collection of ''Fabulae'' ("stories"), the other a "Poetical Astronomy". ''Fabulae'' The ''Fabulae'' consists of some three hundred very brief and plainly, even crudely, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of deities, heroes, and mythological creatures, and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' own cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan and Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century BC; eventually the myths of the heroes of the Trojan War and its aftermath became part of the oral tradition of Homer's epic poems, the '' Iliad'' and the '' Odyssey''. Two poems by Homer's near contemporary Hesiod, the ''Theogony'' and the '' Works and Days'', contain accounts of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |