|
Group Of Twelve
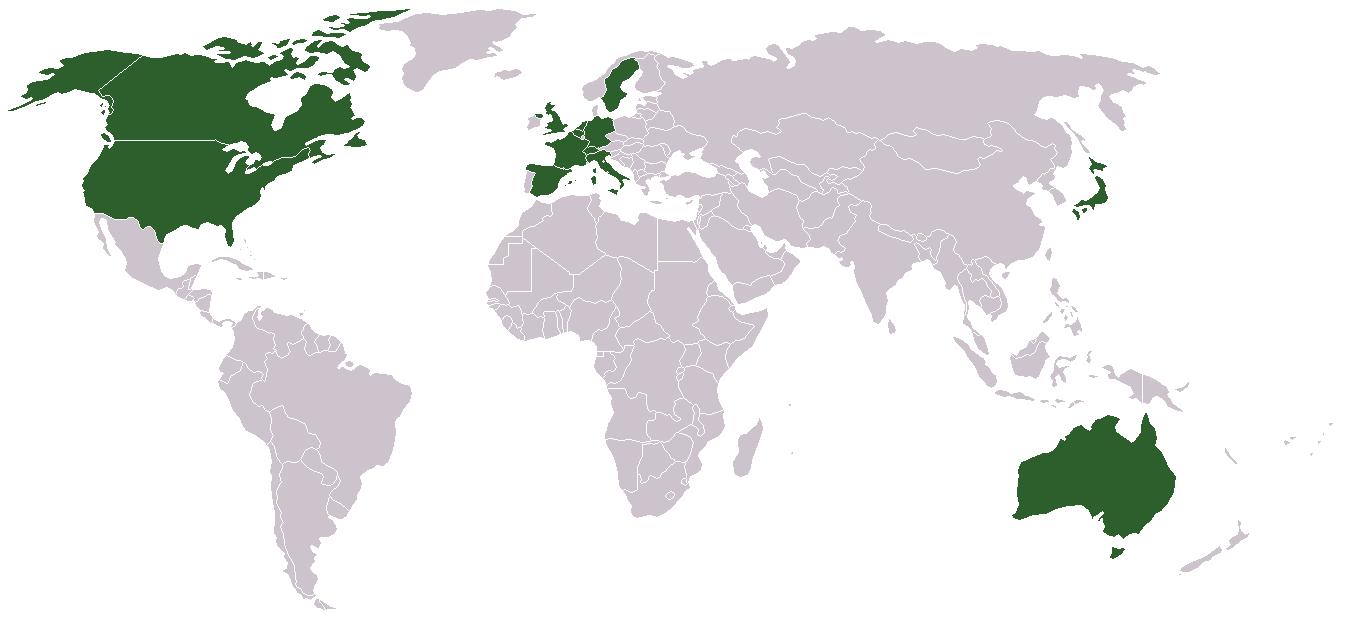
The Group of Twelve or G12 is a group of industrially advanced countries whose central banks co-operate to regulate international finance. Note that the G-12 consists of thirteen countries. It encompasses the initial ten members of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), which formed the original G10, adding Australia and Spain. In 1984, when Switzerland joined the G10 and G12, the names of the groups were not changed. See also * Group of Three (G3) * Group of Four (G4) * Group of Six (G6) * Group of Seven (G7) * Group of Ten (G10) * G10 currencies * Special drawing rights Special drawing rights (SDRs, code ) are supplementary foreign exchange reserve assets defined and maintained by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). SDRs are units of account for the IMF, and not a currency ''per se''. They represent a claim ... References International Monetary Fund International development International finance institutions Intergovernmental organizations Interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G12 Countries
The Group of Twelve or G12 is a group of industrially advanced countries whose central banks co-operate to regulate international finance. Note that the G-12 consists of thirteen countries. It encompasses the initial ten members of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), which formed the original G10, adding Australia and Spain. In 1984, when Switzerland joined the G10 and G12, the names of the groups were not changed. See also * Group of Three (G3) * Group of Four (G4) * Group of Six (G6) * Group of Seven (G7) * Group of Ten (G10) * G10 currencies * Special drawing rights Special drawing rights (SDRs, code ) are supplementary foreign exchange reserve assets defined and maintained by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). SDRs are units of account for the IMF, and not a currency ''per se''. They represent a claim ... References International Monetary Fund International development International finance institutions Intergovernmental organizations Interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G10 Currencies
The G10 currencies are ten of the most heavily traded currencies in the world, which are also ten of the world's most liquid currencies. Traders regularly buy and sell them in an open market with minimal impact on their own international exchange rates. The origin of the term G10 currencies is not clear, however it may be derived from the G10 countries and their agreement to participate in the IMF General Arrangements to Borrow (GAB). There is no longer a one-to-one match between the G10 currencies and the G10 countries. The G10 currencies are: * Australian dollar (AUD) * Canadian dollar (CAD) * Euro (EUR) * Japanese yen (JPY) * New Zealand dollar (NZD) * Norwegian krone (NOK) * Pound sterling (GBP) * Swedish krona (SEK) * Swiss franc (CHF) * United States dollar The United States dollar ( symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Country Classifications
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of scarce resources'. A given economy is a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure, legal systems, and natural resources as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of interrelated human practices and transactions that does not stand alone. Economic agents can be individuals, businesses, organizations, or governments. Economic transactions occur when two groups or parties agree to the value or price of the transacted good or service, commonly expressed in a certain currency. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Economic Organizations
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations". International may also refer to: Music Albums * ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * ''International'' (New Order album), 2002 * ''International'' (The Three Degrees album), 1975 *''International'', 2018 album by L'Algérino Songs * The Internationale, the left-wing anthem * "International" (Chase & Status song), 2014 * "International", by Adventures in Stereo from ''Monomania'', 2000 * "International", by Brass Construction from ''Renegades'', 1984 * "International", by Thomas Leer from ''The Scale of Ten'', 1985 * "International", by Kevin Michael from ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011 * "International", by McGuinness Flint from ''McGuinness Flint'', 1970 * "International", by Orchestral Manoeuvres in the Dark from '' Dazzle Ships'', 1983 * "International (Serious)", by Estelle from '' All of Me'', 2012 Politics * Political international, any transnational organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergovernmental Organizations
An international organization or international organisation (see spelling differences), also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is a stable set of norms and rules meant to govern the behavior of states and other actors in the international system. Organizations may be established by a treaty or be an instrument governed by international law and possessing its own legal personality, such as the United Nations, the World Health Organization and NATO. International organizations are composed of primarily member states, but may also include other entities, such as other international organizations, firms, and nongovernmental organizations. Additionally, entities (including states) may hold observer status. Notable examples include the United Nations (UN), Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), Bank for International Settlements (BIS), Council of Europe (COE), International Labour Organization (ILO) and International Cri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Finance Institutions
An international financial institution (IFI) is a financial institution that has been established (or chartered) by more than one country, and hence is subject to international law. Its owners or shareholders are generally national governments, although other international institutions and other organizations occasionally figure as shareholders. The most prominent IFIs are creations of multiple nations, although some bilateral financial institutions (created by two countries) exist and are technically IFIs. The best known IFIs were established after World War II to assist in the reconstruction of Europe and provide mechanisms for international cooperation in managing the global financial system. Types Multilateral Development Banks A multilateral development bank (MDB) is an institution, created by a group of countries, that provides financing and professional advice to enhance development. An MDB has many members, including developed donor countries and developing borrower co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Development
International development or global development is a broad concept denoting the idea that societies and countries have differing levels of economic or human development on an international scale. It is the basis for international classifications such as developed country, developing country and least developed country, and for a field of practice and research that in various ways engages with international development processes. There are, however, many schools of thought and conventions regarding which are the exact features constituting the "development" of a country. Historically, development was largely synonymous with economic development, and especially its convenient but flawed quantification (see parable of the broken window) through readily gathered (for developed countries) or estimated monetary proxies (estimated for severely undeveloped or isolationist countries) such as gross domestic product (GDP), often viewed alongside actuarial measures such as life expec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Drawing Rights
Special drawing rights (SDRs, code ) are supplementary foreign exchange reserve assets defined and maintained by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). SDRs are units of account for the IMF, and not a currency ''per se''. They represent a claim to currency held by IMF member countries for which they may be exchanged. SDRs were created in 1969 to supplement a shortfall of preferred foreign exchange reserve assets, namely gold and U.S. dollars. The ISO 4217 currency code for special drawing rights is and the numeric code is ''960''. SDRs are allocated by the IMF to countries, and cannot be held or used by private parties. The number of SDRs in existence was around XDR 21.4 billion in August 2009. During the global financial crisis of 2009, an additional XDR 182.6 billion was allocated to "provide liquidity to the global economic system and supplement member countries' official reserves". By October 2014, the number of SDRs in existence was XDR 204 bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G6 (EU)
The G6 (Group of Six) in the European Union was an unofficial group of the interior ministers of the six European Union member states—France, Germany, Italy, Poland, Spain, and the United Kingdom—with the largest populations and thus with the majority of votes in the Council of the European Union. The G6 was established in 2003 as G5 to deal with immigration, terrorism, and law and order. In 2006, Poland joined the group, making it the G6. On the 29th of March 2017, the United Kingdom triggered Article 50, and left the European Union entirely on the 31st of January 2020, ending the G6, and beginning the G5 without the United Kingdom. Under the third pillar of the EU, Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters, powers are largely intergovernmental; this is the one EU policy area where there is no Commission monopoly on proposing law. In other policy areas, the commission can usually create balance among the states, but in this one, the G6 has a great de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Bank
A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the currency and monetary policy of a country or monetary union, and oversees their commercial banking system. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the monetary base. Most central banks also have supervisory and regulatory powers to ensure the stability of member institutions, to prevent bank runs, and to discourage reckless or fraudulent behavior by member banks. Central banks in most developed nations are institutionally independent from political interference. Still, limited control by the executive and legislative bodies exists. Activities of central banks Functions of a central bank usually include: * Monetary policy: by setting the official interest rate and controlling the money supply; *Financial stability: acting as a government's banker and as the bankers' bank ("lender of last resort"); * Reserve management: managing a country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Four (Western Europe)
The Big Four, also known as G4, refers to France, Germany, Italy and the United Kingdom. France and the United Kingdom are official nuclear-weapon states and are permanent members of the United Nations Security Council with the power of veto, which enables any one of them to prevent the adoption of any "substantive" draft Council resolution, regardless of its level of international support. The United Kingdom is the only country of the Big Four which is not a member state of the European Union having ended its membership in 2020, pursuant to a referendum held in 2016. France, Germany, Italy and the United Kingdom are considered major European economic powers and they are the Western European countries individually represented as full members of the G7 and the G20. They have been referred to as the "Big Four of Europe" since the interwar period. The term G4 was used for the first time when French President Nicolas Sarkozy called for a meeting in Paris with Italian Prime Mini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_per_capita_in_2020.png)

