|
Great Renaming
The Great Renaming was a restructuring of Usenet newsgroups that took place in 1987. B News maintainer and UUNET founder Rick Adams is generally considered to be the initiator of the Renaming. Motivation The primary reason for the Great Renaming was said to be the difficulty of maintaining a list of all the existing groups. An alternative explanation was that European networks refused to pay for some of the high-volume and low-content groups such as those regarding religion and racism; this resulted in a need for categorization of all such newsgroups. The suggested category for the newsgroups less popular among European networks was ''talk.*'' History Pre-Renaming Before the Renaming, the newsgroups were categorized into three hierarchies: ''fa.*'' for groups gatewayed from ARPANET, ''mod.*'' for moderated discussions, and ''net.*'' for unmoderated groups. Names of the groups were said to be rather haphazard. While reorganization discussions had occurred earlier, software lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
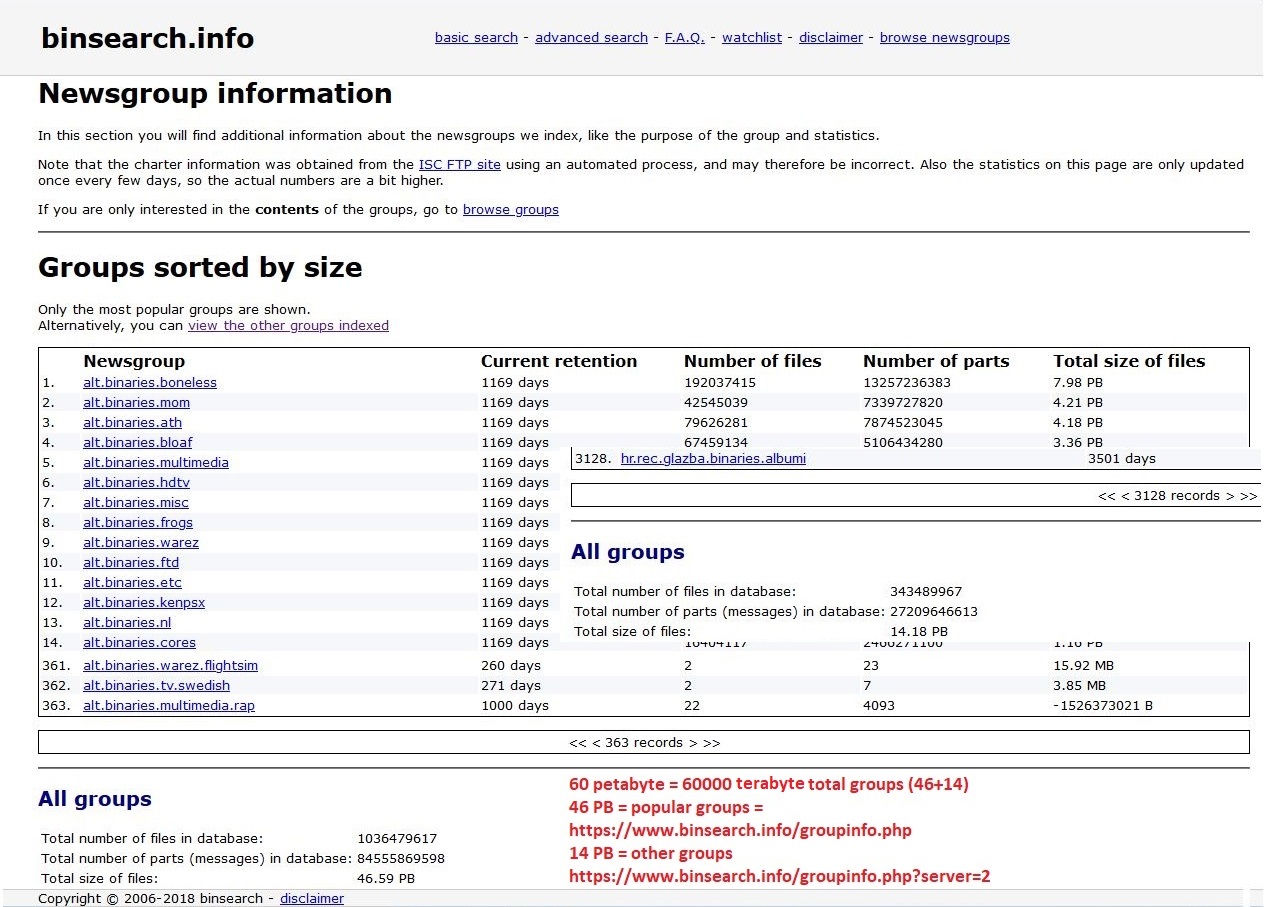
Usenet Newsgroup
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system, for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are discussion groups and are not devoted to publishing news. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read the content of newsgroups. Before the adoption of the World Wide Web, Usenet newsgroups were among the most popular Internet services, and have retained their noncommercial nature in contrast to the increasingly ad-laden web. In recent years, this form of open discussion on the Internet has lost considerable ground to individually-operated browser-accessible forums and big media social networks such as Facebook and Twitter. Communication is facilitated by the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) which allows connection to Usenet servers and data transfer over the internet. Similar to another early (yet still used) pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-mail
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic (digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" meant only physical mail (hence '' e- + mail''). Email later became a ubiquitous (very widely used) communication medium, to the point that in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries. ''Email'' is the medium, and each message sent therewith is also called an ''email.'' The term is a mass noun. Email operates across computer networks, primarily the Internet, and also local area networks. Today's email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver, and store messages. Neither the users nor their computers are required to be online simulta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acronym
An acronym is a word or name formed from the initial components of a longer name or phrase. Acronyms are usually formed from the initial letters of words, as in ''NATO'' (''North Atlantic Treaty Organization''), but sometimes use syllables, as in ''Benelux'' (short for ''Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg''). They can also be a mixture, as in ''radar'' (''Radio Detection And Ranging''). Acronyms can be pronounced as words, like ''NASA'' and ''UNESCO''; as individual letters, like ''FBI'', '' TNT'', and ''ATM''; or as both letters and words, like '' JPEG'' (pronounced ') and ''IUPAC''. Some are not universally pronounced one way or the other and it depends on the speaker's preference or the context in which it is being used, such as '' SQL'' (either "sequel" or "ess-cue-el"). The broader sense of ''acronym''—the meaning of which includes terms pronounced as letters—is sometimes criticized, but it is the term's original meaning and is in common use. Dictionary and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
College
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate or federal university, an institution offering vocational education, or a secondary school. In most of the world, a college may be a high school or secondary school, a college of further education, a training institution that awards trade qualifications, a higher-education provider that does not have university status (often without its own degree-awarding powers), or a constituent part of a university. In the United States, a college may offer undergraduate programs – either as an independent institution or as the undergraduate program of a university – or it may be a residential college of a university or a community college, referring to (primarily public) higher education institutions that aim to provide affordable and accessible education, usually limited to two-year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes compulsory. In these systems, students progress through a series of schools. The names for these schools vary by country (discussed in the '' Regional terms'' section below) but generally include primary school for young children and secondary school for teenagers who have completed primary education. An institution where higher education is taught is commonly called a university college or university. In addition to these core schools, students in a given country may also attend schools before and after primary (elementary in the U.S.) and secondary (middle school in the U.S.) education. Kindergarten or preschool provide some schooling to very young children (typically ages 3–5). University, vocational school, college or seminary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Various researchers emphasize the role of critical thinking in order to distinguish education from indoctrination. Some theorists require that education results in an improvement of the student while others prefer a value-neutral definition of the term. In a slightly different sense, education may also refer, not to the process, but to the product of this process: the mental states and dispositions possessed by educated people. Education originated as the transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. Today, educational goals increasingly encompass new ideas such as the liberation of learners, skills needed for modern society, empathy, and complex vocational skills. Types of education are commonly divided int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big 8 (Usenet)
The Big 8 (previously the Big 7) are a group of newsgroup hierarchies established after the Great Renaming, a restructuring of Usenet Usenet () is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose UUCP, Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis (computing), Jim Ellis conceived th ... that took place in 1987. These hierarchies are managed by the Big 8 Management Board. Groups are added through a process of nomination, discussion and voting. History The original seven hierarchies were comp.*, misc.*, news.*, rec.*, sci.*, soc.*, and talk.*. They were open and free for anyone to participate in (except for the moderated newsgroups), though they were subject to a few general rules governing their naming and distribution. alt.* was not part of the original seven but created separately as a place with more freedom and fewer rules than the Big 7. In April 1995, when Usenet traffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchy
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important concept in a wide variety of fields, such as architecture, philosophy, design, mathematics, computer science, organizational theory, systems theory, systematic biology, and the social sciences (especially political philosophy). A hierarchy can link entities either directly or indirectly, and either vertically or diagonally. The only direct links in a hierarchy, insofar as they are hierarchical, are to one's immediate superior or to one of one's subordinates, although a system that is largely hierarchical can also incorporate alternative hierarchies. Hierarchical links can extend "vertically" upwards or downwards via multiple links in the same direction, following a path. All parts of the hierarchy that are not linked vertically to o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backbone Cabal
The backbone cabal was an informal organization of large-site news server administrators of the worldwide distributed newsgroup-based discussion system Usenet. It existed from about 1983 at least into the 2000s. The cabal was created in an effort to facilitate reliable propagation of new Usenet posts. While in the 1970s and 1980s many news servers only operated during night time to save on the cost of long-distance communication, servers of the backbone cabal were available 24 hours a day. The administrators of these servers gained sufficient influence in the otherwise anarchic Usenet community to be able to push through controversial changes, for instance the Great Renaming of Usenet newsgroups during 1987. History As Usenet has few technologically or legally enforced hierarchies, those that formed were largely social. People acquired power through persuasion (both publicly and privately), public debate, force of will (often via aggressive flames), garnering authority and respe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
News Client
A newsreader is an application program that reads articles on Usenet distributed throughout newsgroups. Newsreaders act as clients which connect to a news server, via the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP), to download articles and post new articles. In addition to text-based articles, Usenet is also used to distribute binary files, generally in dedicated "binaries" newsgroups. The term ''newsreader'' is sometimes (erroneously) used interchangeably with ''news aggregator''. Newsreaders that help users to adhere to the established conventions of Usenet, known as netiquette, are evaluated by the Good Netkeeping Seal of Approval (GNKSA). Types of newsreaders There are several different types of newsreaders, depending on the type of service the user needs—whether intended primarily for discussion or for downloading files posted to the alt.binaries hierarchy: ; Desktop newsreaders : Designed to integrate well with common GUI environments, and often integrated with a web br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B News
B News was a Usenet news server developed at the University of California, Berkeley by Matt Glickman and Mary Ann Horton as a replacement for A News. It was used on Unix systems from 1981 into the 1990s and is the reference implementation for the ''de facto'' Usenet standard described in and . Releases from 2.10.2 were maintained by UUNET founder Rick Adams. B News introduced numerous changes from its predecessor. Articles used an extensible format with named headers, first by using labeled equivalents to the A News format. A further refinement in 1983 with News B2.10 was a move to e-mail-compatible headers, to ease message transfers with the ARPAnet. A history database was introduced, allowing articles to be placed in separate directories by newsgroup, improving retrieval speeds and easing the development of separate newsreader programs such as rn. Support was provided for expiring old articles, and control message Control messages are a special kind of Usenet post t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
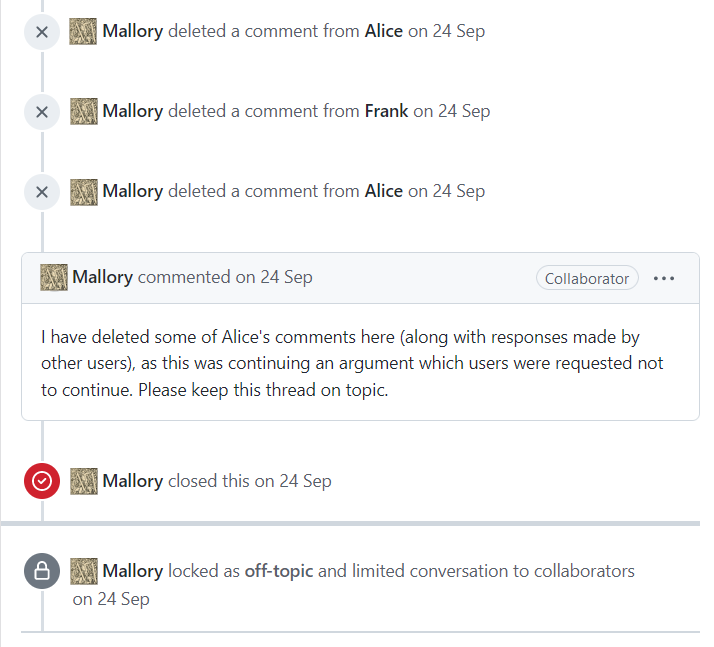
Moderation System
On Internet websites that invite users to post comments, content moderation is the process of detecting contributions that are irrelevant, obscene, illegal, harmful, or insulting with regards to useful or informative contributions. The purpose of content moderation is to remove or apply a warning label to problematic content or allow users to block and filter content themselves. Various types of Internet sites permit user-generated content such as comments, including Internet forums, blogs, and news sites powered by scripts such as phpBB, a Wiki, or PHP-Nuke. Depending on the site's content and intended audience, the site's administrators will decide what kinds of user comments are appropriate, then delegate the responsibility of sifting through comments to lesser moderators. Most often, they will attempt to eliminate trolling, spamming, or flaming, although this varies widely from site to site. Major platforms use a combination of algorithmic tools, user reporting and human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |