|
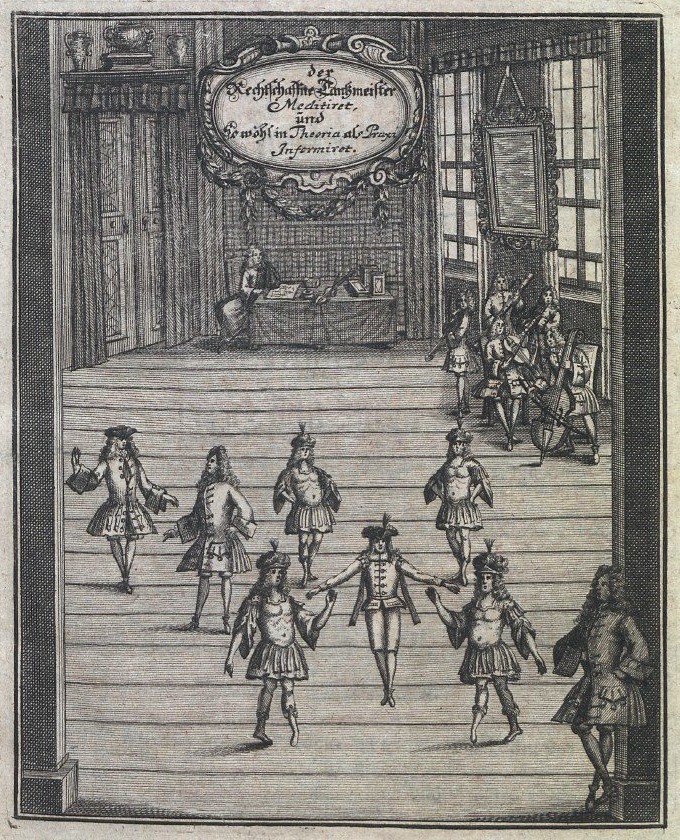
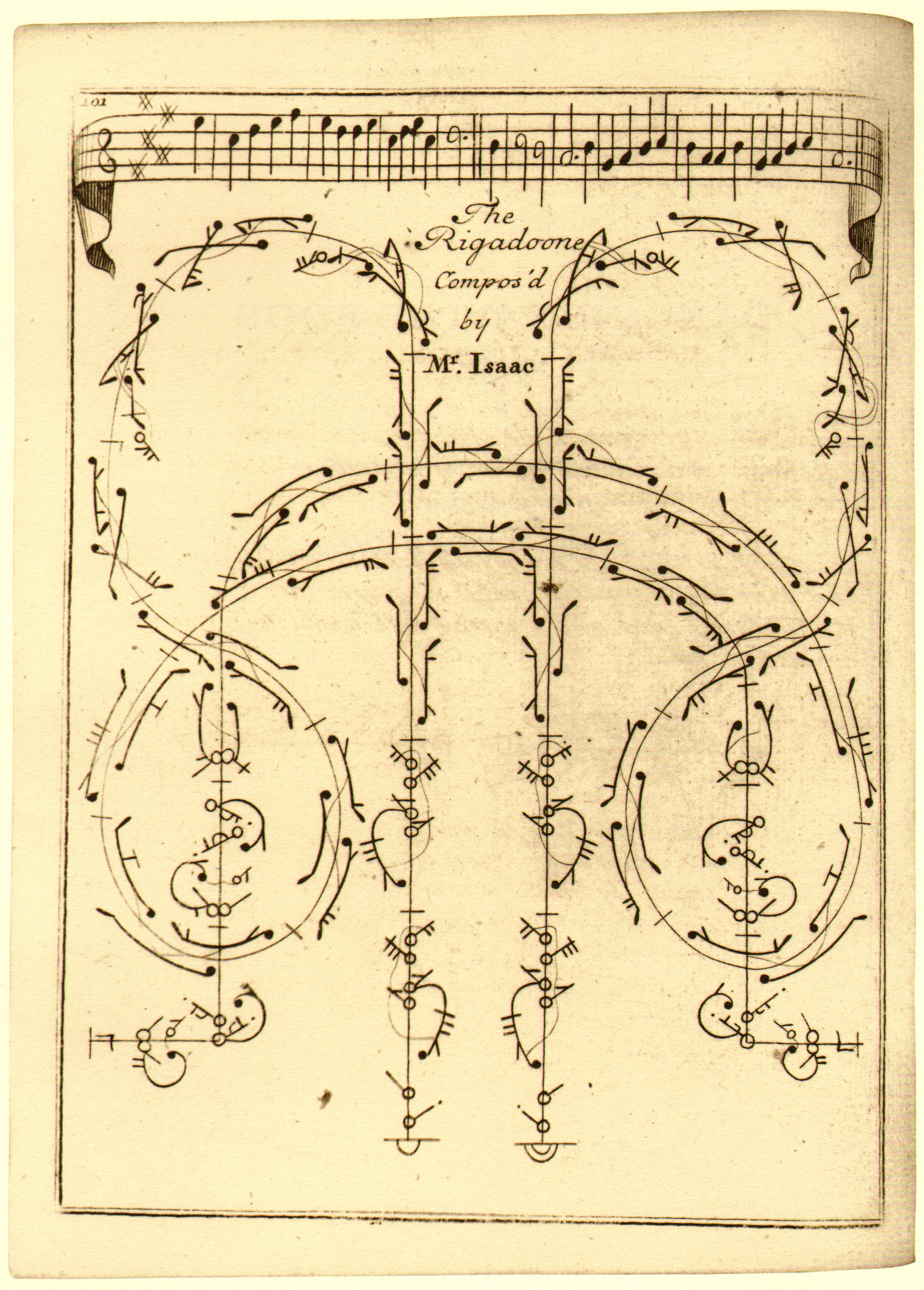
Gottfried Taubert
Gottfried Taubert (baptized 30 Juli 1670-died July 6, 1746) was a German dance master of the Baroque period. Life Taubert was born in Ronneburg, Thuringia, the son of Christoph Tauber and of Anna Brämmer. He attended lectures at Leipzig University from 1686 and from 1693. Until 1695, he studied in the fair city. In 1702, he settled in Danzig, but returned to Leipzig in 1715, where he published his extensive dance book ''Rechtschaffener Tanzmeister'' in 1717. It also contains the first German translation of the French ''Choreography'' by Raoul-Auger Feuillet as well as the instructions of the dances after Raoul-Auger Feuillet and Louis Pécour. From about 1730 until his death, he was court dance master in Zerbst.Stephanie Schroedter: ''Vom „Affect zur Action“: Quellenstudien zur Poetik der Tanzkunst vom späten Ballet de Cour bis zum frühen Ballet en Action.'' Würzburg 2004, f. (). Taubert may have exerted the most lasting influence among German dance book authors. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dance Master
Dance Master UK is a dance competition held annually in the United Kingdom. Overview Dance Master UK was established in the late 1990s by the International Dance Teachers Association, as the male equivalent of their long running competition Miss Dance of Great Britain. Dance Master UK is a theatre dance competition for boys held annually in the UK with a national final held at the Winter Gardens in Blackpool, England. The finals also include the judging of '' Miss Dance of Great Britain'', and the ''International Ballet Championships''. Qualifying Entrants who wish to compete in the national finals of Dance Master, must first qualify for the competition by winning a regional heat. Heats are held at dance festivals nationwide throughout the year. The majority of these festivals are independently run and must apply to the IDTA in order to stage a heat of Dance Master. To enter a regional heat, competitors must be aged 16 years or over on the day of the competition and must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including the Iberian Peninsula it continued, together with new styles, until the first decade of the 19th century. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep colour, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to France, northern Italy, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, and Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronneburg, Thuringia
Ronneburg () is a town in the district of Greiz, in Thuringia, Germany. It is situated 7 km east of Gera. History Within the German Empire (1871–1918), Ronneburg was part of the Duchy of Saxe-Altenburg Saxe-Altenburg (german: Sachsen-Altenburg, links=no) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in present-day Thuringia. It was one of the smallest of the German states with an area of 1323 square kilomete .... References External links District Greiz Towns in Thuringia Greiz (district) Duchy of Saxe-Altenburg {{Greiz-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig University
Leipzig University (german: Universität Leipzig), in Leipzig in Saxony, Germany, is one of the world's oldest universities and the second-oldest university (by consecutive years of existence) in Germany. The university was founded on 2 December 1409 by Frederick I, Elector of Saxony and his brother William II, Margrave of Meissen, and originally comprised the four scholastic faculties. Since its inception, the university has engaged in teaching and research for over 600 years without interruption. Famous alumni include Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Leopold von Ranke, Friedrich Nietzsche, Robert Schumann, Richard Wagner, Tycho Brahe, Georgius Agricola, Angela Merkel and ten Nobel laureates associated with the university. History Founding and development until 1900 The university was modelled on the University of Prague, from which the German-speaking faculty members withdrew to Leipzig after the Jan Hus crisis and the Decree of Kutná Hora. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raoul-Auger Feuillet
Raoul Auger (or Anger) Feuillet (c.1660–1710) was a French dance notator, publisher and choreographer most well-known today for his ''Chorégraphie, ou l'art de décrire la danse'' (Paris, 1700) which described Beauchamp–Feuillet notation, and his subsequent collections of ballroom and theatrical dances, which included his own choreographies as well as those of Pécour. His ''Chorégraphie'' (1700) was translated into English by John Weaver (as ''Orchesography. Or the Art of Dancing'') (1706) and P. Siris (as ''The Art of Dancing''), both published in 1706. Weaver also translated the ''Traité de la cadance'' from Feuillet's 1704 ''Recŭeil de dances'' (as ''A Small Treatise of Time and Cadence in Dancing'', 1706). Feuillet's ''Recŭeil de contredances'' (1706), a collection of English country dance A country dance is any of a very large number of social dances of a type that originated in the British Isles; it is the repeated execution of a predefined sequence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Pécour
Louis may refer to: * Louis (coin) * Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name * Louis (surname) * Louis (singer), Serbian singer * HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy See also Derived or associated terms * Lewis (other) * Louie (other) * Luis (other) * Louise (other) * Louisville (other) * Louis Cruise Lines * Louis dressing, for salad * Louis Quinze, design style Associated names * * Chlodwig, the origin of the name Ludwig, which is translated to English as "Louis" * Ladislav and László - names sometimes erroneously associated with "Louis" * Ludovic, Ludwig, Ludwick Ludwick is a surname of German origin, and may refer to: * Andrew K. Ludwick (born 1946), American businessman *Christopher Ludwick (1720–1801), American baker * Eric Ludwick (born 1971), American baseball player * Robert Ludwick-Forster (born 19 ..., Ludwik, names sometimes translated to English as "Louis" {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Salmen
Walter Salmen (20 September 1926 in Paderborn – 2 February 2013 in Freiburg im Breisgau) was a German musicologist and university lecturer. Salmen taught from 1958 to 1992 as a professor of musicology at the Saarland University and the University of Kiel. Afterwards, he was for many years the full professor of the Musicological Institute of the University of Innsbruck. As a guest lecturer, he also worked in Switzerland, Israel and the United States. After retirement, he lived in Kirchzarten near Freiburg im Breisgau, and worked as honorary professor at the University of Freiburg. Publications * ''Johann Friedrich Reichardt Johann Friedrich Reichardt (25 November 1752 – 27 June 1814) was a German composer, writer and music critic. Early life Reichardt was born in Königsberg, East Prussia, to lutenist and ''Stadtmusiker'' Johann Reichardt (1720–1780). Johann Fr ...: Komponist, Schriftsteller, Kapellmeister und Verwaltungsbeamter der Goethezeit''. Zürich and Freiburg 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zerbst
Zerbst () is a town in the district of Anhalt-Bitterfeld, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Until an administrative reform in 2007, Zerbst was the capital of the former Anhalt-Zerbst district. Geography Zerbst is situated in the Anhalt-Wittenberg region, with its town centre located on the river Nuthe about northeast of the Elbe, halfway between Magdeburg and Wittenberg. With the 1 January 2010 local government reform, the 21 formerly independent communities of the disbanded ''Verwaltungsgemeinschaft'' (municipal association) Elbe-Ehle-Nuthe were incorporated into the town. Zerbst today counts about 24,000 inhabitants and, at , is the fifth largest town in Germany by area. The current municipal area stretches from the Elbe in the southwest up to the Fläming Heath and the state border with Brandenburg in the northeast. Divisions The town Zerbst consists of Zerbst proper and the following 24 ''Ortschaften'' or municipal divisions: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Finscher
Ludwig Finscher (14 March 193030 June 2020) was a German musicologist. He was a professor of music history at the University of Heidelberg from 1981 to 1995 and editor of the encyclopedia ''Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart''. He is respected internationally as an authority on the history of Western Classical music from the 16th century to contemporary classical music, with a view on music in cultural, social, historical and philosophical context, in a clear language for both specialists and lay readers. Life and career Born in Kassel, the youngest of five siblings, Finscher studied musicology, English, German and philosophy at the University of Göttingen from 1949 to 1954. Students at the same time included Gerhard Croll, Carl Dahlhaus and Rudolf Stephan. He earned a doctorate with a thesis about the masses and motets by Loyset Compère, with advisor Rudolf Gerber. From 1954, he worked for the Deutsches Volksliedarchiv (German archive of folk songs) in Freiburg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die Musik In Geschichte Und Gegenwart
''Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart: Allgemeine Enzyklopädie der Musik (MGG)'' is one of the world's most comprehensive encyclopedias of music history and musicology, on account of its scope, content, wealth of research areas, and reference to related subjects. It has appeared in two self-contained printed editions and a continuously updated and expanding digital edition, titled ''MGG Online''. Created by Karl Vötterle, the founder of Bärenreiter-Verlag, and Friedrich Blume, professor of musicology at Kiel University, the first edition was published by Bärenreiter-Verlag in Kassel from 1949 through 1986, comprising a total of 17 volumes (''MGG1''; numbered in columns) and reprinted in paperback in 1989. As early as 1989, its new editor Ludwig Finscher began planning a second, revised edition with 29 volumes, which were published from 1994 through 2008 in cooperation with the publisher J.B. Metzler (''MGG2''; with a topical part in 9 volumes and a persons part in 17 volumes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Maul
Michael Maul (born 1978) is a German musicologist noted for his work on Johann Sebastian Bach. Maul was born in Leipzig, and is still based in the city, although his work at the Bach Archive has involved travel to archives and libraries across Germany in search of new sources relating to Bach. He is also artistic director of Leipzig's annual Bach festival. Education Maul was awarded a PhD by the University of Freiburg for a dissertation on Baroque opera. It formed the basis of his book ''Barockoper in Leipzig (1693-1720)''. Bach discoveries Maul's work attracted international attention with a discovery he made in 2005 in Weimar's Duchess Anna Amalia Library. This was a hitherto overlooked manuscript containing ''Alles mit Gott und nichts ohn' ihn'', BWV 1127, the first previously unknown vocal work by Bach to be found in 70 years. Further research in Weimar identified other previously unknown manuscripts in Bach's hand, this time of music by other composers, throwing light on h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |