|
Giulio Clovio
Giorgio Giulio Clovio or Juraj Julije Klović (1498 – 5 January 1578) was an illuminator, miniaturist, and painter born in the Kingdom of Croatia, who was mostly active in Renaissance Italy. He is considered the greatest illuminator of the Italian High Renaissance, and arguably the last very notable artist in the long tradition of the illuminated manuscript, before some modern revivals. Biography Giulio Clovio was born in Grižane, a village in Kingdom of Croatia (today's Croatia),The Life and Works of Giorgio Giulio Clovio, Miniaturist: with notices of his contemporaries, and of the art of decoration in the Sixteenth Century - by John William Bradley – 1891 He came from a Croatian family. Bradley, 2004 (reprint), pp. 368–369 and he is known as ''Clovio Croata.'' It is not known where he had his early training, but he may have studied art with monks at Rijeka of Novi Bazar when he was young. He moved to Italy at age 18 and entered the household of Cardinal Marino Gri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
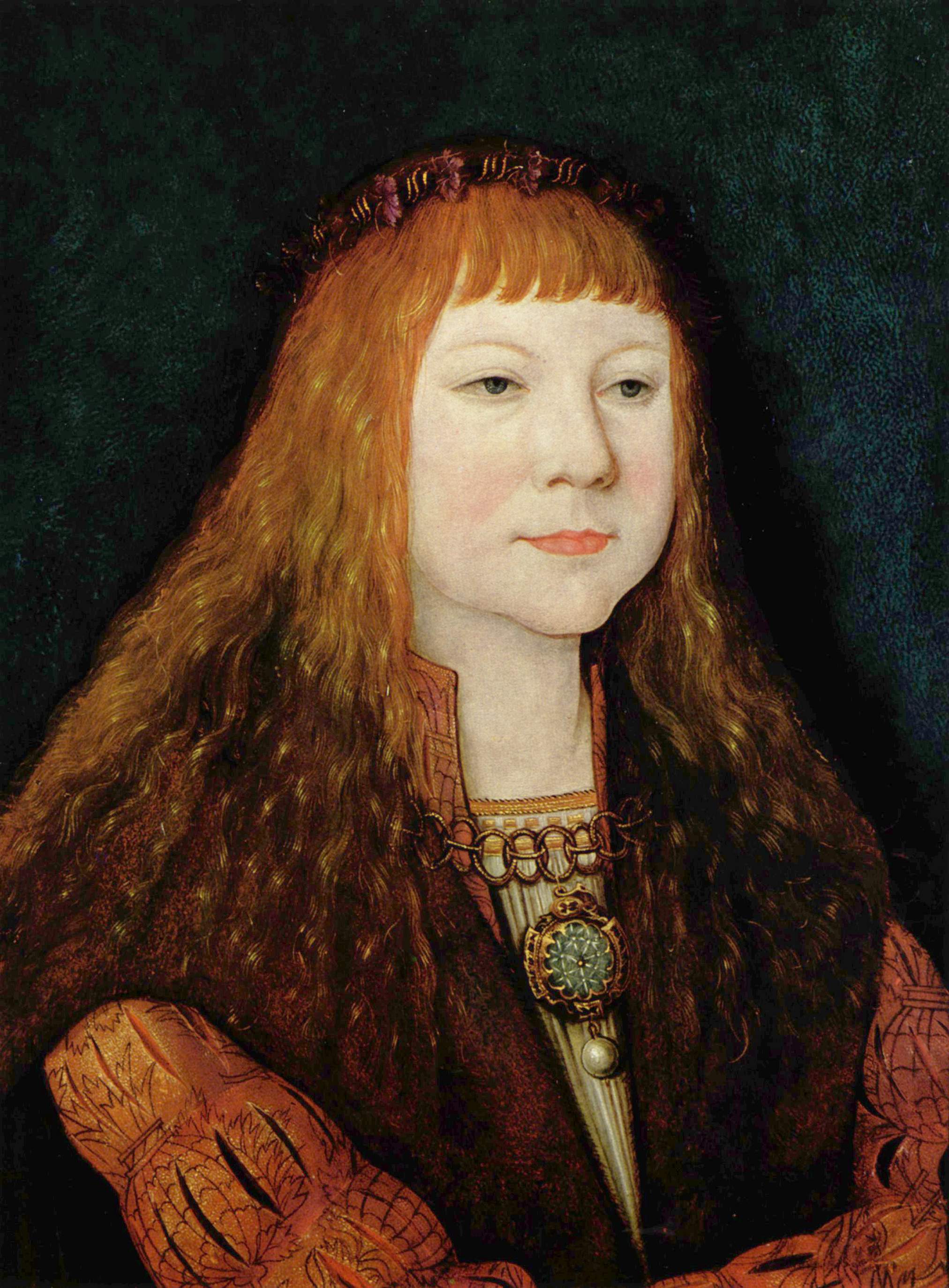
Portrait Of Giulio Clovio
''Portrait of Giulio Clovio'' is a c.1571 painting by El Greco. It was commissioned by cardinal Alessandro Farnese during the artist's stay in Rome. It formed part of the Farnese collection. Charles of Bourbon inherited it in 1734 and moved it to Naples, where it now hangs in the Museo nazionale di Capodimonte. Its subject Giulio Clovio (born 1498, Croatia) was a noted miniaturist, called "the Michelangelo of the miniature" by Giorgio Vasari Giorgio Vasari (, also , ; 30 July 1511 – 27 June 1574) was an Italian Renaissance Master, who worked as a painter, architect, engineer, writer, and historian, who is best known for his work '' The Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculp .... He had helped El Greco settle in Rome. He is shown holding his most famous text, the ''Libro d'Ore della Vergine''. In the background is a landscape and a stormy sky. Bibliography * J. Álvarez Lopera, ''El Greco'', Madrid, Arlanza (2005), Biblioteca «Descubrir el Arte», (colección «Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
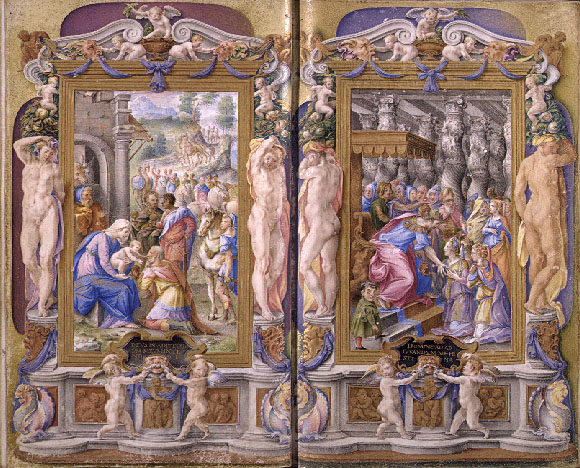
Farnese Hours
The Farnese Hours is an illuminated manuscript created by Giulio Clovio for Cardinal Alessandro Farnese in 1546. Considered the masterpiece of Clovio, this book of hours is now in the possession of the Morgan Library & Museum in New York City. It contains religious stories (both Biblical and apocrypha Apocrypha are works, usually written, of unknown authorship or of doubtful origin. The word ''apocryphal'' (ἀπόκρυφος) was first applied to writings which were kept secret because they were the vehicles of esoteric knowledge considered ...l), and illustrations with architectural borders and classical nudes. Notes {{Commons category Illuminated books of hours 1546 books Collection of the Morgan Library & Museum 1546 in art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco De Hollanda
Francisco de Holanda (originally ''Francisco d'Olanda;'' 6 September 1517 – 19 June 1585) was a Portuguese court painter and sculptor for King John III of Portugal, and later for Sebastian of Portugal. He wrote what is regarded as the first treatise on portrait painting in Europe, '' Do tirar polo natural'' (1549). He is considered to be one of the most important figures of the Portuguese Renaissance, also being an essayist, architect and historian. He represented the intelligible reality of the Holy Trinity through a "hypothetical" syntax of geometrical figures. He insisted on the contrast between the ideal plane, the incorporeal form and the "imperfect copy in the terrestrial zone". His visual language demonstrated a mixture of Neoplatonism, Christian Kabbalah and finally Lullism. In education, Francisco de Holanda emphasized mathematics and geometry, subsequently anticipating Clavius's reforms of the late 16th century. Sylvie Deswarte said that "Francisco de Holanda gives a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soane Museum
Sir John Soane's Museum is a house museum, located next to Lincoln's Inn Fields in Holborn, London, which was formerly the home of neo-classical architect, John Soane. It holds many drawings and architectural models of Soane's projects, and a large collection of paintings, sculptures, drawings and antiquities that he acquired over many years. The museum was established during Soane's own lifetime by a Private Act of Parliament in 1833, which took effect on his death in 1837. Soane engaged in this lengthy parliamentary campaign in order to disinherit his son, whom he disliked intensely. The act stipulated that on Soane's death his house and collections would pass into the care of a Board of Trustees, acting on behalf of the nation, and that they would be preserved as nearly as possible exactly in the state they were at his death. The museum's trustees remained completely independent, relying only on Soane's original endowment, until 1947. Since then, the museum has received an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perugia
Perugia (, , ; lat, Perusia) is the capital city of Umbria in central Italy, crossed by the River Tiber, and of the province of Perugia. The city is located about north of Rome and southeast of Florence. It covers a high hilltop and part of the valleys around the area. The region of Umbria is bordered by Tuscany, Lazio, and Marche. The history of Perugia goes back to the Etruscan period; Perugia was one of the main Etruscan cities. The city is also known as the universities town, with the University of Perugia founded in 1308 (about 34,000 students), the University for Foreigners (5,000 students), and some smaller colleges such as the Academy of Fine Arts "Pietro Vannucci" ( it, Accademia di Belle Arti "Pietro Vannucci") public athenaeum founded in 1573, the Perugia University Institute of Linguistic Mediation for translators and interpreters, the Music Conservatory of Perugia, founded in 1788, and other institutes. Perugia is also a well-known cultural and art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canons Regular Of St
Canon or Canons may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Canon (fiction), the conceptual material accepted as official in a fictional universe by its fan base * Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture ** Western canon, the body of high culture literature, music, philosophy, and works of art that is highly valued in the West * Canon of proportions, a formally codified set of criteria deemed mandatory for a particular artistic style of figurative art * Canon (music), a type of composition * Canon (hymnography), a type of hymn used in Eastern Orthodox Christianity. * ''Canon'' (album), a 2007 album by Ani DiFranco * ''Canon'' (film), a 1964 Canadian animated short * ''Canon'' (game), an online browser-based strategy war game * ''Canon'' (manga), by Nikki * Canonical plays of William Shakespeare * ''The Canon'' (Natalie Angier book), a 2007 science book by Natalie Angier * ''The Canon'' (podcast), concerning film Brands and enterprises * Cano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; hu, mohácsi csata, tr, Mohaç Muharebesi or Mohaç Savaşı) was fought on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, Kingdom of Hungary, between the forces of the Kingdom of Hungary and its allies, led by Louis II, and those of the Ottoman Empire, led by Suleiman the Magnificent. The Ottoman victory led to the partition of Hungary for several centuries between the Ottoman Empire, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Principality of Transylvania. Further, the death of Louis II as he fled the battle marked the end of the Jagiellonian dynasty in Hungary and Bohemia, whose dynastic claims passed to the House of Habsburg. Background Decline of Hungarian royal power (1490–1526) After the death of the absolutist King Matthias Corvinus in 1490, the Hungarian magnates, who did not want another heavy-handed king, procured the accession of the notoriously weak-willed King Vladislaus of Bohemia, who reigned as King Vladislaus II of Hungary from 1490 to 1516. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis II Of Hungary And Bohemia
Louis II ( cs, Ludvík, hr, Ludovik , hu, Lajos, sk, Ľudovít; 1 July 1506 – 29 August 1526) was King of Hungary, Croatia and Bohemia from 1516 to 1526. He was killed during the Battle of Mohács fighting the Ottomans, whose victory led to the Ottoman annexation of large parts of Hungary. Early life At his premature birth in Buda on 1 July 1506, the court doctors kept him alive by slaying animals and wrapping him in their warm carcasses as a primitive incubator. He was the only son of Vladislaus II Jagiellon and his third wife, Anne of Foix-Candale. Coronation Vladislaus II took steps to ensure a smooth succession by arranging for the boy to be crowned in his own lifetime; the coronation of Louis as king of Hungary took place on 4 June 1508 in Székesfehérvár Basilica, and his coronation as king of Bohemia was held on 11 March 1509 in St. Vitus Cathedral in Prague. King of Hungary and Croatia In 1515 Louis II was married to Mary of Austria, granddaughter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population of 1,752,286 over a land area of about . Budapest, which is both a city and county, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of and a population of 3,303,786; it is a primate city, constituting 33% of the population of Hungary. The history of Budapest began when an early Celtic settlement transformed into the Roman town of Aquincum, the capital of Lower Pannonia. The Hungarians arrived in the territory in the late 9th century, but the area was pillaged by the Mongols in 1241–42. Re-established Buda became one of the centres of Renaissance humanist culture by the 15th century. The Battle of Mohács, in 1526, was followed by nearly 150 years of Ottoman rule. After the reconquest of Buda in 1686, the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir John Soane's Museum
Sir John Soane's Museum is a house museum, located next to Lincoln's Inn Fields in Holborn, London, which was formerly the home of neo-classical architect, John Soane. It holds many drawings and architectural models of Soane's projects, and a large collection of paintings, sculptures, drawings and antiquities that he acquired over many years. The museum was established during Soane's own lifetime by a Private Act of Parliament in 1833, which took effect on his death in 1837. Soane engaged in this lengthy parliamentary campaign in order to disinherit his son, whom he disliked intensely. The act stipulated that on Soane's death his house and collections would pass into the care of a Board of Trustees, acting on behalf of the nation, and that they would be preserved as nearly as possible exactly in the state they were at his death. The museum's trustees remained completely independent, relying only on Soane's original endowment, until 1947. Since then, the museum has received an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girolamo Dai Libri
Girolamo dai Libri (1474/1475 – July 2, 1555) was an Italian illuminator of manuscripts and painter of altarpieces, working in an early-Renaissance style. Accademia - Madonna col Bambino e angeli musicanti - Girolamo Dai Libri.jpg, Virgin and child with angels musicians Gallerie dell'Accademia God the Father with His Right Hand Raised in Blessing.jpg, God the Father with His Right Hand Raised in Blessing (drawing by Girolamo dai Libri) Santa Anastasia (Verona) - Centrego altar.jpg, Our Lady enthroned between St. Thomas and St. Augustine", Sant'Anastasia (Verona) Girolamo Dai Libri - Madonna della quercia - 1533 after - Museo Castelvecchio, Verona (ITALY).jpg, Madonna della Quercia, 1533 or after, Museo di Castelvecchio, Verona Girolamo dai Libri - Madonna dell'ombrello (in trono con Bambino Gesù tra san Giuseppe - san Raffaele Arcangelo e Tobiolo-Tobia) - Verona - Museo di Castelvecchio 1530 - 1530 - Photo Paolo Villa 2006 - MiBAC disclaimer warning.jpg, Madonna dell'Om ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giulio Romano
Giulio Romano (, ; – 1 November 1546), is the acquired name of Giulio Pippi, who was an Italian painter and architect. He was a pupil of Raphael, and his stylistic deviations from High Renaissance classicism help define the sixteenth-century style known as Mannerism. Giulio's drawings have long been treasured by collectors; contemporary prints of them engraved by Marcantonio Raimondi were a significant contribution to the spread of sixteenth-century Italian style throughout Europe. Biography Giulio Pippi was born in Rome and he began his career there as a young assistant to the renown Renaissance artist, Raphael. He was an important member of Raphael's studio. He worked on the frescos in the Vatican loggias using designs by Raphael and, in Raphael's ''Stanze'' in the Vatican, painted a group of figures in the '' Fire in the Borgo'' fresco. He also collaborated on the decoration of the ceiling of the Villa Farnesina. Despite his relative youth, increasingly he became in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |