|
Geoparsing
In geographic information systems, toponym resolution is the relationship process between a toponym, i.e. the mention of a place, and an unambiguous spatial footprint of the same place. The places mentioned in digitized text collections constitute a rich data source for researchers in many disciplines. However, toponyms in language use are ambiguous, and difficult to assign a definite real-world referent. Over time, established geographic names may change (as in "Byzantium" > "Constantinople" > "Istanbul"); or they may be reused verbatim (("Boston" in England, UK vs. "Boston" in Massachusetts, USA), or with modifications (as in "York" vs. "New York"). To map a set of place names or toponyms that occur in a document to their corresponding latitude/longitude coordinates, a polygon, or any other spatial footprint, a disambiguation step is necessary. A toponym resolution algorithm is an automatic method that performs a mapping from a toponym to a spatial footprint. Some methods for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geocoding
Address geocoding, or simply geocoding, is the process of taking a text-based description of a location, such as an address or the name of a place, and returning geographic coordinates, frequently latitude/longitude pair, to identify a location on the Earth's surface. Reverse geocoding, on the other hand, converts geographic coordinates to a description of a location, usually the name of a place or an addressable location. Geocoding relies on a computer representation of address points, the street / road network, together with postal and administrative boundaries. * Geocode (''verb''): provide geographical coordinates corresponding to (a location). * Geocode (''noun''): is a code that represents a geographic entity (location or object).Sometimes the term can be used in a broader sense: the characterization of a neighborhood, locality, etc., according to such demographic features as ethnic composition or the average income or educational level of its inhabitants, especially as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information Systems
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system to also include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations. The uncounted plural, ''geographic information systems'', also abbreviated GIS, is the most common term for the industry and profession concerned with these systems. It is roughly synonymous with geoinformatics and part of the broader geospatial field, which also includes GPS, remote sensing, etc. Geographic information science, the academic discipline that studies these systems and their underlying geographic principles, may also be abbreviated as GIS, but the unambiguous GIScience is more common. GIScience is often considered a subdi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Extraction
Information extraction (IE) is the task of automatically extracting structured information from unstructured and/or semi-structured machine-readable documents and other electronically represented sources. In most of the cases this activity concerns processing human language texts by means of natural language processing (NLP). Recent activities in multimedia document processing like automatic annotation and content extraction out of images/audio/video/documents could be seen as information extraction Due to the difficulty of the problem, current approaches to IE (as of 2010) focus on narrowly restricted domains. An example is the extraction from newswire reports of corporate mergers, such as denoted by the formal relation: :\mathrm(company_1, company_2, date), from an online news sentence such as: :''"Yesterday, New York based Foo Inc. announced their acquisition of Bar Corp."'' A broad goal of IE is to allow computation to be done on the previously unstructured data. A more sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information System
A geographic information system (GIS) is a type of database containing geographic data (that is, descriptions of phenomena for which location is relevant), combined with software tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing those data. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system to also include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations. The uncounted plural, ''geographic information systems'', also abbreviated GIS, is the most common term for the industry and profession concerned with these systems. It is roughly synonymous with geoinformatics and part of the broader geospatial field, which also includes GPS, remote sensing, etc. Geographic information science, the academic discipline that studies these systems and their underlying geographic principles, may also be abbreviated as GIS, but the unambiguous GIScience is more common. GIScience is often considered a sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Coordinates
The geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or ellipsoidal coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on the Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest and most widely used of the various spatial reference systems that are in use, and forms the basis for most others. Although latitude and longitude form a coordinate tuple like a cartesian coordinate system, the geographic coordinate system is not cartesian because the measurements are angles and are not on a planar surface. A full GCS specification, such as those listed in the EPSG and ISO 19111 standards, also includes a choice of geodetic datum (including an Earth ellipsoid), as different datums will yield different latitude and longitude values for the same location. History The invention of a geographic coordinate system is generally credited to Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who composed his now-lost ''Geography'' at the Library of Alexandria in the 3rd century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set Cover Problem
The set cover problem is a classical question in combinatorics, computer science, operations research, and complexity theory. It is one of Karp's 21 NP-complete problems shown to be NP-complete in 1972. Given a set of elements (called the universe) and a collection of sets whose union equals the universe, the set cover problem is to identify the smallest sub-collection of whose union equals the universe. For example, consider the universe and the collection of sets Clearly the union of is . However, we can cover all of the elements with the following, smaller number of sets: More formally, given a universe \mathcal and a family \mathcal of subsets of \mathcal, a ''cover'' is a subfamily \mathcal\subseteq\mathcal of sets whose union is \mathcal. In the set covering decision problem, the input is a pair (\mathcal,\mathcal) and an integer k; the question is whether there is a set covering of size k or less. In the set covering optimization problem, the input is a pair ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
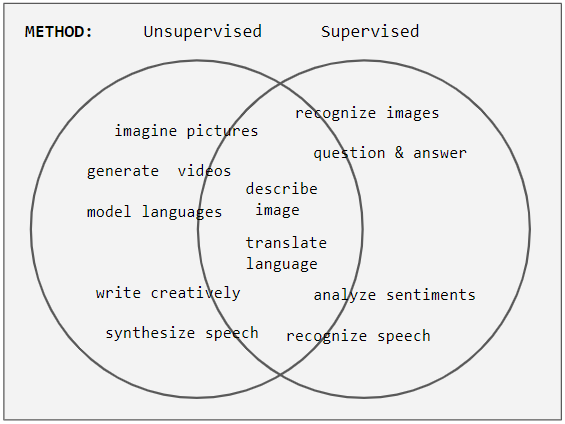
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning is a type of algorithm that learns patterns from untagged data. The hope is that through mimicry, which is an important mode of learning in people, the machine is forced to build a concise representation of its world and then generate imaginative content from it. In contrast to supervised learning where data is tagged by an expert, e.g. tagged as a "ball" or "fish", unsupervised methods exhibit self-organization that captures patterns as probability densities or a combination of neural feature preferences encoded in the machine's weights and activations. The other levels in the supervision spectrum are reinforcement learning where the machine is given only a numerical performance score as guidance, and semi-supervised learning where a small portion of the data is tagged. Neural networks Tasks vs. methods Neural network tasks are often categorized as discriminative (recognition) or generative (imagination). Often but not always, discriminative tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning (SL) is a machine learning paradigm for problems where the available data consists of labelled examples, meaning that each data point contains features (covariates) and an associated label. The goal of supervised learning algorithms is learning a function that maps feature vectors (inputs) to labels (output), based on example input-output pairs. It infers a function from ' consisting of a set of ''training examples''. In supervised learning, each example is a ''pair'' consisting of an input object (typically a vector) and a desired output value (also called the ''supervisory signal''). A supervised learning algorithm analyzes the training data and produces an inferred function, which can be used for mapping new examples. An optimal scenario will allow for the algorithm to correctly determine the class labels for unseen instances. This requires the learning algorithm to generalize from the training data to unseen situations in a "reasonable" way (see inductive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metonymy
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that thing or concept. Etymology The words ''metonymy'' and ''metonym'' come from grc, μετωνυμία, 'a change of name', from , 'after, post, beyond' and , , a suffix that names figures of speech, from , or , 'name'. Background Metonymy and related figures of speech are common in everyday speech and writing. Synecdoche and metalepsis are considered specific types of metonymy. Polysemy, the capacity for a word or phrase to have multiple meanings, sometimes results from relations of metonymy. Both metonymy and metaphor involve the substitution of one term for another. In metaphor, this substitution is based on some specific analogy between two things, whereas in metonymy the substitution is based on some understood association or contiguity. American literary theorist Kenneth Burke considers metonymy as one of four "master tropes": metaphor, meto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Canada, it is Canada's most populous province, with 38.3 percent of the country's population, and is the second-largest province by total area (after Quebec). Ontario is Canada's fourth-largest jurisdiction in total area when the territories of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut are included. It is home to the nation's capital city, Ottawa, and the nation's most populous city, Toronto, which is Ontario's provincial capital. Ontario is bordered by the province of Manitoba to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay to the north, and Quebec to the east and northeast, and to the south by the U.S. states of (from west to east) Minnesota, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York. Almost all of Ontario's border with the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenStreetMap
OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a free, open geographic database updated and maintained by a community of volunteers via open collaboration. Contributors collect data from surveys, trace from aerial imagery and also import from other freely licensed geodata sources. OpenStreetMap is freely licensed under the Open Database License and as a result commonly used to make electronic maps, inform turn-by-turn navigation, assist in humanitarian aid and data visualisation. OpenStreetMap uses its own topology to store geographical features which can then be exported into other GIS file formats. The OpenStreetMap website itself is an online map, geodata search engine and editor. In 2004, OpenStreetMap was created by Steve Coast in response to the Ordnance Survey, the United Kingdom's national mapping agency, failing to release its data to the public and under free licences. Initially, maps were created only via GPS traces, but it was quickly populated by importing public domain geographi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GeoNames
GeoNames (or GeoNames.org) is a user editable geographical database available and accessible through various web services, under a Creative Commons attribution license. The project was founded in late 2005. The GeoNames dataset differs from, but includes data from, the US Government's similarly named GEOnet Names Server. Database and web services The GeoNames database contains over 25,000,000 geographical names corresponding to over 11,800,000 unique features. All features are categorized into one of nine feature classes and further subcategorized into one of 645 feature codes. Beyond names of places in various languages, data stored include latitude, longitude, elevation, population, administrative subdivision and postal codes. All coordinates use the World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS84). Those data are accessible free of charge through a number of Web services and a daily database export. Wiki interface The core of GeoNames database is provided by official public sourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |