|
Genomes OnLine Database
The Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) is a web-based resource for comprehensive information regarding genome and metagenome sequencing projects, and their associated metadata, around the world. Since 2011, the GOLD database has been run by the DOE Joint Genome Institute The GOLD database was created in 1997; the first version of the database contained information for 350 sequencing projects, of which 48 had been completely sequenced with their analyses published. GOLD v.5 was released on 28 May 2014. , the GOLD database contains information for 67,879 genome sequencing projects, of which 7,210 have been completed. In order to facilitate comparative analysis between the information in GOLD and other databases (for example, GenBank and the EMBL), GOLD supports the minimum information standards metadata specifications recommended by the Genomic Standards Consortium, in particular, the MIxS (Minimum Information about any (x) Sequence) specification. GOLD also allows the annotation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome Project
Genome projects are scientific endeavours that ultimately aim to determine the complete genome sequence of an organism (be it an animal, a plant, a fungus, a bacterium, an archaean, a protist or a virus) and to annotate protein-coding genes and other important genome-encoded features. The genome sequence of an organism includes the collective DNA sequences of each chromosome in the organism. For a bacterium containing a single chromosome, a genome project will aim to map the sequence of that chromosome. For the human species, whose genome includes 22 pairs of autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes, a complete genome sequence will involve 46 separate chromosome sequences. The Human Genome Project is a well known example of a genome project. Genome assembly Genome assembly refers to the process of taking a large number of short DNA sequences and reassembling them to create a representation of the original chromosomes from which the DNA originated. In a shotgun sequencing project, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
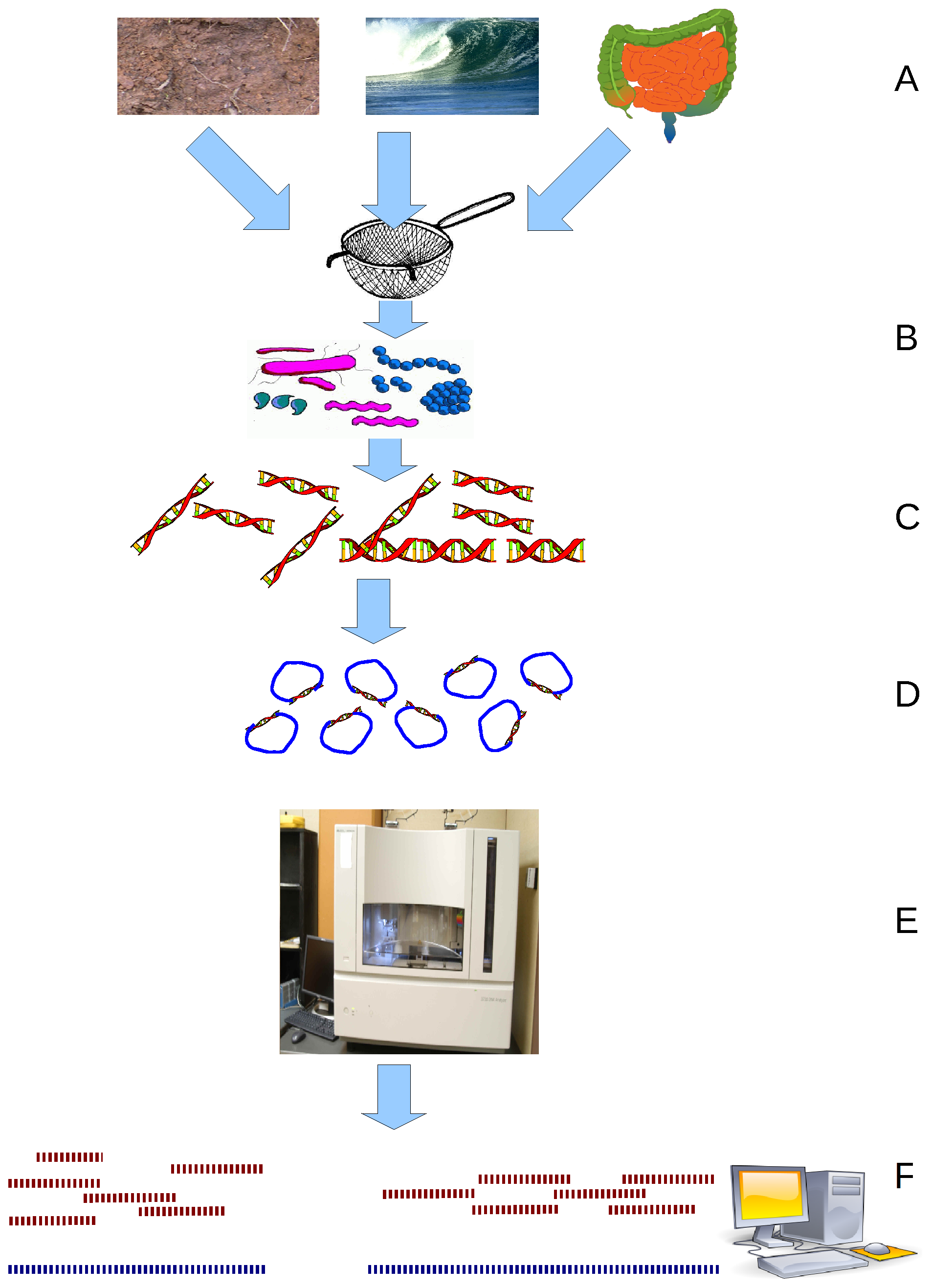
Metagenome
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microbiomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Genome Institute
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Joint Genome Institute (JGI), first located in Walnut Creek then Berkeley, California, was created in 1997 to unite the expertise and resources in genome mapping, DNA sequencing, technology development, and information sciences pioneered at the DOE genome centers at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). As a DOE Office of Science User Facility of Berkeley Lab, the JGI staff is composed of employees from Berkeley Lab, LLNL and the HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology. The JGI also collaborates with other DOE-supported programs and facilities, such as the Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center, or NERSC, and the DOE Bioenergy Research Centers. History In 1999, the University of California, which manages the three national labs for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome Sequencing
Whole genome sequencing (WGS), also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is the process of determining the entirety, or nearly the entirety, of the DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast. Whole genome sequencing has largely been used as a research tool, but was being introduced to clinics in 2014. In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data may be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of gene sequencing at SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response. Whole genome sequencing should not be confused with DNA profiling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GenBank
The GenBank sequence database is an open access, annotated collection of all publicly available nucleotide sequences and their protein translations. It is produced and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI; a part of the National Institutes of Health in the United States) as part of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC). GenBank and its collaborators receive sequences produced in laboratories throughout the world from more than 500,000 formally described species. The database started in 1982 by Walter Goad and Los Alamos National Laboratory. GenBank has become an important database for research in biological fields and has grown in recent years at an exponential rate by doubling roughly every 18 months. Release 250.0, published in June 2022, contained over 17 trillion nucleotide bases in more than 2,45 billion sequences. GenBank is built by direct submissions from individual laboratories, as well as from bulk submis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Molecular Biology Laboratory
The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) is an intergovernmental organization dedicated to molecular biology research and is supported by 27 member states, two prospect states, and one associate member state. EMBL was created in 1974 and is funded by public research money from its member states. Research at EMBL is conducted by approximately 110 independent research and service groups and teams covering the spectrum of molecular biology and bioinformatics. The list of Groups and Teams at EMBL can be found at . The Laboratory operates from six sites: the main laboratory in Heidelberg, and sites in Hinxton (the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), in England), Grenoble (France), Hamburg (Germany), Rome (Italy) and Barcelona (Spain). EMBL groups and laboratories perform basic research in molecular biology and molecular medicine as well as train scientists, students, and visitors. The organization aids in the development of services, new instruments and methods, and techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum Information Standards
Minimum information standards are sets of guidelines and formats for reporting data derived by specific high-throughput methods. Their purpose is to ensure the data generated by these methods can be easily verified, analysed and interpreted by the wider scientific community. Ultimately, they facilitate the transfer of data from journal articles (unstructured data) into databases (structured data) in a form that enables data to be mined across multiple data sets. Minimal information standards are available for a vast variety of experiment types including microarray (MIAME), RNAseq ( MINSEQE), metabolomics (MSI) and proteomics ( MIAPE). Minimum information standards typically have two parts. Firstly, there is a set of reporting requirements – typically presented as a table or a checklist. Secondly, there is a data format. Information about an experiment needs to be converted into the appropriate data format for it to be submitted to the relevant database. In the case of MIAME, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metadata
Metadata is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including: * Descriptive metadata – the descriptive information about a resource. It is used for discovery and identification. It includes elements such as title, abstract, author, and keywords. * Structural metadata – metadata about containers of data and indicates how compound objects are put together, for example, how pages are ordered to form chapters. It describes the types, versions, relationships, and other characteristics of digital materials. * Administrative metadata – the information to help manage a resource, like resource type, permissions, and when and how it was created. * Reference metadata – the information about the contents and quality of statistical data. * Statistical metadata – also called process data, may describe processes that collect, process, or produce s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genomic Standards Consortium
The Genomic Standards Consortium (GSC) is an initiative working towards richer descriptions of our collection of genomes, metagenomes and marker genes. Established in September 2005, this international community includes representatives from a range of major sequencing and bioinformatics centres (including NCBI, EMBL, DDBJ, JCVI, JGI, EBI, Sanger, FIG) and research institutions. The goal of the GSC is to promote mechanisms for standardizing the description of (meta)genomes, including the exchange and integration of (meta)genomic data. The number and pace of genomic and metagenomic sequencing projects will only increase as the use of ultra-high-throughput methods becomes common place and standards are vital to scientific progress and data sharing. Mission Community-driven standards have the best chance of success if developed within the auspices of international working groups. Participants in the GSC include biologists, computer scientists, those building genomic databases an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Microbial Genomes System
The Integrated Microbial GenomesIMG system is a genome browsing and annotation platform developed by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)- Joint Genome Institute. IMG contains all the draft and complete microbial genomes sequenced by the DOE-JGI integrated with other publicly available genomes (including Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya, Viruses and Plasmids). IMG provides users a set of tools for comparative analysis of microbial genomes along three dimensions: genes, genomes and functions. Users can select and transfer them in the comparative analysis carts based upon a variety of criteria. IMG also includes a genome annotation pipeline that integrates information from several tools, including KEGG, Pfam, InterPro, and the Gene Ontology, among others. Users can also type or upload their own gene annotations (called MyIMG gene annotations) and the IMG system will allow them to generate Genbank or EMBL format files containing these annotations. In successive releases IMG has expanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BioMed Central
BioMed Central (BMC) is a United Kingdom-based, for-profit scientific open access publisher that produces over 250 scientific journals. All its journals are published online only. BioMed Central describes itself as the first and largest open access science publisher. It was founded in 2000 and has been owned by Springer, now Springer Nature, since 2008. History BioMed Central was founded in 2000 as part of the Current Science Group (now Science Navigation Group, SNG), a nursery of scientific publishing companies. SNG chairman Vitek Tracz developed the concept for the company after NIH director Harold Varmus's PubMed Central concept for open-access publishing was scaled back. The first director of the company was Jan Velterop. Chemistry Central was established in 2006 and the PhysMath Central journal imprint in 2007. In 2002, the company introduced article processing charges, and these have since been the primary source of revenue. In 2007 Yale University Libraries stop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MicrobesOnline
MicrobesOnline is a publicly and freely accessible website that hosts multiple comparative genomic tools for comparing microbial species at the genomic, transcriptomic and functional levels. MicrobesOnline was developed by the Virtual Institute for Microbial Stress and Survival, which is based at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in Berkeley, California. The site was launched in 2005, with regular updates until 2011. The main aim of MicrobesOnline is to provide an easy-to-use resource that integrates a wealth of data from multiple sources. This integrated platform facilitates studies in comparative genomics, metabolic pathway analysis, genome composition, functional genomics as well as in protein domain and protein family, family data. It also provides tools to search or browse the database with genes, species, sequences, homology (biology), orthologous groups, gene ontology (GO) terms or pathway keywords, etc. Another one of its main features is the Gene Cart, which allows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_milestones.jpg)