|
Gaap
Gaap (also ''Tap'', ''Coap'', ''Taob'', ''Goap'') is a demon that is described in demonological grimoires such as ''the Lesser Key of Solomon'', Johann Weyer's ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'', and the Munich Manual of Demonic Magic, as well as Jacques Collin de Plancy's ''Dictionnaire Infernal'', These works describe Gaap as a prince in human form who incites love. The Munich Manual also says that "Taob" also provides medical care for women, transforms them to make it easier to get to a lover, renders them infertile, and rules twenty-five legions of spirits. The other sources instead describe Gaap as a president, giving him the power to teach philosophy and liberal arts, make others invisible, steal familiars from other magicians, make men stupid, and carry men between kingdoms; in addition to ruling sixty-six legions of demons. Johann Weyer also connects Gaap to necromancers, and states that he was first called upon by Noah's son Ham, along with Beleth. He was of the order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaap
Gaap (also ''Tap'', ''Coap'', ''Taob'', ''Goap'') is a demon that is described in demonological grimoires such as ''the Lesser Key of Solomon'', Johann Weyer's ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'', and the Munich Manual of Demonic Magic, as well as Jacques Collin de Plancy's ''Dictionnaire Infernal'', These works describe Gaap as a prince in human form who incites love. The Munich Manual also says that "Taob" also provides medical care for women, transforms them to make it easier to get to a lover, renders them infertile, and rules twenty-five legions of spirits. The other sources instead describe Gaap as a president, giving him the power to teach philosophy and liberal arts, make others invisible, steal familiars from other magicians, make men stupid, and carry men between kingdoms; in addition to ruling sixty-six legions of demons. Johann Weyer also connects Gaap to necromancers, and states that he was first called upon by Noah's son Ham, along with Beleth. He was of the order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livre Des Esperitz
The ''Livre des Esperitz'' (or ''Book of Spirits'') is a 15th or 16th century French grimoire that inspired later works including Johann Weyer's ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' and the ''Lesser Key of Solomon''."Les who's who démonologiques de la Renaissance et leurs ancêtres médiévaux" by Jean-Patrice Boudet, ''Médiévales'' 44, Spring 2003(online link) Twilit Grotto -- Esoteric Archives, 2000.''Forbidden Rites: A Necromancer's Manual of the Fifteenth Century''; Richard Kieckhefer; Pennsylvania State University Press, University Park, PA; 1997. P. 161The Goetia of Dr Rudd; Thomas Rudd, Ed. Stephen Skinner & David Rankine; 2007, Golden Hoard Press. p.32-33Entre science et nigromance: astrologie, divination et magie dans l'occident médiév ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
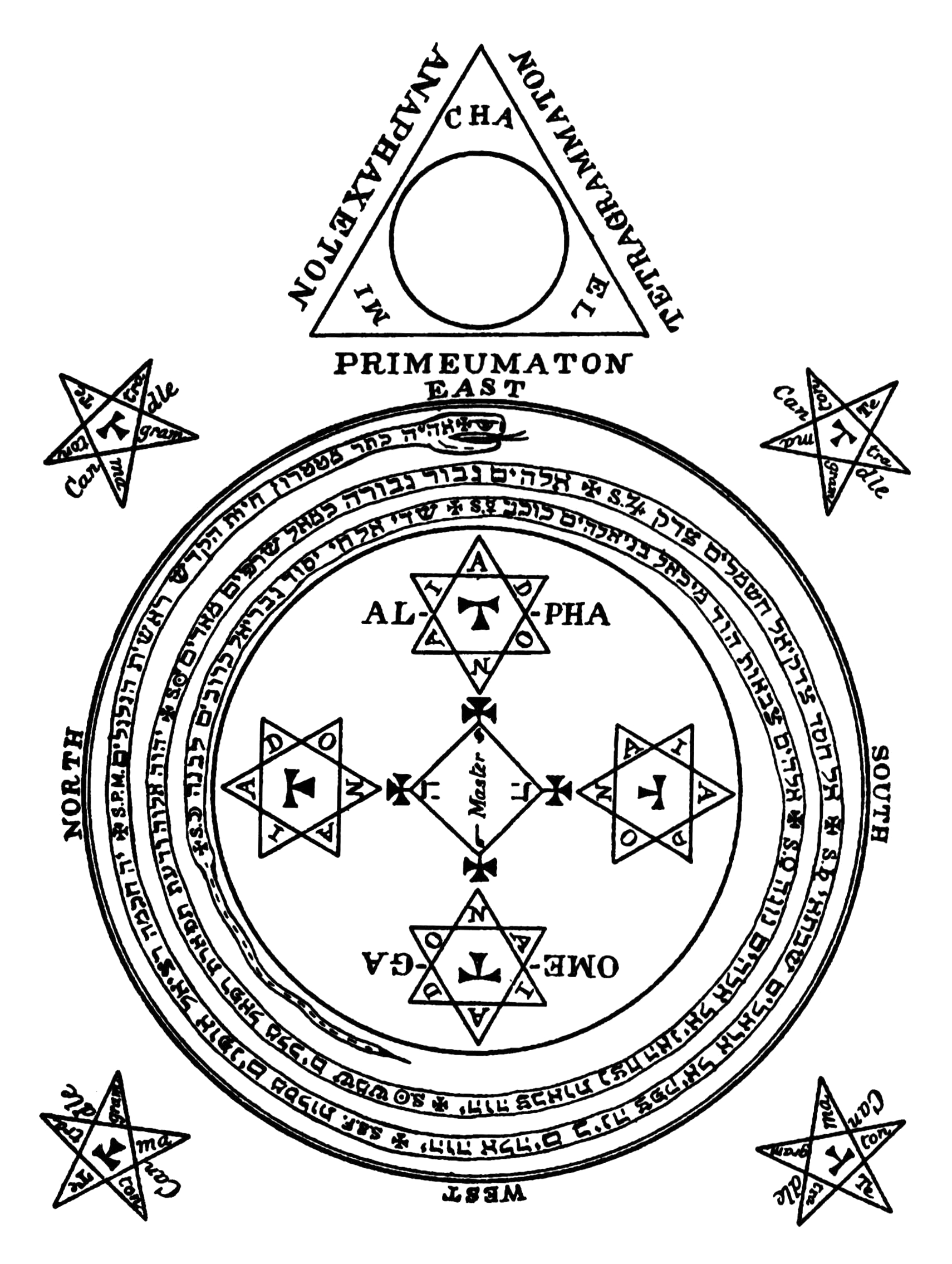
Ziminiar
In demonology, Ziminiar or Zymymar is one of the four principal kings that have power over the seventy-two demons that are supposedly constrained by King Solomon, according to the Lesser Key of Solomon. Ziminiar is not to be conjured except on great occasions. The other three demon-kings are Amaymon, Corson, and Gaap (although some translations of ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' consider the four kings to be Belial, Beleth, Asmodai, and Gaap, not specifying the cardinal direction that they rule over). He is the king of the north according to both The Lesser Key of Solomon and Pseudomonarchia Daemonum. See also * Amaymon In demonology, Amaymon (also Amaimon, or Amoymon) is a prince of Hell, and, according to some grimoires, the only one who has power over Asmodai. A curious characteristic of this spirit is alleged in almost all copies of the Ars Goetia in Englis ... is also one of the four cardinal spirits, of the east in the Lesser Key of Solomon. * Corson is also one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corson (demon)
In demonology, Corson is one of the four principal kings that have power over the seventy-two demons that are supposedly constrained by King Solomon, according to the Lesser Key of Solomon. Corson is not to be conjured except on great occasions. He is the king of the west according to some translations of The Lesser Key of Solomon, and king of the south according to Pseudomonarchia Daemonum. The other three demon-kings of the cardinal directions are Amaymon, Ziminiar, and Gaap (although some translations of ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' consider Belial, Beleth, Asmodai, and Gaap to be the kings of different cardinal directions, not specifying the cardinal direction that they rule over). Other spelling *Gorson See also * Amaymon is also one of the four cardinal spirits, of the east in the Lesser Key of Solomon. * Ziminiar In demonology, Ziminiar or Zymymar is one of the four principal kings that have power over the seventy-two demons that are supposedly constrained by King Solo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lesser Key Of Solomon
''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', also known as ''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis'' or simply ''Lemegeton'', is an anonymous grimoire on demonology. It was compiled in the mid-17th century, mostly from materials a couple of centuries older.''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis: The Lesser Key of Solomon, Detailing the Ceremonial Art of Commanding Spirits Both Good and Evil''; ed. Joseph H. Peterson; Weiser Books Maine; 2001. pp. xi–xvii.''The Goetia of Dr Rudd''; Thomas Rudd, Eds. Stephen Skinner & David Rankine; 2007, Golden Hoard Press. p. 399. It is divided into five books—the ''Ars Goetia'', ''Ars Theurgia-Goetia'', ''Ars Paulina'', ''Ars Almadel'', and ''Ars Notoria''. ''Ars Goetia'' Etymology The text is more properly called "Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis, or, The little Key of Solomon". The title most commonly used, "The Lesser Key of Solomon," does not in fact occur in the manuscripts. A.E. Waite, in his 1898 ''Book of Black Magic and of Pacts'' does use the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonarchia Daemonum
''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'', or ''False Monarchy of Demons'', first appears as an Appendix to '' De praestigiis daemonum'' (1577) by Johann Weyer.Pseudomonarchia Daemonum (Liber officiorum spirituum); Johann Weyer, ed. Joseph Peterson; 2000. Available online aEsoteric Archives/ref> An abridgment of a grimoire similar in nature to the ''Ars Goetia'' (first book of ''The Lesser Key of Solomon''), it contains a list of demons, and the appropriate hours and rituals to conjure them. The ''Pseudomonarchia'' predates, and differs somewhat from, ''Ars Goetia''. The ''Pseudomonarchia'' lists sixty-nine demons (in contrast to the later seventy-two), and their sequence varies, along with some of their characteristics. The demon Pruflas appears only in ''Pseudomonarchia'',''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' add the demons Vassago, Seere, Dantalion, and Andromalius. and ''Pseudomonarchia'' does not attribute any sigils to the demons. Weyer referred to his source manuscript as ''Liber officiorum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictionnaire Infernal
The ''Dictionnaire infernal'' ( en, "Infernal Dictionary") is a book on demonology, describing demons organised in hierarchies. It was written by Jacques Collin de Plancy and first published in 1818. There were several editions of the book; perhaps the most famous is the 1863 edition, which included sixty-nine illustrations by Louis Le Breton depicting the appearances of several of the demons. Many but not all of these images were later used in S. L. MacGregor Mathers's edition of '' The Lesser Key of Solomon''. History ''Dictionnaire Infernal'' was first published in 1818 and then divided into two volumes, with six reprints—and many changes—between 1818 and 1863. This book attempts to provide an account of all the knowledge concerning superstitions and demonology. A review in 1822 read: The cover page for the 1826 edition reads: Influenced by Voltaire, Collin de Plancy initially did not believe in superstition. For example, the book reassures its contemporaries as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shemhamphorasch
''Shem HaMephorash'' ( he, שֵׁם הַמְּפֹרָשׁ ''Šēm hamMəfōrāš'', also ''Shem ha-Mephorash''), meaning "the explicit name," is originally a Tannaitic term describing the Tetragrammaton. In Kabbalah, it may refer to a name of God composed of either 4, 12, 22, 42, or 72 letters (or triads of letters), the latter version being the most common. 12-, 22-, and 42-letter names Early sources, from the Mishnah to Maimonides, only use "Shem ha-Mephorash" to refer to the four letter Tetragrammaton. b. Qiddushin 72a describes a 12-letter name (apparently a mundane euphemism, YHWH-EHYH-ADNY or YHWH-YHWH-YHWH) and a 42-letter name (holy but unknown; Hayy Gaon says it is the acronym of the medieval piyyut Ana b'Koachתשובה אל יוסף בן ברכיה ותלמידי יעקב בן נסים בעניין שמות והשבעות, קונטרס "הדר עם הנכרי בחצר"). A 22-letter name appears in '' Sefer Raziel HaMalakh'', without interpretation, as ('). I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amaymon
In demonology, Amaymon (also Amaimon, or Amoymon) is a prince of Hell, and, according to some grimoires, the only one who has power over Asmodai. A curious characteristic of this spirit is alleged in almost all copies of the Ars Goetia in English, that during the evocation of Asmodai to visible appearance, the exorcist must stand upright with his cap or headdress removed in a show of respect, because if he does not do so, then Amaymon will deceive him and doom all of his work. According to Joseph H. Peterson, editor of "The Lesser Key of Solomon" (Weiser 2001) this is a "bizarre translation of 'si vero coopertus fuerit'" (Page 21 Footnote 57) by Scot in his "Discoverie of Witchcraft" which contains a translation by Scot of Pseudomonarchia Daemonum by Johannes Weyer. Peterson's edition includes as an appendix, a copy of Weyer's Pseudomonarchia Daemonum in the original Latin where we find (Page 242) "''Cum hujus officia exercet exorcista, fit fortis, cautus & in pedibus stans: si v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Weyer
Johann Weyer or Johannes Wier ( la, Ioannes Wierus or '; 1515 – 24 February 1588) was a Dutch physician, occultist and demonologist, disciple and follower of Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa. He was among the first to publish against the persecution of witches. His most influential work is ('On the Illusions of the Demons and on Spells and Poisons'; 1563). Biography Weyer was born in Grave, a small town in the Duchy of Brabant in the Habsburg Netherlands. He attended the Latin schools in 's-Hertogenbosch and Leuven and when he was about 14 years of age, he became a live-in student of Agrippa, in Antwerp. Agrippa had to leave Antwerp in 1532 and he and Weyer settled in Bonn, under the protection of prince-bishop Hermann von Wied. (Agrippa completed a work on demons in 1533 and perished two years later while on a trip to France). From 1534, Weyer studied medicine in Paris and later in Orléans, but it appears unlikely that he obtained the title of Doctor through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich Manual Of Demonic Magic
The ''Munich Manual of Demonic Magic'' or ''Liber incantationum, exorcismorum et fascinationum variarum'' (CLM 849 of the Bavarian State Library, Munich) is a fifteenth-century grimoire manuscript. The text, composed in Latin, is largely concerned with demonology and necromancy. Richard Kieckhefer edited the text of the manuscript in 1998 under the title ''Forbidden Rites: A Necromancer's Manual of the Fifteenth Century''. Portions of the text, in English translation, are presented in ''Forbidden Rites'' as well, embedded within the author's essays and explanations on the ''Munich Manual'' in specific and grimoires in general. The book has yet to be published in English translation in its entirety. The Russian translation of this Latin grimoire was published in 2019. Pages 130 to 133 include a list of 11 demons, similar in part to the one from Ars Goetia. # Count / Duke Barbarus # Duke Cason # President / Count Otius # King Curson # Duke Alugor # Prince Taob # President Volach # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Collin De Plancy
Jacques Albin Simon Collin de Plancy (28 January 1793 in Plancy-l'Abbaye – 1881 in Paris) was a French occultist, demonologist and writer. He published several works on occultism and demonology. Biography He was born Jacques Albin Simon Collin on 28 (in some sources 30) January 1793 in Plancy (presently Plancy-l'Abbaye), the son of Edme-Aubin Collin and Marie-Anne Danton, the sister of Georges-Jacques Danton who was executed the year after Jacques was born. He later added the aristocratic ''de Plancy'' himself – an addition which later caused accusations against his son in his career as a diplomat. He was a free-thinker influenced by Voltaire. He worked as a printer and publisher in Plancy-l'Abbaye and Paris. Between 1830 and 1837, he resided in Brussels, and then in the Netherlands, before he returned to France after having converted to the Catholic religion. Collin de Plancy followed the tradition of many previous demonologists of cataloguing demons by name and titl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |