|
Gurnard Head
Gurnard's Head (, meaning ''desolate one''; ) is a prominent headland on the north coast of the Penwith peninsula in Cornwall, England. The name is supposed to reflect that the rocky peninsula resembles the head of the Sea robin, gurnard fish. Geography and geology Gurnard's Head is the site of basaltic pillow lavas, formed by underwater volcanic eruptions up to 400 million years ago. It is north of the hamlet of Treen (Zennor), Treen in the parish of Zennor, to the west of Zennor Head. Almost entirely owned by the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust, the headland is within the Aire Point to Carrick Du SSSI, and the South West Coast Path crosses the southern part of the headland. The area is designated as part of the heritage coast, Penwith Heritage Coast and also designated as part of the Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. A pub and hotel on the B3306 road, B3306 coast road shares a name with the headland. History The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Gurnard's Head Hotel, Cornwall
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Pilchard
The European pilchard (''Sardina pilchardus'') is a species of ray-finned fish in the monotypic genus ''Sardina''. The young of the species are among the many fish that are sometimes called sardines. This common species is found in the northeast Atlantic, the Mediterranean, and the Black Sea at depths of . It reaches up to in length and mostly feeds on planktonic crustaceans. This schooling species is a batch spawner where each female lays 50,000–60,000 eggs. Description The European pilchard is a small to medium-sized, somewhat elongated, herring-like fish. The origin of the pelvic fins is well behind that of the dorsal fin, and the last two soft rays on the anal fin are larger than the remainder. The upper parts are green or olive, the flanks are golden and the belly is silvery. Not to be confused with its American counterpart, the California sardine, ''Sardina sagax,'' the European sardine ''S. pilchardus'' does not have a row of dark blotches. They also have scales that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seine Fishing
Seine fishing (or seine-haul fishing; ) is a method of fishing that employs a surrounding net, called a seine, that hangs vertically in the water with its bottom edge held down by weights and its top edge buoyed by floats. Seine nets can be deployed from the shore as a beach seine, or from a boat. Boats deploying seine nets are known as Fishing vessel#Seiners, seiners. Two main types of seine net are deployed from seiners: ''purse seines'' and ''Danish seines''. A seine differs from a Gillnetting, gillnet, in that a seine encloses fish, where a gillnet directly snares fish. Etymology The word ''seine'' has its origins in the Old English ''segne'', which entered the language via Latin ''sagena'', from the original Greek σαγήνη ''sagēnē'' (a drag-net). History Seines have been used widely in the past, including by Stone Age societies. For example, the Māori people, Māori used large canoes to deploy seine nets which could be over a kilometer long. The nets were woven fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
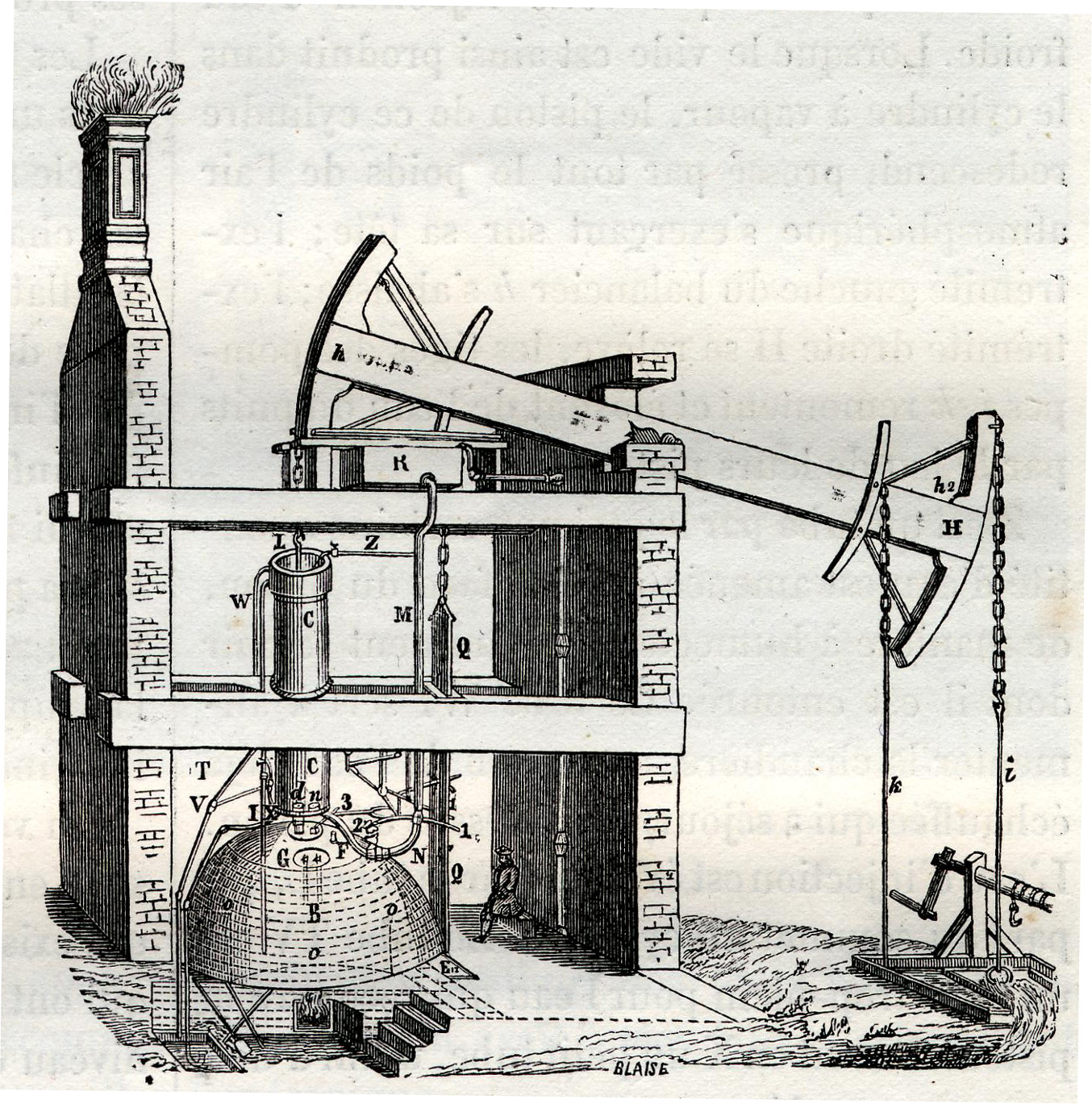
House-built Engine
A house-built engine is a stationary steam engine that is built into an engine house, such that it uses the masonry of the engine house as an integral part of the support of the engine. Beam engines Most house-built engines were early beam engines. A 'bob wall' in the engine house supported the pivot axle of the beam or 'bob'. This wall could be an internal wall, with both ends of the beam inside the house, but it was commonly the end wall of the house and so the beam projected to the outside. For a heavy beam, the bob wall was required to be extremely substantial. Early engines were used for pumping mines or wells, so as well as the weight of the beam, the house had to also support the weight of the long pump rod, reaching down to the depths of the mine. Beam engines appeared during the 18th century. The only technologies at this time that could support the weight of an engine's beam were masonry and timber-framing, as the work of either shipwrights or millwrights. Cast iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Well
A holy well or sacred spring is a well, Spring (hydrosphere), spring or small pool of water revered either in a Christianity, Christian or Paganism, pagan context, sometimes both. The water of holy wells is often thought to have healing qualities, through the numen, numinous presence of its guardian spirit or Christian saint. They often have local legends associated with them; for example in Christian mythology, Christian legends, the water is often said to have been made to flow by the action of a saint. Holy wells are often also places of ritual and pilgrimage, where people Prayer, pray and leave votive offerings. In Celtic nations, Celtic regions, strips of cloth are often tied to trees at holy wells, known as clootie wells. Names The term ''haeligewielle'' is in origin an Old English language, Anglo-Saxon toponym attached to specific springs in the landscape; its current use has arisen through folklore scholars, antiquarians, and other writers generalising from those actual ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isles Of Scilly
The Isles of Scilly ( ; ) are a small archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall, England. One of the islands, St Agnes, Isles of Scilly, St Agnes, is over farther south than the most southerly point of the Great Britain, British mainland at Lizard Point, Cornwall, Lizard Point, and has the southernmost inhabited settlement in England, Troy Town. The total population of the islands at the 2021 United Kingdom census was 2,100 (rounded to the nearest 100). A majority live on one island, St. Mary's, Isles of Scilly, St Mary's, and close to half live in Hugh Town; the remainder live on four inhabited "off-islands". Scilly forms part of the ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Cornwall, and some services are combined with those of Cornwall. However, since 1890, the islands have had Council of the Isles of Scilly, a separate local authority. Since the passing of the Isles of Scilly Order 1930, this authority has held the status of county council, and today it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teän
Teän ( , sometimes written ''Tean'' without the Diaeresis (diacritic), diaeresis; ) is an uninhabited island to the north of the Isles of Scilly archipelago between Tresco, Isles of Scilly, Tresco, to the west, and St Martin's, Isles of Scilly, St Martin's, to the east. Approximately in area, the island consists of a series of granite Tor (rock formation), tors with the highest point, Great Hill, rising to at its eastern end. The low-lying land is overlain with glacial till and outwash gravels with glacial erratics abundant on the north coast beaches, which indicates the southern limit of outwash from an ice sheet for which it is designated a Geological Conservation Review site. There is evidence of occupation from the Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age to the early 19th century and the island was still being grazed in 1945.Parslow, R. (2007) ''The Isles of Scilly''. New Naturalist Library. London: HarperCollins An early Christian chapel exists on the island; it was possibly de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Helen's, Isles Of Scilly
St Helen's ( or ) is one of the fifty or so uninhabited islands in the archipelago of the Isles of Scilly and has an approximate area of . On the south side of the island is one of the earliest Christian sites in Scilly, an early medieval religious complex, which is thought to be the remains of St Elidius Hermitage, an 8th-century chapel lived in by Saint Lide, (also known as Elid or Elidius). There are also the remains of an isolation hospital used to quarantine sailors with plague. The island is the major part of a Site of Special Scientific Interest and some features have been given the designation of scheduled ancient monument. Access to the island is through chartered or private boat, although there are some season trips throughout the summer. St Helen's is currently managed by the Isles of Scilly Wildlife Trust. Geography St Helen's is the third largest of the uninhabited islands and is situated in the northern part, between Tresco and St Martin's. It has an area of and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular territory. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradespeople belonging to a professional association. They sometimes depended on grants of letters patent from a monarch or other ruler to enforce the flow of trade to their self-employed members, and to retain ownership of tools and the supply of materials, but most were regulated by the local government. Guild members found guilty of cheating the public would be fined or banned from the guild. A lasting legacy of traditional guilds are the guildhalls constructed and used as guild meeting-places. Typically the key "privilege" was that only guild members were allowed to sell their goods or practice their skill within the city. There might be controls on minimum or maximum prices, hours of trading, numbers of apprentices, and many other things. Critics argued that these rules reduced Free market, fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treryn Dinas
Treryn Dinas is a headland near Treen, on the Penwith peninsula between Penberth Cove and Porthcurno in Cornwall, England. It is a scheduled monument, and is owned by the National Trust. It is the site of a promontory fort dated to the Iron Age. The promontory slopes away steeply to the sea on three sides, and on the landward (north) side there are widely spaced defensive earthworks. The innermost rampart, up to high, crosses the narrowest part of the headland. Beyond this there are two low curving ramparts, and a massive outer rampart, up to high, with a ditch on its northern side and a causewayed entrance. The South West Coast Path runs alongside the outer rampart.Treryn Dinas Cliff Castle, Treen and Rospletha Cliffs Penberth Valley and Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |