|
Gunter's Chain
Gunter's chain (also known as Gunter's measurement) is a distance-measuring device used for surveying. It was designed and introduced in 1620 by English clergyman and mathematician Edmund Gunter (1581–1626). It enabled plots of land to be accurately surveyed and plotted, for legal and commercial purposes. Gunter developed an actual measuring chain of 100 links. These, the chain and the link, became statutory measures in England and subsequently the British Empire. Description The chain is divided into 100 links, usually marked off into groups of 10 by brass rings or tags which simplify intermediate measurement. Each link is thus long. A quarter chain, or 25 links, measures and thus measures a rod (or pole). Ten chains measure a furlong and 80 chains measure a statute mile. Gunter's chain reconciled two seemingly incompatible systems: the traditional English land measurements, based on the number four, and decimals based on the number 10. Since an acre measured 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acre
The acre ( ) is a Unit of measurement, unit of land area used in the Imperial units, British imperial and the United States customary units#Area, United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), chain by one furlong (66 by 660 Foot (unit), feet), which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the International yard and pound, international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac, but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".National Institute of Standards and Technolog(n.d.) General Tables of Units of Measurement . Traditionally, in the Middle Ages, an acre was conceived of as the area of land that could be ploughed by one man using a team of eight oxen in one day. The acre is still a statutory measure in the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
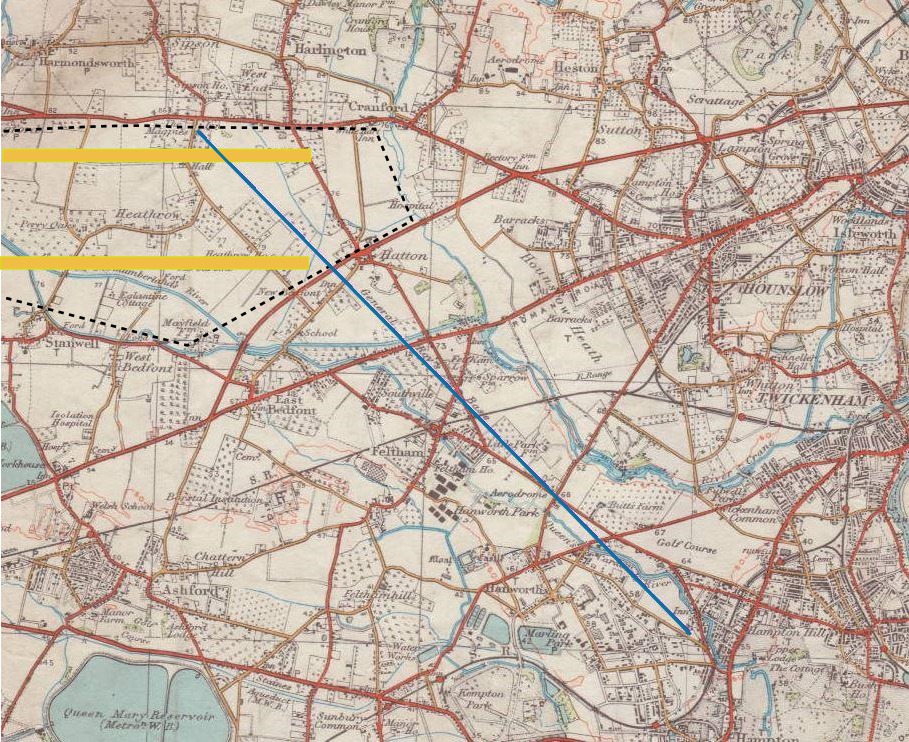
Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790)
The Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790) was the geodetic survey to measure the relative position of the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, Royal Greenwich Observatory and the Paris Observatory via triangulation (surveying), triangulation. The English operations, executed by William Roy, consisted of the measurements of bases at Hounslow Heath (1784) and Romney Marsh (1787), the measurements of the angles of the triangles (1787–1788) and finally the calculation of all the triangles (1788–1790). The survey is very significant as the first precise survey within Britain, and the forerunner of the work of the Ordnance Survey which was founded in 1791, one year after Roy's death. Cassini's memoir Late in life, when he was 57, Roy was granted the opportunity to establish his lasting reputation in the world of geodesy. The opening came from a completely unexpected direction. In 1783 the director of the Paris Observatory, César-François Cassini de Thury, Cassini de Thury, addressed a me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foot (unit)
The foot (standard symbol: ft) is a Units of measurement, unit of length in the imperial units, British imperial and United States customary units, United States customary systems of metrology, measurement. The prime (symbol), prime symbol, , is commonly used to represent the foot. In both customary and imperial units, one foot comprises 12 inches, and one yard comprises three feet. Since international yard and pound, an international agreement in 1959, the foot is defined as equal to exactly 0.3048 meters. Historically, the "foot" was a part of many local systems of units, including the Ancient Greek units of measurement, Greek, Ancient Roman units of measurement, Roman, Chinese units of measurement, Chinese, Units of measurement in France before the French Revolution, French, and English units, English systems. It varied in length from country to country, from city to city, and sometimes from trade to trade. Its length was usually between 250 mm and 335 mm and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesse Ramsden
Jesse Ramsden Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (6 October 1735 – 5 November 1800) was a British mathematician, astronomy, astronomical and scientific instrument maker. His reputation was built on the engraving and design of dividing engines which allowed high accuracy measurements of angles and lengths in instruments. He produced instruments for astronomy that were especially well known for maritime use where they were needed for the measurement of latitudes and for his surveying instruments which were widely used for cartography and land survey both across the British Empire and outside. An achromatic eyepiece that he invented for telescopes and microscopes continues to be known as the Ramsden eyepiece. Life Ramsden was born at Salterhebble, Halifax, West Yorkshire, Halifax, West Riding of Yorkshire, England the son of Thomas Ramsden, an innkeeper and his wife Abigail née Flather. Having attended the free school at Halifax from 1744 to 1747, he was sent at the age of twe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricket Pitch
A cricket pitch is the rectangular central strip of a cricket field between the two wickets, where most of the action takes place. It is long (1 Chain (unit), chain) and wide. The surface is flat and is normally covered with extremely short grass, but can be completely dry or dusty soil with barely any grass or, in some circumstances (that are rarely seen in high level cricket), made from an artificial material. Over the course of a cricket match, the pitch is not repaired or altered other than in special circumstances - meaning that it will change condition. Any grass on the pitch at the start of the game, for example, may disappear due to wear. As almost all Delivery (cricket), deliveries bowled will bounce off the pitch towards the Batting (cricket), batter, the state and type of a cricket pitch can significantly affect the outcome of a match. For example, a dusty, very dry, pitch will favour spin bowling because the ball will grip more on a dusty pitch - giving the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The Geography of New Zealand, country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps (), owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. Capital of New Zealand, New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and subsequently developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller islands. It has a total area of , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country in the world and the largest in Oceania. Australia is the world's flattest and driest inhabited continent. It is a megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and Climate of Australia, climates including deserts of Australia, deserts in the Outback, interior and forests of Australia, tropical rainforests along the Eastern states of Australia, coast. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south-east Asia 50,000 to 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last glacial period. By the time of British settlement, Aboriginal Australians spoke 250 distinct l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Lands Survey System
The Public Land Survey System (PLSS) is the surveying method developed and used in the United States to plat, or divide, real property for sale and settling. Also known as the Rectangular Survey System, it was created by the Land Ordinance of 1785 to survey land ceded to the United States by the Treaty of Paris in 1783, following the end of the American Revolution. Beginning with the Seven Ranges in present-day Ohio, the PLSS has been used as the primary survey method in the United States. Following the passage of the Northwest Ordinance in 1787, the Surveyor General of the Northwest Territory platted lands in the Northwest Territory. The Surveyor General was later merged with the United States General Land Office, which later became a part of the U.S. Bureau of Land Management (BLM). Today, the BLM controls the survey, sale, and settling of lands acquired by the United States. History Originally proposed by Thomas Jefferson to create a nation of "yeoman farmers", the PLSS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tape Measure
A tape measure or measuring tape is a long, flexible ruler used to measure length or distance. It usually consists of a ribbon of cloth, plastic, fibreglass, or metal (usually - hard steel alloy) strip with linear measurement markings. Types Tape measures are often designed for specific uses or trades. Tapes may have different scales, be made of different materials, and be of different lengths depending on the intended use. Tape measures used in sewing, tailoring are called "sewing tape". Originally made from flexible cloth or plastic, fiberglass is now the preferred material due to its resistance from stretching or tearing. Sewing tape is mainly used for the measuring of the subject's waist line.Measuring tapes designed for carpenter, carpentry or construction often use a curved metallic ribbon that can remain stiff and straight when extended, but can also retract into a coil for convenient storage. This type of tape measure will have a hook on the end to aid measuring. The hoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranging
Length measurement, distance measurement, or range measurement (ranging) all refer to the many ways in which length, distance, or range can be measured. The most commonly used approaches are the rulers, followed by transit-time methods and the interferometer methods based upon the speed of light. Surveying is one ancient use of measuring long distances. For tiny objects such as crystals and diffraction gratings, diffraction is used with X-ray light, or even electron beams. Measurement techniques for three-dimensional structures very small in every dimension use specialized instruments such as ion microscopy coupled with intensive computer modeling. These techniques are employed, for example, to measure the tiny features on wafers during the manufacture of chips. Standard rulers The ruler the simplest kind of length measurement tool: lengths are defined by printed marks or engravings on a stick. The metre was initially defined using a ruler before more accurate methods bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |