|
Guangyuanolimulus
''Guangyuanolimulus'' is an extinct genus of limulid xiphosuran that lived during the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Distribution ''Guangyuanolimulus shangsiensis'' fossils are known from South China South China ( zh, s=, p=Huá'nán, j=jyut6 naam4) is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is .... References {{Taxonbar, from=Q133657463 Permian arthropods Fossils of China Fossil taxa described in 2022 Xiphosura Prehistoric chelicerate genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and recover. As a species' potential Range (biology), range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxon, Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the Fossil, fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include Dinosaur, non-avian dinosaurs, Machairodontinae, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
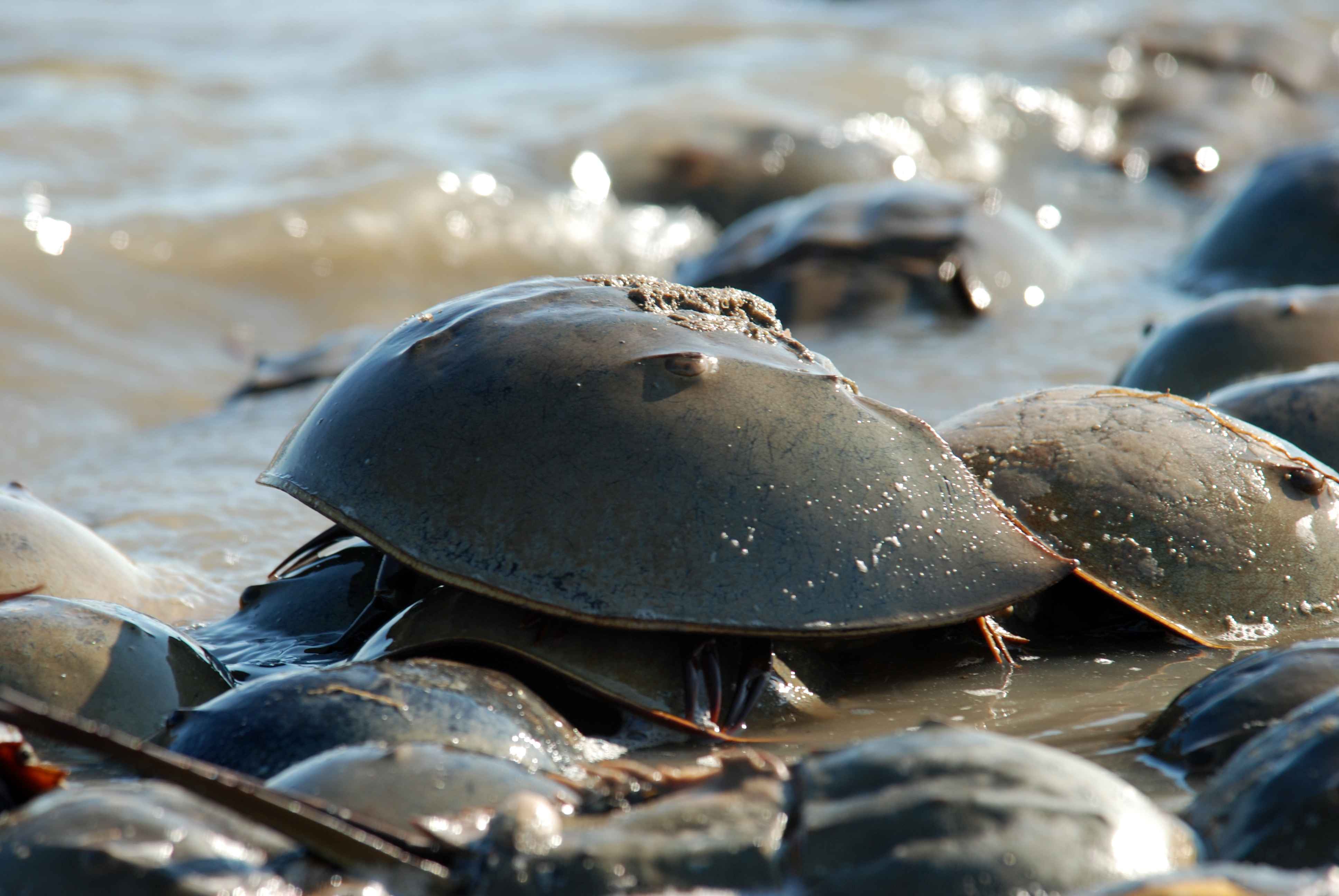
Horseshoe Crab
Horseshoe crabs are arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only surviving xiphosurans. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or even crustaceans; they are chelicerates, more closely related to arachnids like spiders, ticks, and scorpions. The body of a horseshoe crab is divided into three main parts: the cephalothorax, abdomen, and telson. The largest of these, the cephalothorax, houses most of the animal's eyes, limbs, and internal organs. It is also where the animal gets its name, as its shape somewhat resembles that of a horseshoe. Horseshoe crabs have been described as "living fossils", having changed little since they first appeared in the Triassic. Only four species of horseshoe crab are extant today. Most are marine, though the mangrove horseshoe crab is often found in brackish water, and the Atlantic horseshoe crab is resident in brackish estuarine ecosystems such as the Delaware and Chesapeake bays. Additionally, certain extinct species transitioned t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiphosura
Xiphosura (; , in reference to its sword-like telson) is an order of arthropods related to arachnids. They are more commonly known as horseshoe crabs (a name applied more specifically to the only extant family, Horseshoe crab, Limulidae). They first appeared in the Hirnantian (Late Ordovician). Currently, there are only four living species. Xiphosura contains one suborder, Xiphosurida, and several stem-genera. The group has hardly changed in appearance in hundreds of millions of years; the modern horseshoe crabs look almost identical to prehistoric genera and are considered to be living fossils. The most notable difference between ancient and modern forms is that the abdominal segments in present species are fused into a single unit in adults. Xiphosura were historically placed in the class Merostomata, although this term was intended to encompass also the Eurypterida, eurypterids, whence it denoted what is now thought to be an unnatural (paraphyletic) group (although this is a gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian–Triassic Extinction Event
The Permian–Triassic extinction event (also known as the P–T extinction event, the Late Permian extinction event, the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian extinction event, and colloquially as the Great Dying,) was an extinction event that occurred approximately 251.9 Million years ago, million years ago (mya), at the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, and with them the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras. It is Earth's most severe known extinction event, with the extinction of 57% of Family (biology), biological families, 62% of genera and 81% of marine biology, marine species, (previous estimates of 90–96% marine species extinction were due to historical conflation with the End-Capitanian mass extinction event, end-Capitanian mass extinction which occurred 7–10 million years earlier) and 70% of terrestrial vertebrate species. It is also the greatest known mass extinction of insects. It is the greatest of the "Big Five" mass extinctions of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
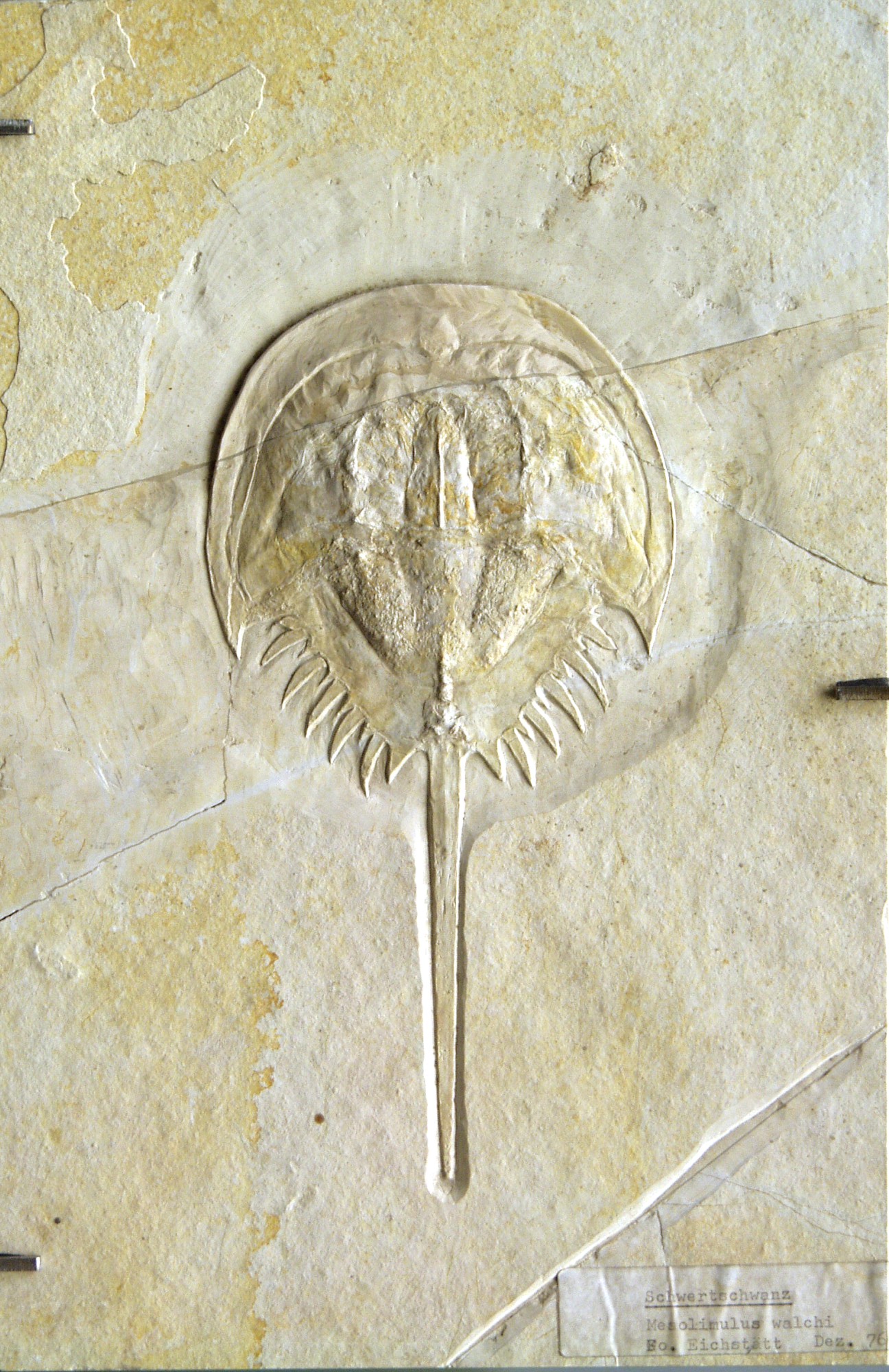
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of '' Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South China
South China ( zh, s=, p=Huá'nán, j=jyut6 naam4) is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not native speakers of Standard Chinese. Cantonese is the most common language in the region while the Hong Kong region contains the largest concentration of China's ethnic minorities. Administrative divisions Cities with urban area over one million in population Provincial capitals in bold. Namesake * South China tiger (southern China) * ''South China Morning Post'' (Hong Kong, South China) * Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market (Wuhan, Central China) * South China Normal University, a university in Guangzhou, Guangdong, China * South China Athletic Association (Hong Kong SR, China) See also * Lingnan * List of regions of China ** Northern and southern China, Southern China *** South Central China — ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology
''Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology'' ("''Palaeo3''") is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing multidisciplinary studies and comprehensive reviews in the field of palaeoenvironmental geology. The journal is edited by Howard Falcon-Lang, Shuzhong Shen, Alex Dickson, Mary Elliot, Meixun Zhao, Lucia Angiolini. It was established in 1965 and is currently published by Elsevier. Indexing and abstracting ''Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology'' is indexed and abstracted in the following databases: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', ''Advance in Space Research'' has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 3.318. References External links * Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian Arthropods
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the sixth and last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the Sauropsida, sauropsids (reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of China
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2022
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, seashell, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in #Resin, amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiphosura
Xiphosura (; , in reference to its sword-like telson) is an order of arthropods related to arachnids. They are more commonly known as horseshoe crabs (a name applied more specifically to the only extant family, Horseshoe crab, Limulidae). They first appeared in the Hirnantian (Late Ordovician). Currently, there are only four living species. Xiphosura contains one suborder, Xiphosurida, and several stem-genera. The group has hardly changed in appearance in hundreds of millions of years; the modern horseshoe crabs look almost identical to prehistoric genera and are considered to be living fossils. The most notable difference between ancient and modern forms is that the abdominal segments in present species are fused into a single unit in adults. Xiphosura were historically placed in the class Merostomata, although this term was intended to encompass also the Eurypterida, eurypterids, whence it denoted what is now thought to be an unnatural (paraphyletic) group (although this is a gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |