|
Gribbio
Gribbio is an Italian-speaking village in Ticino, Switzerland, in the district of Chironico. It is situated in the Lepontine Alps, more specifically in Alta Leventina between Chironico and Dalpe at an altitude of 1,300 metres. The village consists of one church with an ambulatory priest, approximately 30 houses and a cafe/restaurant (Ul Ciurlin - The Little Coffee) with a small menu of typical dishes from the area. As the village is inaccessible in winter there are no permanent residents, but in summer there is a population of 80-100 people. Originally farmers took their cows higher up into the mountains to graze over the summer, using Gribbio as a 'base camp' before returning down the valley for the winter. However, in recent years the village has become more popular as a summer holiday home. Gribbio, unlike Osadigo, Cala, Doro or Olina Ces, has access to a passable road from Chironico, however the road is not cleared of snow and therefore is not accessible by car in winter exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chironico
Chironico is a former municipality located in the district of Leventina in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland. On 1 April 2012, it was incorporated into the municipality of Faido along with the former municipalities of Anzonico, Calpiogna, Campello, Cavagnago, Mairengo and Osco.Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz published by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office . Retrieved 23 May 2012 History Chironico is first mentioned in 1202 as ''Cuirono''. The village lies on a terrace that was partly created by a prehistoric landslide on the opposite side of the valley. The core of the settlement, is made up of the sections of Grumo and Nivo, the latter is the only one in the valley bottom. Above the village center, sit ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
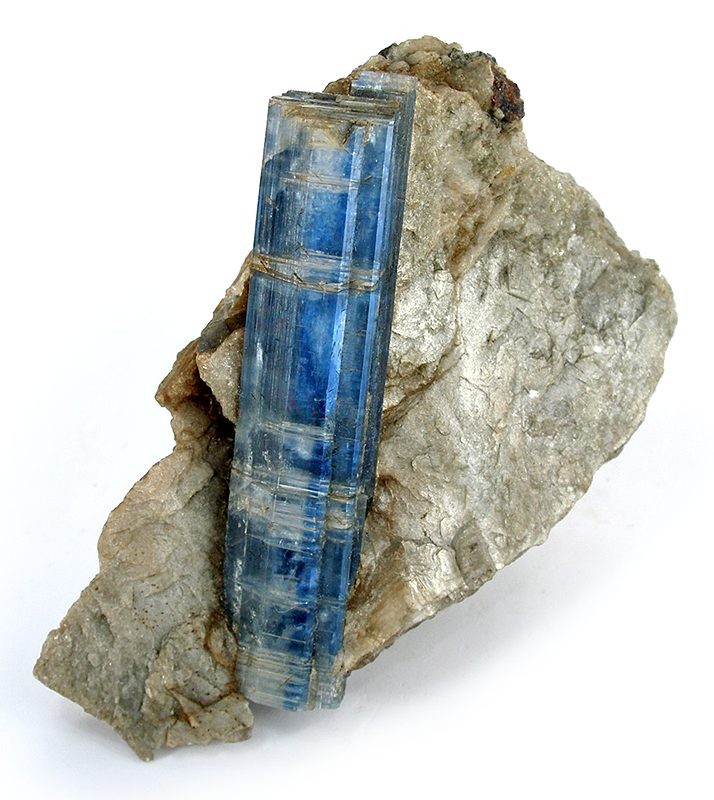
Pizzo Forno
Pizzo Forno is a mountain of the Swiss Lepontine Alps, overlooking Chironico in the canton of Ticino. It is to be found between Piumogna Valley, Chironico Valley and Leventina Valley. It is in pyramid form and is separate from Pizzo Campo Tencia in the east. It is visible from the municipalities of Faido, Giornico and Chironico. The north-east face is particularly striking which rises nearly 1,500 metres from the Piumogna Valley - this face is best viewed from the village of Gribbio. The rock is soft and is subject to frequent landslides. It is famous for its disten and staurolite crystals and for having given the surname ''Forni'' which is now common throughout the Leventina The Leventina District is one of the eight districts of the largely Italian-speaking canton of Ticino in Switzerland. The capital of the district is Faido but the largest town is Airolo on the southern flank of the Gotthard Pass. Situated to the ... region. References External links Pizzo Forno on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leventina (district)
The Leventina District is one of the eight districts of the largely Italian-speaking canton of Ticino in Switzerland. The capital of the district is Faido but the largest town is Airolo on the southern flank of the Gotthard Pass. Situated to the north of the canton, its territory covers the area of the Ticino River as far south as Biasca, in particular the Bedretto Valley and the Leventina Valley. Leventina is divided into four sub-districts, termed 'circles' ( it, circoli), and a total area of with a population of (as of ). Its capital is the municipality ( it, comune) of Faido. The valley became part of Switzerland on 5 March 1480, following the treaty of Lucerne with the Duchy of Milan. Geography The Leventina District has an area, , of . Of this area, or 4.2% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 36.5% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 2.8% is settled (buildings or roads), or 1.9% is either rivers or lakes and or 36.5% is unproductive land. Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, rites of sacrifice to, and propitiation of, a deity or deities. Their office or position is the 'priesthood', a term which also may apply to such persons collectively. A priest may have the duty to hear confessions periodically, give marriage counseling, provide prenuptial counseling, give spiritual direction, teach catechism, or visit those confined indoors, such as the sick in hospitals and nursing homes. Description According to the trifunctional hypothesis of prehistoric Proto-Indo-European society, priests have existed since the earliest of times and in the simplest societies, most likely as a result of agricultural surplus and consequent social stratification. The necessity to read sacred texts and keep temple or church rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Roch
Roch (lived c. 1348 – 15/16 August 1376/79 (traditionally c. 1295 – 16 August 1327, also called Rock in English, is a Catholic saint, a confessor whose death is commemorated on 16 August and 9 September in Italy; he is especially invoked against the plague. He has the designation of Rollox in Glasgow, Scotland, said to be a corruption of Roch's Loch, which referred to a small loch once near a chapel dedicated to Roch in 1506. He is a patron saint of dogs, invalids, falsely accused people, bachelors, and several other things. He is the patron saint of Dolo (near Venice) and Parma, as well as Casamassima, Cisterna di Latina and Palagiano (Italy). He is also the patron saint of the town of Albanchez, in Almeria, southern Spain. Saint Roch is known as "São Roque" in Portuguese, as "Sant Roc" in Catalan, as "San Roque" in Spanish (including in former colonies of the Spanish colonial empire such as the Philippines) and as "San Rocco" in Italian. Etymology Roch is given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ticinese Dialect
The Ticinese dialect is the set of dialects, belonging to the Alpine and Western branch of the Lombard language, spoken in the northern part of the Canton of Ticino (Sopraceneri); the dialects of the region can generally vary from valley to valley, often even between single localities, while retaining the mutual intelligibility that is typical of the Lombard linguistic continuum. ''Ticinese koiné'' refers instead to a koiné form used by speakers of local dialects (particularly those diverging from the ''koinè'' itself, as, e.g., Leventinese, etc.) when communicating with speakers of other Western Lombard dialects of Ticino, the Grisons (collectively known as Swiss Italian) or Italian Lombardy. Status Ticinese is generally more lively than the Western Lombard varieties spoken in Italy, with a significant number of young speakers. Some radio and television programmes in Ticinese, mostly comedies are broadcast by the Italian language broadcasting company RTSI. A dictionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Italian
The Italian language in Switzerland or Swiss Italian ( it, italiano svizzero) is the variety of the Italian language taught in the Italian-speaking area of Switzerland. Italian is spoken natively by about 700,000 people in the canton of Ticino, in the southern part of Graubünden (Canton Grigioni) and in the rest of the country. Characteristics The presence of calques from French and German means that there are some differences in vocabulary between the standard registers of the Italian language used in Italy and Switzerland. An example would be the words for driving licence: in Italy, it is called a ''patente di guida'' but in Swiss Italian, it becomes ''licenza di condurre'', from the French ''permis de conduire''. Another example is the interurban bus: in Italy it would be ''autobus'' or ''corriera'' but in Switzerland, it is the '' Autopostale'' or ''posta'' since nearly all interurban lines are run by a subsidiary of the Swiss Post. Another notable difference is the us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Marmot
The alpine marmot (''Marmota marmota'') is a large ground-dwelling squirrel, from the genus of marmots. It is found in high numbers in mountainous areas of central and southern Europe, at heights between in the Alps, Carpathians, Tatras and Northern Apennines. In 1948 they were reintroduced with success in the Pyrenees, where the alpine marmot had disappeared at end of the Pleistocene epoch. Evolution The alpine marmot originates as an animal of Pleistocene cold steppe, exquisitely adapted to this ice-age climate. As such, alpine marmots are excellent diggers, able to penetrate soil that even a pickaxe would have difficulty with, and spend up to nine months per year in hibernation. Since the disappearance of the Pleistocene cold steppe, the alpine marmot persists in the high altitude alpine meadow. During the colonisation of Alpine habitat, the alpine marmot has lost most of its genetic diversity through a bottleneck effect. It could not rebuild its genetic diversity ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of western Asia. It also inhabits the Atlas Mountains of Northern Africa; its early ancestors are thought to have crossed over to Morocco, then to Algeria, Libya and Tunisia via the Strait of Gibraltar, becoming the only species of true deer ( Cervidae) to inhabit Africa. Red deer have been introduced to other areas, including Australia, New Zealand, the United States, Canada, Peru, Uruguay, Chile and Argentina. In many parts of the world, the meat (venison) from red deer is used as a food source. Red deer are ruminants, characterized by a four-chambered stomach. Genetic evidence indicates that the red deer, as traditionally defined, is a species group, rather than a single species, though exactly how many species the group includes remains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
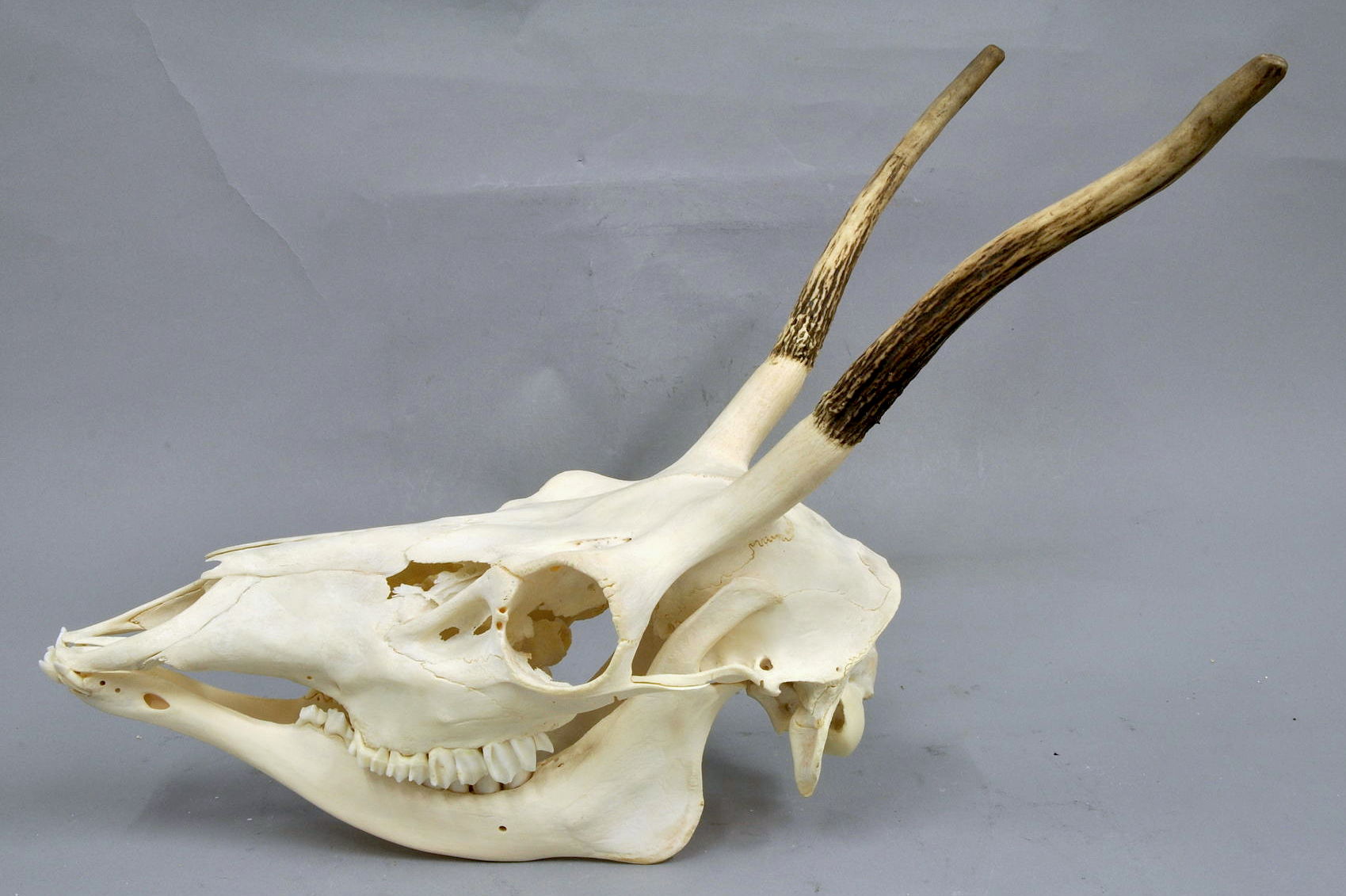
Chamois
The chamois (''Rupicapra rupicapra'') or Alpine chamois is a species of Caprinae, goat-antelope native to mountains in Europe, from west to east, including the Alps, the Dinarides, the Tatra Mountains, Tatra and the Carpathian Mountains, the Balkan Mountains, the Rila–Rhodope Mountains, Rhodope massif, Pindus, the northeastern mountains of Turkey, and the Caucasus. The chamois has also been introduced to the South Island of New Zealand. Some subspecies of chamois are strictly protected in the EU under the European Habitats Directive. Names The English name comes from French language, French . The latter is derived from Gaulish ''camox'' (attested in Latin, 5th century), itself perhaps borrowing from some Alpine language (Raetic language, Raetic, Ligurian (ancient language), Ligurian). The Gaulish form also underlies German language, German , , , Italian language, Italian , Ladin language, Ladin . The usual pronunciation for the animal is or , approximating the French lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Alps
The Alpine region of Switzerland, conventionally referred to as the Swiss Alps (german: Schweizer Alpen, french: Alpes suisses, it, Alpi svizzere, rm, Alps svizras), represents a major natural feature of the country and is, along with the Swiss Plateau and the Swiss portion of the Jura Mountains, one of its three main physiographic regions. The Swiss Alps extend over both the Western Alps and the Eastern Alps, encompassing an area sometimes called Central Alps. While the northern ranges from the Bernese Alps to the Appenzell Alps are entirely in Switzerland, the southern ranges from the Mont Blanc massif to the Bernina massif are shared with other countries such as France, Italy, Austria and Liechtenstein. The Swiss Alps comprise almost all the highest mountains of the Alps, such as Dufourspitze (4,634 m), the Dom (4,545 m), the Liskamm (4,527 m), the Weisshorn (4,506 m) and the Matterhorn (4,478 m). The other following major summits can be found in this list of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leventina
The Leventina District is one of the eight districts of the largely Italian-speaking canton of Ticino in Switzerland. The capital of the district is Faido but the largest town is Airolo on the southern flank of the Gotthard Pass. Situated to the north of the canton, its territory covers the area of the Ticino River as far south as Biasca, in particular the Bedretto Valley and the Leventina Valley. Leventina is divided into four sub-districts, termed 'circles' ( it, circoli), and a total area of with a population of (as of ). Its capital is the municipality ( it, comune) of Faido. The valley became part of Switzerland on 5 March 1480, following the treaty of Lucerne with the Duchy of Milan. Geography The Leventina District has an area, , of . Of this area, or 4.2% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 36.5% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 2.8% is settled (buildings or roads), or 1.9% is either rivers or lakes and or 36.5% is unproductive land. Of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Chamois.png)

