|
Google Neural Machine Translation
Google Neural Machine Translation (GNMT) was a neural machine translation (NMT) system developed by Google and introduced in November 2016 that used an artificial neural network to increase fluency and accuracy in Google Translate. The neural network consisted of two main blocks, an encoder and a decoder, both of LSTM architecture with 8 1024-wide layers each and a simple 1-layer 1024-wide feedforward attention mechanism connecting them. The total number of parameters has been variously described as over 160 million, 210 million, 278 million or 380 million. It used WordPiece tokenizer, and beam search decoding strategy. It ran on Tensor Processing Units. By 2020, the system had been replaced by another deep learning system based on a Transformer encoder and an RNN decoder. GNMT improved on the quality of translation by applying an example-based (EBMT) machine translation method in which the system learns from millions of examples of language translation. GNMT's proposed archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Machine Translation
Neural machine translation (NMT) is an approach to machine translation that uses an artificial neural network to predict the likelihood of a sequence of words, typically modeling entire sentences in a single integrated model. It is the dominant approach today and can produce translations that rival human translations when translating between high-resource languages under specific conditions. However, there still remain challenges, especially with languages where less high-quality data is available, and with domain shift between the data a system was trained on and the texts it is supposed to translate. NMT systems also tend to produce fairly literal translations. Overview In the translation task, a sentence \mathbf = x_ (consisting of I tokens x_i) in the source language is to be translated into a sentence \mathbf = x_ (consisting of J tokens x_j) in the target language. The source and target tokens (which in the simple event are used for each other in order for a particular gam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in San Bruno, California, it is the second-most-visited website in the world, after Google Search. In January 2024, YouTube had more than 2.7billion monthly active users, who collectively watched more than one billion hours of videos every day. , videos were being uploaded to the platform at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute, and , there were approximately 14.8billion videos in total. On November 13, 2006, YouTube was purchased by Google for $1.65 billion (equivalent to $ billion in ). Google expanded YouTube's business model of generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by and for YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Internal Medicine
''Annals of Internal Medicine'' is an academic medical journal published by the American College of Physicians (ACP). It is one of the most widely cited and influential specialty medical journals in the world. ''Annals'' publishes content relevant to the field of internal medicine Internal medicine, also known as general medicine in Commonwealth nations, is a medical specialty for medical doctors focused on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases in adults. Its namesake stems from "treatment of diseases of ... and related sub-specialties. ''Annals'' publishes a wide variety of original research, review articles, practice guidelines, and commentary relevant to clinical practice, health care delivery, public health, health care policy, medical education, ethics, and research methodology. In addition, the journal publishes personal narratives that convey the feeling and the art of medicine. Selected articles in the journal are freely available; these include pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Target Language (translation)
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''translating'' (a written text) and ''interpreting'' (oral or signed communication between users of different languages); under this distinction, translation can begin only after the appearance of writing within a language community. A translator always risks inadvertently introducing source-language words, grammar, or syntax into the target-language rendering. On the other hand, such "spill-overs" have sometimes imported useful source-language calques and loanwords that have enriched target languages. Translators, including early translators of sacred texts, have helped shape the very languages into which they have translated. Because of the laboriousness of the translation process, since the 1940s efforts have been made, with varying degrees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Source Language (translation)
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''translating'' (a written text) and ''interpreting'' (oral or signed communication between users of different languages); under this distinction, translation can begin only after the appearance of writing within a language community. A translator always risks inadvertently introducing source-language words, grammar, or syntax into the target-language rendering. On the other hand, such "spill-overs" have sometimes imported useful source-language calques and loanwords that have enriched target languages. Translators, including early translators of sacred texts, have helped shape the very languages into which they have translated. Because of the laboriousness of the translation process, since the 1940s efforts have been made, with varying degrees o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlingual Machine Translation
Interlingual machine translation is one of the classic approaches to machine translation. In this approach, the source language, i.e. the text to be translated is transformed into an interlingua, i.e., an abstract language-independent representation. The target language is then generated from the interlingua. Within the rule-based machine translation paradigm, the interlingual approach is an alternative to the direct approach and the transfer approach. In the direct approach, words are translated directly without passing through an additional representation. In the transfer approach the source language is transformed into an abstract, less language-specific representation. Linguistic rules which are specific to the language pair then transform the source language representation into an abstract target language representation and from this the target sentence is generated. The interlingual approach to machine translation has advantages and disadvantages. The advantages are tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformer (deep Learning Architecture)
The transformer is a deep learning architecture based on the multi-head attention mechanism, in which text is converted to numerical representations called tokens, and each token is converted into a vector via lookup from a word embedding table. At each layer, each token is then contextualized within the scope of the context window with other (unmasked) tokens via a parallel multi-head attention mechanism, allowing the signal for key tokens to be amplified and less important tokens to be diminished. Transformers have the advantage of having no recurrent units, therefore requiring less training time than earlier recurrent neural architectures (RNNs) such as long short-term memory (LSTM). Later variations have been widely adopted for training large language models (LLM) on large (language) datasets. The modern version of the transformer was proposed in the 2017 paper " Attention Is All You Need" by researchers at Google. Transformers were first developed as an improvement ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VentureBeat
''VentureBeat'' is an American technology website headquartered in San Francisco, California. ''VentureBeat'' is a tech news source that publishes news, analysis, long-form features, interviews, and videos. The ''VentureBeat'' company was founded in 2006 by Matt Marshall, an ex-correspondent for ''The Mercury News ''The Mercury News'' (formerly ''San Jose Mercury News'', often locally known as ''The Merc'') is a morning daily newspaper published in San Jose, California, in the San Francisco Bay Area. It is published by the Bay Area News Group, a subsidia ...''. History In March 2009, ''VentureBeat'' signed a partnership agreement with IDG to produce DEMO Conference, a conference for startups to announce their launches and raise funding from venture capitalists and angel investors. The partnership with IDG ended in 2012. In September 2009, Matt Marshall took on the role of executive producer for the DEMO conference. Over the years, a variety of companies have launched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
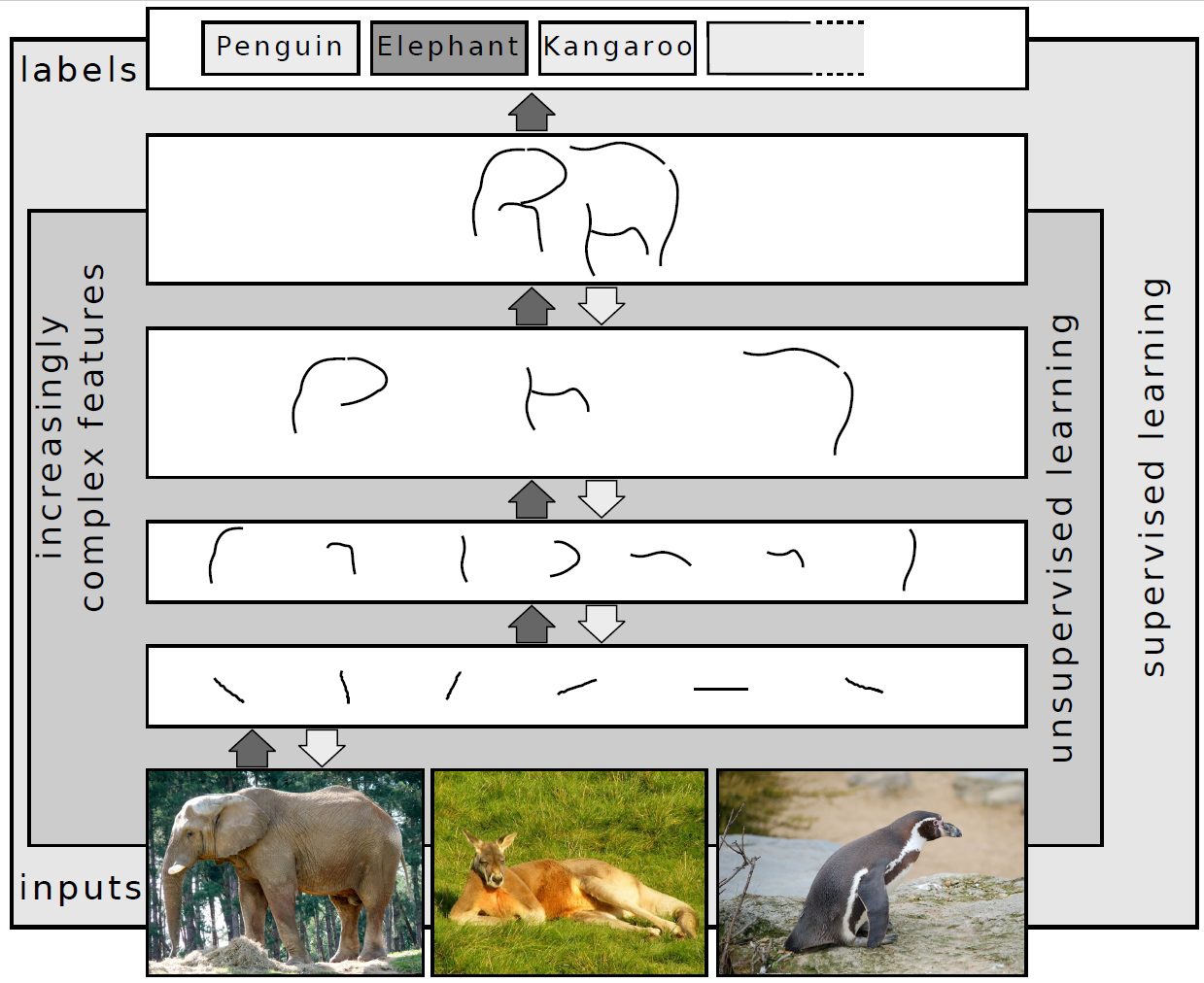
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience and is centered around stacking artificial neurons into layers and "training" them to process data. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers (ranging from three to several hundred or thousands) in the network. Methods used can be either supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Some common deep learning network architectures include fully connected networks, deep belief networks, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks, generative adversarial networks, transformers, and neural radiance fields. These architectures have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug tracking system, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, GitHub, Inc. has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. GitHub reported having over 100 million developers and more than 420 million Repository (version control), repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the world's largest source code host Over five billion developer contributions were made to more than 500 million open source projects in 2024. About Founding The development of the GitHub platform began on October 19, 2005. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPT-J
GPT-J or GPT-J-6B is an open-source large language model (LLM) developed by EleutherAI in 2021. As the name suggests, it is a generative pre-trained transformer model designed to produce human-like text that continues from a prompt. The optional "6B" in the name refers to the fact that it has 6 billion parameters. The model is available on GitHub, but the web interface no longer communicates with the model. Development stopped in 2021. Architecture GPT-J is a GPT-3-like model with 6 billion parameters. Like GPT-3, it is an autoregressive, decoder-only transformer model designed to solve natural language processing (NLP) tasks by predicting how a piece of text will continue. Its architecture differs from GPT-3 in three main ways. * The attention and feedforward neural network were computed in parallel during training, allowing for greater efficiency. * The GPT-J model uses rotary position embeddings, which has been found to be a superior method of injecting positional informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seq2seq
Seq2seq is a family of machine learning approaches used for natural language processing. Applications include language translation, image captioning, conversational models, speech recognition, and text summarization. Seq2seq uses sequence transformation: it turns one sequence into another sequence. History seq2seq is an approach to machine translation (or more generally, Finite-state transducer, sequence transduction) with roots in information theory, where communication is understood as an encode-transmit-decode process, and machine translation can be studied as a special case of communication. This viewpoint was elaborated, for example, in the noisy channel model of machine translation. In practice, seq2seq maps an input sequence into a real-numerical vector by using a neural network (the ''encoder''), and then maps it back to an output sequence using another neural network (the ''decoder''). The idea of encoder-decoder sequence transduction had been developed in the early 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |