|
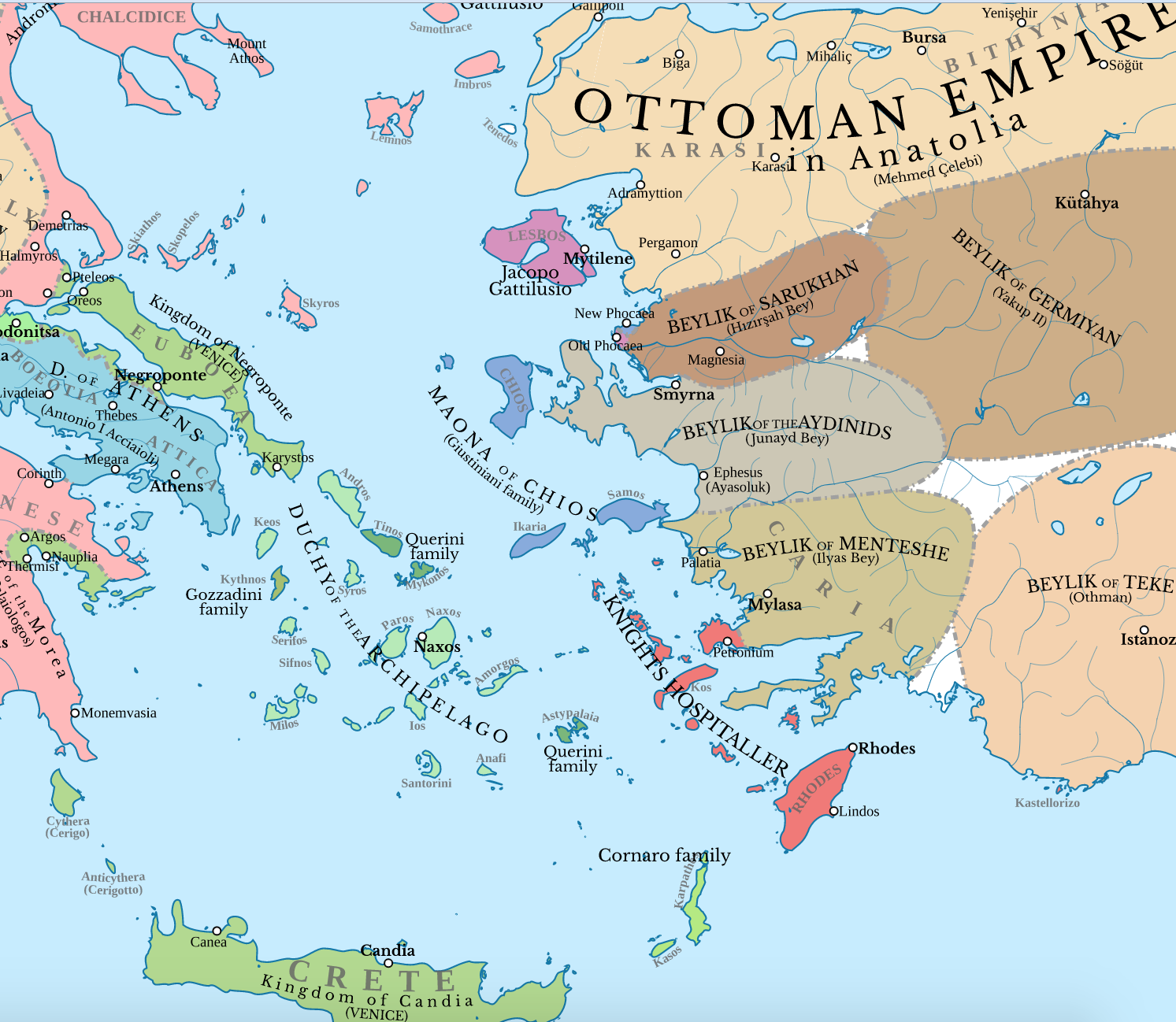
Germiyanids
Germiyan, or the Germiyanids (Old Anatolian Turkish: ; or ), were a dynasty that controlled parts of western Anatolia from to 1429. Germiyan first appeared in 1239 near Malatya tasked with suppressing the Babai revolt. The tribe relocated to western Anatolia with the encroaching Mongol invasions and conquests, Mongol invasion. During the reign of Yakub I of Germiyan, Yakub I (), Germiyan gained sovereignty with the demise of the Sultanate of Rum and forged war with the neighboring Ottoman Empire, Ottomans and the Byzantine Empire, which continued during his successor Mehmed of Germiyan, Mehmed's rule (). Amidst the political tension caused by the neighboring Karamanids, Suleiman of Germiyan, Suleiman () married his daughter Devletşah Hatun to the Ottoman prince and future sultan, Bayezid I (). The process saw a major dowry payment that transferred much of the Germiyanid realm to Ottoman control, including the capital Kütahya. Yakub II () was initially on friendly terms with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devletşah Hatun
Devletşah Sultan Hatun (, "''reign of the Şah''" or "''sovereign of the reign''", - 23 January 1414), was the daughter of Süleyman of Germiyan, Süleyman Şah Bey, the ruler of the Germiyanids. She was a consort of Sultan Bayezid I of the Ottoman Empire. Family Devletşah Hatun was born to an Anatolian prince, Suleiman of Germiyan, Süleyman Şah Bey, the ruler of the Germiyanids. Her mother Mutahhare Abide Hatun was a granddaughter of Mawlānā Jalal al-Din Muhammad Rumi, the founder of the Mevlevi Order, Sufi order of Mevlevis, through his son Sultan Walad. She had three full-brothers, Ilyas Pasha, Hızır Pasha and Qurd Abdal. Marriage In 1378, Süleyman Şah, sent an envoy to sultan Murad I, proposing a marriage between his daughter, Devletşah Hatun and his son Bayezid I, Bayezid. He wished to protect his territory against the invasions of the Karamanids, had proposed this marriage and had offered, as a dowry to his daughter, Kütahya, his seat of power and several other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakub I Of Germiyan
Yakub I (died ) was the founder of the beylik of Germiyan, located in western Anatolia around Kütahya. Although Germiyan revolted against Mesud II (), the Sultan of Rum, Yakub accepted vassalage under Kayqubad III (). The Sultanate of Rum disintegrated shortly after. At that point, Yakub's realm extended as far east as Ankara and incorporated various towns taken from the Byzantine Empire and the Catalan Company. Yakub was the suzerain of many of his neighbors, and his reign was described as economically prosperous by contemporary historians. He was succeeded by his son Mehmed, nicknamed ''Chakhshadan''. Background During the 11th century, much of West Asia was subject to Seljuk rule. A branch of the Seljuk dynasty formed the Sultanate of Rum, a Turkish Muslim state in Anatolia, which saw its height from the late 12th century to 1237. The Germiyan first appeared in 1239 under Kaykhusraw II's rule of the Sultanate of Rum. Muzaffar al-Din, Yakub I's paternal grandfather, was ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed II Of Karaman
Nasiraeddin Mehmed II of Karaman, also Mehmed Beg (), Mehmed Beg II or Nasir al-Din Mehmed Beg (1379 - 1423) was the ''Bey'' ruler of Karaman. His mother was Nefise Hatun, a daughter of Ottoman Sultan Murad I. Karamanids Karamanid was a Turkmen state in central Anatolia after the disintegration of Seljuq Sultanate of Rûm. The capital of Karamanid state was usually Karaman (ancient Larende, renamed by the Karamanids) and sometimes Konya and other cities as well. It was the main rival of the rising Ottoman Empire. The opponents of the Ottoman Turks in Eastern Europe usually sought for alliances with Karamanid to catch Ottomans between two fires. Background While Sultan Bayezid I of the Ottoman Empire was in Rumeli in 1398, Mehmet's father Alaattin Ali raided Ankara, an important Ottoman city. Beyazıt returned to Anatolia, defeated and killed Mehmet's father. Then he laid a siege on Karaman. Mehmet and his brother Bengi Ali surrendered on the condition that the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed Of Germiyan
Mehmed Chakhshadan was Bey of Germiyan from 1340 to 1361. He retook Kula and Angir from the Catalan Company The Catalan Company or the Great Catalan Company (; , , , or ) was a company of mercenaries led by Roger de Flor in the early 14th century and hired by Byzantine Emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos to combat the increasing power of the Anatolian b .... References Bibliography * People from Kütahya History of Kütahya Province Germiyanid monarchs Year of birth unknown Year of death unknown {{Asia-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ankara
The Battle of Ankara or Angora () was fought on 28 July 1402, at the Çubuk plain near Ankara, between the forces of the Ottoman sultan Bayezid I and the emir of the Timurid Empire, Timur. The battle was a major victory for Timur, and it led to the Ottoman Interregnum. Background Timur, a Turco-Mongol from Transoxiana (now Uzbekistan), had built an empire in Central Asia over the years, and became the most powerful ruler in Central Asia since Genghis Khan. He sought to rebuild the once great Mongol Empire. In the 1380s and 1390s, he invaded and conquered parts of Persia (including Azerbaijan and Upper Mesopotamia), ravaged southern Russia and Ukraine (1395–96), and sacked Delhi (1398). Although there had been tensions between the Ottomans and Mongols, nothing would warrant a war, until Bayezid demanded tribute from an emir loyal to Timur, which he understood to be a personal affront and a reason for war. In 1400–01 Timur took Sivas from the Ottomans, parts of Syria from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakub II
Yakub II (died January 1429), also known as Yakub Chelebi, was Bey of Germiyan in western Anatolia from 1387 to 1390, 1402 to 1411, and 1414 until his death. Yakub was the patron of several literary and architectural works produced during his reign. He was initially on friendly terms with the Ottomans, but turned against Sultan Bayezid I () and attempted to reclaim considerable territory, including the former capital Kütahya. He was jailed by Bayezid in 1390, and Germiyan wholly came under Ottoman control. Nine years later, Yakub escaped from prison and sought the protection of Timur (), who, after crushing Bayezid with the help of Yakub at the Battle of Ankara in 1402, restored Germiyan's former boundaries. In 1411, Kütahya fell to Mehmed II of Karaman (), interrupting Yakub's reign a second time. His rule was reinstated by the Ottoman sultan, Mehmed I (), upon the defeat of the Karamanids. Although Yakub initially supported Mustafa Chelebi as a claimant to the Ottoman thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murad II
Murad II (, ; June 1404 – 3 February 1451) was twice the sultan of the Ottoman Empire, from 1421 to 1444 and from 1446 to 1451. Early life Murad was born in June 1404 to Mehmed I, while the identity of his mother is disputed according to various accounts. According to 15th century historian Şükrullah, Murad's mother was a concubine. Hüseyin Hüsâmeddin Yasar, an early 20th century historian, wrote in his work ''Amasya Tarihi'' that his mother was Şahzade Hatun, daughter of Divitdar Ahmed Pasha. According to historians İsmail Hami Danişmend, and Heath W. Lowry, his mother was Emine Hatun, a Dulkadirids, Dulkadirid princess. He spent his early childhood in Amasya. In 1410, Murad came along with his father to the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman capital, Edirne. After his father ascended to the Ottoman throne, he made Murad governor of the Amasya Sanjak. Murad remained at Amasya until the death of Mehmed I in 1421. He was solemnly recognized as sultan of the Ottoman Sultanate at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Külliye
A külliye () is a complex of buildings associated with Turkish architecture centered on a mosque and managed within a single institution, often based on a waqf (charitable foundation) and composed of a madrasa, a Dar al-Shifa (clinic), kitchens, bakery, hammam, other buildings for various charitable services for the community and further annexes. The tradition of külliye is particularly marked in Turkish architecture, starting in Anatolian Seljuk architecture, Seljuq, then especially in Ottoman architecture, Ottoman, and also in Timurid architecture, Timurid architectural legacies., pages 200–205 The word is derived from Turkish , meaning "complete". History The külliye concept is based on the earliest form of the mosque. The mosque was not only used as a house of praying but also as a place for eating, teaching and as a hostel for the poor. The structure of the külliye derived from such concept. Instead of using one mosque for various services, other buildings were built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed I
Mehmed I (; – 26 May 1421), also known as Mehmed Çelebi (, "the noble-born") or ''Kirişçi'' (, "lord's son"), was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1413 to 1421. Son of Sultan Bayezid I and his concubine Devlet Hatun, he fought with his brothers over control of the Ottoman realm in the Ottoman Interregnum (1402–1413). Starting from the province of Rûm he managed to bring first Anatolia and then the European territories (Rumelia) under his control, reuniting the Ottoman state by 1413, and ruling it until his death in 1421. Called "The Restorer," he reestablished central authority in Anatolia, and he expanded the Ottoman presence in Europe by the conquest of Wallachia in 1415. Venice destroyed his fleet off Gallipoli in 1416 as the Ottomans lost a naval war. Early life Mehmed was born in 1386 or 1387 as the fourth son of Sultan Bayezid I () and one of his consorts, the slave girl Devlet Hatun. Following Ottoman custom, when he reached adolescence in 1399, he was sent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Türbe
''Türbe'' refers to a Muslim mausoleum, tomb or grave often in the Turkish-speaking areas and for the mausolea of Ottoman sultans, nobles and notables. A typical türbe is located in the grounds of a mosque or complex, often endowed by the deceased. However, some are more closely integrated into surrounding buildings. Many are relatively small buildings, often domed and hexagonal or octagonal in shape, containing a single chamber. More minor türbes are usually kept closed although the interior can be sometimes be glimpsed through metal grilles over the windows or door. The exterior is typically masonry, perhaps with tiled decoration over the doorway, but the interior often contains large areas of painted tilework, which may be of the highest quality. Inside, the body or bodies repose in plain sarcophagi, perhaps with a simple inscription, which are, or were originally, covered by rich cloth drapes. Usually these sarcophagi are symbolic, and the actual body lies below t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaret
Imaret, sometimes also known as a ''darüzziyafe'', is one of several names used to identify the public soup kitchens built throughout the Ottoman Empire from the 14th to the 19th centuries. These public kitchens were often part of a larger complex known as a ''külliye'', which could include hospices, mosques, caravanserais, and colleges. The imarets provided food that was free of charge to specific groups of people and unfortunate individuals. Imarets were not invented by the Ottomans but developed under their rule as highly structured groups of buildings. Etymology The Turkish word comes from Arabic , which signified "habitation and cultivation" or "the act of building, making habitable". The shift in the word's meaning to denote a religious complex or public kitchen appears to be unique to the Ottoman context. History According to historian Amy Singer, the ''imaret'' is an institution that is "perhaps unique to the Ottomans in its proliferation and purpose." It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masjid
A mosque ( ), also called a masjid ( ), is a place of worship for Muslims. The term usually refers to a covered building, but can be any place where Islamic prayers are performed; such as an outdoor courtyard. Originally, mosques were simple places of prayer for the early Muslims, and may have been open spaces rather than elaborate buildings. In the first stage of Islamic architecture (650–750 CE), early mosques comprised open and closed covered spaces enclosed by walls, often with minarets, from which the Islamic call to prayer was issued on a daily basis. It is typical of mosque buildings to have a special ornamental niche (a ''mihrab'') set into the wall in the direction of the city of Mecca (the ''qibla''), which Muslims must face during prayer, as well as a facility for ritual cleansing (''wudu''). The pulpit (''minbar''), from which public sermons (''khutbah'') are delivered on the event of Friday prayer, was, in earlier times, characteristic of the central city mosque, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |