|
Gerardo Turcatti
Gerardo Turcatti (born 1959 in Montevideo, Uruguay) is a Swiss-Uruguayan chemist who specialises in chemical biology and drug discovery. He is a professor at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) and director of the Biomolecular Screening Facility at the School of Life Sciences there. Career Turcatti studied chemistry at the University of the Republic in Uruguay. In 1981, he moved to Switzerland to earn a Master's degree in chemical engineering from the University of Geneva. Discovering the world of life sciences while working at the biotech company Biogen during his studies, he pursued a career as a chemical biologist. While working at the Glaxo Biomedical Research Institute in Geneva, he studied under Professor Horst Vogel at EPFL for an industry PhD thesis in chemistry and biochemistry titled "Novel fluorescence-based approaches to probe ligand recognition and structure of the tachykinin NK2 receptor". His thesis earned him the EPFL Doctorate Award in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montevideo
Montevideo () is the capital and largest city of Uruguay. According to the 2011 census, the city proper has a population of 1,319,108 (about one-third of the country's total population) in an area of . Montevideo is situated on the southern coast of the country, on the northeastern bank of the Río de la Plata. The city was established in 1724 by a Spanish soldier, Bruno Mauricio de Zabala, as a strategic move amidst the Spanish- Portuguese dispute over the platine region. It was also under brief British rule in 1807, but eventually the city was retaken by Spanish criollos who defeated the British invasions of the River Plate. Montevideo is the seat of the administrative headquarters of Mercosur and ALADI, Latin America's leading trade blocs, a position that entailed comparisons to the role of Brussels in Europe. The 2019 Mercer's report on quality of life, rated Montevideo first in Latin America, a rank the city has consistently held since 2005. , Montevideo was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Biology
Chemical biology is a scientific discipline spanning the fields of chemistry and biology. The discipline involves the application of chemical techniques, analysis, and often small molecules produced through synthetic chemistry, to the study and manipulation of biological systems. In contrast to biochemistry, which involves the study of the chemistry of biomolecules and regulation of biochemical pathways within and between cells, chemical biology deals with chemistry ''applied to'' biology (synthesis of biomolecules, the simulation of biological systems, etc.). Introduction Some forms of chemical biology attempt to answer biological questions by studying biological systems at the chemical level. In contrast to research using biochemistry, genetics, or molecular biology, where mutagenesis can provide a new version of the organism, cell, or biomolecule of interest, chemical biology probes systems '' in vitro'' and '' in vivo'' with small molecules that have been designed for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massively Parallel Amplification , a blog about MMOs
{{disambiguation ...
Massively may refer to: *Mass *Massively (blog) ''Joystiq'' was a video gaming blog founded in June 2004 as part of the Weblogs, Inc. family of weblogs, now owned by AOL. It was AOL's primary video game blog, with sister blogs dealing with MMORPG gaming in general and the popular MMORPG ''World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss National Science Foundation
The Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF, German: ''Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung'', SNF; French: ''Fonds national suisse de la recherche scientifique'', FNS; Italian: ''Fondo nazionale svizzero per la ricerca scientifica'') is a science research support organisation mandated by the Swiss Federal Government. The Swiss National Science Foundation was established under private law by physicist and medical doctor Alexander von Muralt in 1952. Organisation The SNSF consists of three main bodies: Foundation Council, National Research Council and Administrative Offices. The Foundation Council is the highest authority and makes strategic decisions. The National Research Council is composed of distinguished researchers who mostly work at Swiss institutions of higher education. They assess research proposals submitted to the SNSF and make funding decisions. The National Research Council comprises up to 100 members and is subdivided in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
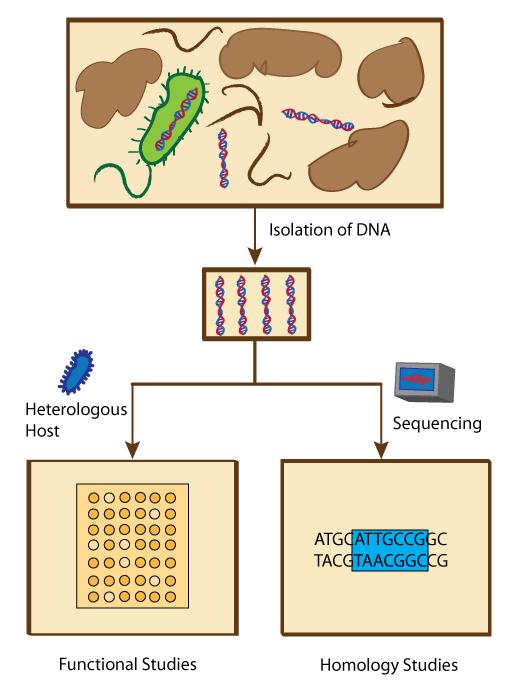
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manteia Predictive Medicine
Manteia Predictive Medicine S.A. (initially incorporated under the name "GenInEx S.A.") was a start-up company created in November 2000 as a spin-off of Serono, a Swiss-based biotechnology company, now part of Merck-Serono, by private founders. Its aim was to provide preventive and curative treatment guidelines for common and complex diseases. These guidelines were envisaged as composed of two parts: * a "personal genome card" containing the entire genome sequence of the person holding the card * an Internet link to a treatment database to be referenced by doctors The company was basing its strategy on the development of so-called "DNA colony sequencing" technology (now commercialized by Illumina), its proprietary massive parallel sequencing technology whose development had been initiated in late 1996 at Glaxo-Welcome's Geneva Biomedical Research Institute (GBRI), by Pascal Mayer and Laurent Farinelli. This work has been protected by several patents and patents applications, publica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serono
Serono was a biotechnology company (law), company headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. It was acquired by the German pharmaceutical company Merck Group, Merck in 2006. The company was founded as the Serono Pharmacological Institute by Cesare Serono in 1906 in Rome, Italy. A key step in its development was the discovery of a method of extracting urinary gonadotropins by Dr. Piero Donini. Serono was incorporated in 1987 and the holding company, Ares-Serono S.A., changed its name to Serono S.A. in May 2000. Serono develops and markets pharmaceuticals in the fields of reproductive health, multiple sclerosis, growth & metabolism and dermatology. The eight biotechnology products are available in four core therapeutic areas: neurology for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis, reproductive health for treatments of infertility, dermatology, where Serono has launched biologics in Europe for moderate-to-severe psoriasis, and growth and metabolism for treatments for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) license. Ligands can bind either to extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site within transmembrane helices (Rhodopsin-like family). They are all activated by agonists although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor can also be observed. G protein-coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horst Vogel
Horst may refer to: Science * Horst (geology), a raised fault block bounded by normal faults or graben People * Horst (given name) * Horst (surname) * ter Horst, Dutch surname * van der Horst, Dutch surname Places Settlements Germany * Horst, Steinburg, a municipality in the district of Steinburg in Schleswig-Holstein * Horst, Lauenburg, a municipality in the district of Lauenburg in Schleswig-Holstein * Horst, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, a village and district in the municipality of Sundhagen, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern * , a district in the city of Gelsenkirchen, North Rhine-Westphalia * , a town in the municipality of Seevetal, Lower Saxony Netherlands * Horst aan de Maas, a municipality in the province of Limburg ** Horst, Limburg, the municipal seat of Horst aan de Maas * , a hamlet in the municipality of Ermelo, Gelderland * , a village in the municipality of Gilze en Rijen, North Brabant * Schothorst, , and , districts in the city and municipality of Amersfoort, Utrecht Poland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GlaxoSmithKline
GSK plc, formerly GlaxoSmithKline plc, is a British Multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with global headquarters in London, England. Established in 2000 by a Mergers and acquisitions, merger of Glaxo Wellcome and SmithKline Beecham. GSK is the tenth largest pharmaceutical company and #294 on the 2022 Fortune Global 500, ''Fortune'' Global 500, ranked behind other pharmaceutical companies China Resources, Sinopharm (company), Sinopharm, Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, Roche, AbbVie, Novartis, Bayer, and Merck Group, Merck. The company has a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. , it had a market capitalisation of £70 billion, the eighth largest on the London Stock Exchange. It has a secondary listing on the New York Stock Exchange. The company developed the first malaria vaccine, RTS,S, which it said in 2014 it would make available for five percent above cost. Legacy products develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biogen
Biogen Inc. is an American multinational biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, specializing in the discovery, development, and delivery of therapies for the treatment of neurological diseases to patients worldwide. History Biogen was founded in 1978 in Geneva as ''Biotechnology Geneva'' by several prominent biologists, including Kenneth Murray from the University of Edinburgh, Phillip Allen Sharp from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Walter Gilbert from Harvard University (Gilbert served as CEO during the start-up phase of Biogen), Heinz Schaller from the University of Heidelberg, and Charles Weissmann from the University of Zurich (Weissmann contributed the first product interferon alpha).Werner Grundlehner''Zürcher Antikörper gegen Alzheimer hat Milliardenpotenzial – und Gegenwind.''Neue Zürcher Zeitung, June 8, 2021. Retrieved June 8, 2021. Gilbert and Sharp were subsequently honored with Nobel Prizes: Gilbert was recognized in 1980 wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |