|
Geodetic Facility For The Advancement Of Geoscience (GAGE)
The U.S. National Science Foundation's Geodetic Facility for the Advancement of Geoscience (NSF GAGE) is a geophysical facility for geoscience research and education. It focuses on research of Earth's surface deformation with enhanced temporal and spatial resolution—the field of geodesy. GAGE is one of the two premier geophysical facilities in support of geoscience and geoscience education of the National Science Foundation (NSF). The other geophysical facility is the Seismological Facility for the Advancement of Geoscience. It operates and maintains the Network of the Americas (NOTA), supports researchers with access to instrumentation (including polar research projects such as POLENET), archives data, and provides education and workforce development resources. It is operated by EarthScope Consortium. The previous operator was UNAVCO, until its merger with the Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology (IRIS) to become EarthScope Consortium. Network of the Americas (N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and Physical property, properties of Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists conduct investigations across a wide range of scientific disciplines. The term ''geophysics'' classically refers to solid earth applications: Earth's figure of the Earth, shape; its gravitational, Earth's magnetic field, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic fields; its structure of the Earth, internal structure and Earth#Chemical composition, composition; its geodynamics, dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; geophysical fluid dynamics, fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; atmospheric electricity, electricity and magnetism in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
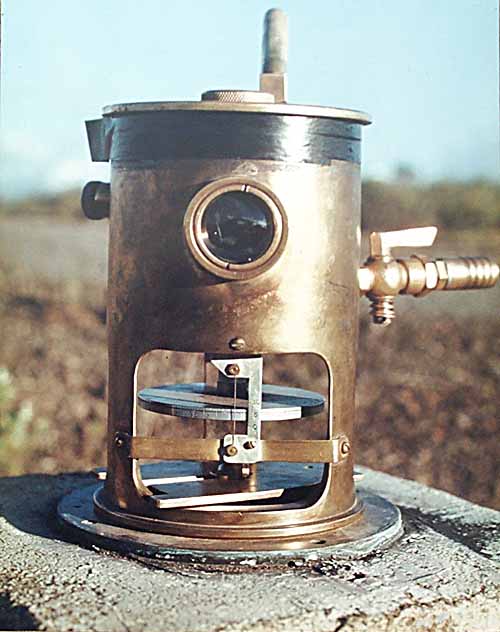
Tiltmeter
A tiltmeter is a sensitive inclinometer designed to measure very small changes from the vertical level, either on the ground or in structures. Tiltmeters are used extensively for monitoring volcanoes, the response of dams to filling, the small movements of potential landslides, the orientation and volume of Hydraulic fracturing, hydraulic fractures, and the response of structures to various influences such as loading and foundation settlement. Tiltmeters may be purely mechanical or incorporate vibrating-wire or electrolytic sensors for electronic measurement. A sensitive instrument can detect changes of as little as one Minute of arc, arc second. Tiltmeters have a long, diverse history, somewhat parallel to the history of the seismometer. The very first tiltmeter was a long-length stationary pendulum. These were used in the very first large concrete dams, and are still in use today, augmented with newer technology such as laser reflectors. Although they had been used for other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Terrestrial Reference System And Frame
The International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS) describes procedures for creating reference frames suitable for use with measurements on or near the Earth's surface. This is done in much the same way that a physical standard might be described as a set of procedures for creating a ''realization'' of that standard. The ITRS defines a geocentric system of coordinates using the SI system of measurement. An International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF) is a realization of the ITRS. Its origin is at the center of mass of the whole earth including the oceans and atmosphere. New ITRF solutions are produced every few years, using the latest mathematical and surveying techniques to attempt to realize the ITRS as precisely as possible. Due to experimental error, any given ITRF will differ very slightly from any other realization of the ITRF. The difference between the latest as of 2006 WGS 84 (frame realisation G1150) and the latest ITRF2000 is only a few centimeters and RMS d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Association Of Geodesy
The International Association of Geodesy (IAG) is a constituent association of the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics focusing on the science which measures and describes the Figure of the Earth, Earth's shape, its rotation and gravity field. History The precursors to the IAG were arc measurement campaigns. The IAG was founded in 1862 as the ''Mitteleuropäische Gradmessung'' (Central European Arc Measurement), later became the ''Europäische Gradmessung'' (European Arc Measurement) in 1867, the ''Internationale Erdmessung'' (''Association Geodésique Internationale'' in French and "International Geodetic Association" in English) in 1886, and took its present name in 1946. In the second half of the 19th century, the creation of the International Geodetic Association marked, following Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel and Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve examples, the systematic adoption of more rigorous methods among them the application of the least squares in geodesy. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundary, maritime boundaries with the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Caribbean Sea to the southeast, and the Gulf of Mexico to the east. Mexico covers 1,972,550 km2 (761,610 sq mi), and is the List of countries by area, thirteenth-largest country in the world by land area. With a population exceeding 130 million, Mexico is the List of countries by population, tenth-most populous country in the world and is home to the Hispanophone#Countries, largest number of native Spanish speakers. Mexico City is the capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city, which ranks among the List of cities by population, most populous metropolitan areas in the world. Human presence in Mexico dates back to at least 8,000 BC. Mesoamerica, considered a cradle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TLALOCNet
The Trans-boundary, Land, and Atmosphere Long-term Observational and Collaborative Network (TLALOCNet) is a network of continuous Global Positioning System (GPS) and meteorology stations in Mexico to study atmospheric and solid earth processes. This completed network spans most of Mexico with a strong coverage emphasis on southern and western Mexico. The network created a collection of continuous GPS meteorology or cGPS/Met sites based on the EarthScope Plate Boundary Observatory standards for the study of atmospheric and geological processes.TLALOCNet continuous GPS-Met Array in Mexico supporting the 2017 NAM GPS Hydrometeorological Network. - NASA/ADS (harvard.edu) The network's name is play with the name of an Aztec deity, Tlaloc, the god of rain. Discharge rain, hail and lightning over the earth were associated with this character in ancient Mexico. As the network has pointed in a presentation concerning the capabilities of scientific measurements and forecasts for rain, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the United States under the designation of Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth. Located about southeast of Miami, Miami, Florida between the Dominican Republic in the Greater Antilles and the United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands in the Lesser Antilles, it consists of the eponymous main island and numerous smaller islands, including Vieques, Puerto Rico, Vieques, Culebra, Puerto Rico, Culebra, and Isla de Mona, Mona. With approximately 3.2 million Puerto Ricans, residents, it is divided into Municipalities of Puerto Rico, 78 municipalities, of which the most populous is the Capital city, capital municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico, San Juan, followed by those within the San Juan–Bayamón–Caguas metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contiguous United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The term excludes the only two non- contiguous states and the last two to be admitted to the Union, which are Alaska and Hawaii, and all other offshore insular areas, such as the U.S. territories of American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. The colloquial term ''Lower48'' is also used, especially in relation to Alaska. The term The Mainland is used in Hawaii. The related but distinct term ''continental United States'' includes Alaska, which is also on North America, but separated from the 48 states by British Columbia in Canada, but excludes Hawaii and all the insular areas in the Caribbean and the Pacific. The greatest distance on a great-circle route entirely within the contiguous U.S. i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the northernmost, westernmost, and easternmost (the Aleutian Islands cross the 180th meridian into the eastern hemisphere) state in the United States. It borders the Canadian territory of Yukon and the province of British Columbia to the east. It shares a western maritime border, in the Bering Strait, with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean lie to the north, and the Pacific Ocean lies to the south. Technically, it is a semi-exclave of the U.S., and is the largest exclave in the world. Alaska is the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the following three largest states of Texas, California, and Montana combined, and is the seventh-largest subnational division i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Boundary Observatory
The Plate Boundary Observatory (PBO) was the geodetic component of the EarthScope Facility. EarthScope was an Earth science program that explored the 4-dimensional structure of the North American Continent. EarthScope (and PBO) was a 15-year project (2003-2018) funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF) in conjunction with NASA. PBO construction (an NSF MREFC) took place from October 2003 through September 2008. Phase 1 of operations and maintenance concluded in September 2013. Phase 2 of operations ended in September 2018, along with the end of the EarthScope project. In October 2018, PBO was assimilated into a broader Network of the Americas (NOTA), along with networks in Mexico ( TLALOCNet) and the Caribbean ( COCONet), as part of the NSF's Geodetic Facility for the Advancement of Geosciences (GAGE). GAGE is operated by EarthScope Consortium. PBO precisely measured Earth deformation resulting from the constant motion of the Pacific and North American tectonic plates in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |