|
Genesi Pegasos
Pegasos is a discontinued brand of computer systems produced by Genesi USA, Inc., and designed by their research and design partner bplan GmbH based in Frankfurt, Germany. It is a MicroATX motherboard powered by a PowerPC 750CXe or PowerPC 7447 microprocessor, featuring three PCI slots, one AGP slot, two Ethernet ports (10/100/1000 & 10/100), USB, DDR, AC'97 sound, and FireWire. Like the PowerPC Macintosh counterparts, it boots via Open Firmware. For hard disk drive booting the Open Firmware implementation called SmartFirmware requires an RDB boot partition that contains either an affs1 or ext2 partition. Note that any changes to the ext2 on-disc format may prevent booting. It is, however, possible to add some ext3 features so long as the volume can still be recognized as ext2. There are two versions of the system: The Pegasos I, followed by the Pegasos II. The Pegasos II was discontinued in 2006. Pegasos I The Pegasos I supports the IBM Microprocessor 750CXe CPU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pegasos 1
Pegasos may refer to: * Pegasus, a winged horse in Greek mythology * Genesi Pegasos Pegasos is a discontinued brand of computer systems produced by Genesi USA, Inc., and designed by their research and design partner bplan GmbH based in Frankfurt, Germany. It is a MicroATX motherboard powered by a PowerPC 750CXe or PowerPC ..., a brand of computer systems produced by Genesi * Pegasos Swiss Association, a nonprofit group supporting assisted suicide See also * Pegasus (other) {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Firmware
Open Firmware is a standard defining the interfaces of a computer firmware system, formerly endorsed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). It originated at Sun Microsystems where it was known as OpenBoot, and has been used by multiple vendors including Sun Microsystems, Sun, Apple Inc., Apple, IBM and Arm Holdings, ARM. Open Firmware allows a system to load platform (computing), platform-independent device driver, drivers directly from a PCI device, improving compatibility. Open Firmware may be accessed through its command line interface, which uses the Forth programming language. History Open Firmware was described by Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, IEEE standard as ''IEEE 1275-1994''. This standard was not reaffirmed by the Open Firmware Working Group (OFWG) since 1998, and was therefore officially withdrawn by IEEE in May 2005. Features Open Firmware defines a standard way to describe the hardware configuration of a syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATI (brand)
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California and maintains significant operations in Austin, Texas. AMD is a hardware and fabless company that designs and develops central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), system-on-chip (SoC), and high-performance computer solutions. AMD serves a wide range of business and consumer markets, including gaming, data centers, artificial intelligence (AI), and embedded systems. AMD's main products include microprocessors, motherboard chipsets, embedded processors, and graphics processors for servers, workstations, personal computers, and embedded system applications. The company has also expanded into new markets, such as the data center, gaming, and high-performance computing markets. AMD's processors are used in a wide range of computing devices, including personal computers, se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restriction Of Hazardous Substances Directive
The Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive 2002/95/EC (RoHS 1), short for Directive on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, was adopted in February 2003 by the European Union. The initiative was to limit the amount of hazardous chemicals in electronics. The RoHS 1 directive took effect on 1 July 2006, and is required to be enforced and became a law in each member state. This directive restricts (with exceptions) the use of ten hazardous materials in the manufacture of various types of electronic and electrical equipment. In addition to the exceptions, there are exclusions for products such as solar panels. It is closely linked with the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE) 2002/96/EC (now superseded) which sets collection, recycling and recovery targets for electrical goods and is part of a legislative initiative to solve the problem of huge amounts of toxic electronic waste. In s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pegasos 2 01
Pegasos may refer to: * Pegasus, a winged horse in Greek mythology * Genesi Pegasos, a brand of computer systems produced by Genesi * Pegasos Swiss Association Pegasos Swiss Association or Pegasos is a non-profit group based in Basel, Switzerland with a minimal-bureaucracy approach to assisted suicide. They also used to have an office in Melbourne, Australia, which is now closed. In Greek mythology, P ..., a nonprofit group supporting assisted suicide See also * Pegasus (other) {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northbridge (computing)
In computing, a northbridge (also host bridge, or memory controller hub) is a microchip that comprises the core logic chipset architecture on motherboards to handle high-performance tasks, especially for older personal computers. It is connected directly to a CPU via the front-side bus (FSB), and is usually used in conjunction with a slower southbridge to manage communication between the CPU and other parts of the motherboard. Historically, separation of functions between CPU, northbridge, and southbridge chips was necessary due to the difficulty of integrating all components onto a single chip die. However, as CPU speeds increased over time, a bottleneck emerged due to limitations caused by data transmission between the CPU and its support chipset. The trend for integrated northbridges began near the end of the 2000s for example, the Nvidia GeForce 320M GPU in the 2010 MacBook Air was a northbridge/southbridge/GPU combo chip. On older Intel based PCs, the northbridge was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cache Coherency
In computer architecture, cache coherence is the uniformity of shared resource data that is stored in multiple local caches. In a cache coherent system, if multiple clients have a cached copy of the same region of a shared memory resource, all copies are the same. Without cache coherence, a change made to the region by one client may not be seen by others, and errors can result when the data used by different clients is mismatched. A cache coherence protocol is used to maintain cache coherency. The two main types are snooping and directory-based protocols. Cache coherence is of particular relevance in multiprocessing systems, where each CPU may have its own local cache of a shared memory resource. Overview In a shared memory multiprocessor system with a separate cache memory for each processor, it is possible to have many copies of shared data: one copy in the main memory and one in the local cache of each processor that requested it. When one of the copies of data is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
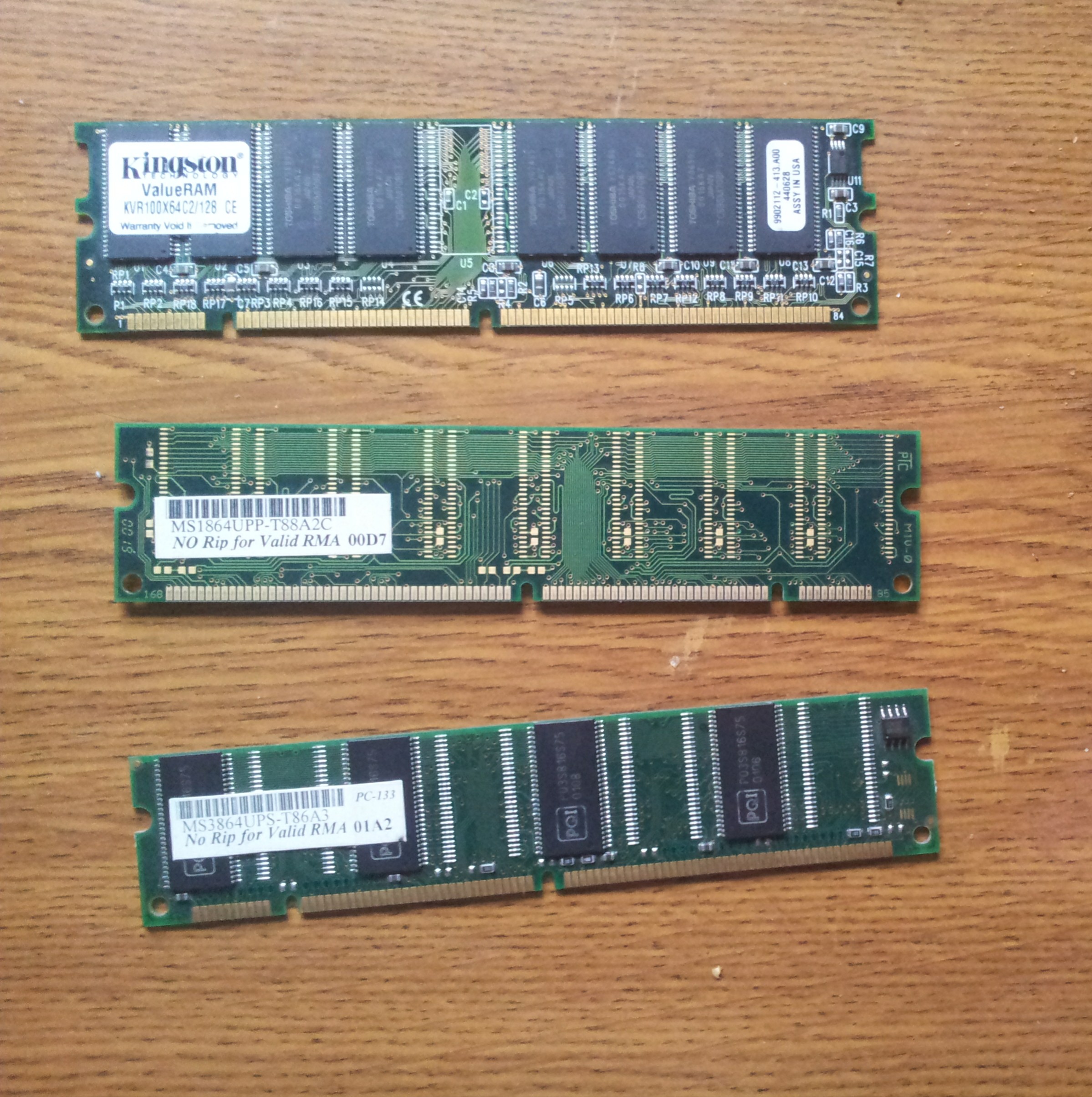
SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to the early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions delayed only by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ext3
ext3, or third extended filesystem, is a journaling file system, journaled file system that is commonly used with the Linux kernel. It used to be the default file system for many popular Linux distributions but generally has been supplanted by its successor version ext4. The main advantage of ext3 over its predecessor, ext2, is journaling file system, journaling, which improves reliability and eliminates the need to check the file system after an unclean or improper Shutdown (computing), shutdown. History Stephen Tweedie first revealed that he was working on extending ext2 in ''Journaling the Linux ext2fs Filesystem'' in a 1998 paper, and later in a February 1999 kernel mailing list posting. The filesystem was merged with the mainline Linux kernel in November 2001 from 2.4.15 onward. Advantages The speed performance of ext3 is less attractive than competing Linux filesystems, such as ext4, JFS (file system), JFS, ReiserFS, and XFS, but ext3 has a significant advantage in tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ext2
ext2, or second extended file system, is a file system for the Linux kernel (operating system), kernel. It was initially designed by French software developer Rémy Card as a replacement for the extended file system (ext). Having been designed according to the same principles as the Berkeley Fast File System from Berkeley Software Distribution, BSD, it was the first commercial-grade filesystem for Linux. The canonical implementation of ext2 is the "ext2fs" filesystem driver in the Linux kernel. Other implementations (of varying quality and completeness) exist in GNU Hurd, MINIX 3, some BSD kernels, in MiNT, Haiku (operating system), Haiku and as third-party Microsoft Windows and macOS (via Filesystem_in_Userspace, FUSE) drivers. This driver was deprecated in Linux version 6.9 in favor of the ext4 driver, as the ext4 driver works with ext2 filesystems. ext2 was the default filesystem in several Linux distributions, including Debian and Red Hat Linux, until supplanted by ext3, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amiga Fast File System
The Amiga Fast File System (abbreviated AFFS, or more commonly historically as FFS) is a file system used on the Amiga personal computer from the computer-manufacturer Commodore Int'l.. The previous Amiga filesystem was never given a specific name and known originally simply as "DOS" or ''AmigaDOS''. Upon the release of FFS and for purposes of differentiation, the original filesystem became retrospectively known as Amiga's ''Old File System'', shortened OFS. The former file-system OFS, which was primarily designed for use with floppy disks, had been proving slow to keep up with hard drives of the era. FFS was designed as a full replacement for the original Amiga filesystem. FFS differs from its predecessor mainly in the removal of redundant information. Data blocks contain nothing but data, allowing the filesystem to manage the transfer of large chunks of data directly from the host adapter to the final destination. Characteristics OFS was the predecessor to FFS. Before FFS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |