|
Geminga By Chandra And Spitzer
Geminga is a gamma ray and x-ray pulsar source thought to be a neutron star approximately 250 parsecs (around 800 light-years) from the Sun in the constellation Gemini. Its name, attributed by its discoverer Giovanni Bignami, is both a contraction of ''Gemini gamma-ray source'', and a transcription of the words ''ghè minga'' (), meaning "it's not there" in the Milanese dialect of Lombard. The name was approved by the International Astronomic Union on 4 April 2022. Pulsar The nature of Geminga was quite unknown for 20 years after its discovery by NASA's Second Small Astronomy Satellite (SAS-2). Finally, in March 1991 the ROSAT satellite detected a periodicity of 0.237 seconds in soft x-ray emission. Thus, it is supposed that Geminga is a sort of neutron star: the decaying core of a massive star that exploded as a supernova about 300,000 years ago. It was once thought that this nearby explosion was responsible for the low density of the interste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halo Around Pulsar Geminga
Halo, halos or haloes usually refer to: * Halo (optical phenomenon) * Halo (religious iconography), a ring of light around the image of a head HALO, halo, halos or haloes may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Video games * ''Halo'' (franchise), a video game franchise ** '' Halo: Combat Evolved'', the first game in the series ** Halo Array, fictional megastructures and superweapons in the franchise Film and television * ''Halo'' (1996 film), a drama film made in India * ''Halo'' (2007 cancelled film), a cancelled movie based on ''Halo'' video game franchise * ''Halo'' (TV series), a 2022 TV series based on the ''Halo'' video game franchise * Nickelodeon HALO Awards, annual American television special (2008–2018) Comics * Comics in the ''Halo'' franchise * Halo (DC Comics), a fictional superheroine * the title character of ''The Ballad of Halo Jones'', a science-fiction comic strip Music * Halo Records Bands and musicians * Halo (Christian rock band), an American ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supershell
A superbubble or supershell is a cavity which is hundreds of light years across and is populated with hot (106 K) gas atoms, less dense than the surrounding interstellar medium, blown against that medium and carved out by multiple supernovae and stellar winds. The winds, passage and gravity of newly born stars strip superbubbles of any other dust or gas. The Solar System lies near the center of an old superbubble, known as the Local Bubble, whose boundaries can be traced by a sudden rise in dust extinction of exterior stars at distances greater than a few hundred light years. Formation The most massive stars, with masses ranging from eight to roughly one hundred solar masses and spectral types of O and early B, are usually found in groups called OB associations. Massive O stars have strong stellar winds, and most of these stars explode as supernovae at the end of their lives. The strongest stellar winds release kinetic energy of 1051 ergs (1044 J) over the lifetime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy And Astrophysics
''Astronomy & Astrophysics'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering theoretical, observational, and instrumental astronomy and astrophysics. The journal is run by a Board of Directors representing 27 sponsoring countries plus a representative of the European Southern Observatory. The journal is published by EDP Sciences and the editor-in-chief is . History Origins ''Astronomy and Astrophysics'' (A&A) was created as an answer to the publishing scenario found in Europe in the 1960s. At that time, multiple journals were being published in several countries around the continent. These journals usually had a limited number of subscribers, and published articles in languages other than English, resulting in a small number of citations compared to American and British journals. Starting in 1963, conversations between astronomers from European countries assessed the need for a common astronomical journal. On 8 April 1968, leading astronomers from Belgium, Denmark, Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleiades
The Pleiades (), also known as The Seven Sisters, Messier 45 and other names by different cultures, is an asterism and an open star cluster containing middle-aged, hot B-type stars in the north-west of the constellation Taurus. At a distance of about 444 light years, it is among the nearest star clusters to Earth. It is the nearest Messier object to Earth, and is the most obvious cluster to the naked eye in the night sky. It is also observed to house the reflection nebula NGC 1432, an HII Ionized region. The cluster is dominated by hot blue luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Reflection nebulae around the brightest stars were once thought to be left over material from their formation, but are now considered likely to be an unrelated dust cloud in the interstellar medium through which the stars are currently passing. This dust cloud is estimated to be moving at a speed of approximately 18 km/s relative to the stars in the cluster. Compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arecibo Observatory
The Arecibo Observatory, also known as the National Astronomy and Ionosphere Center (NAIC) and formerly known as the Arecibo Ionosphere Observatory, is an observatory in Barrio Esperanza, Arecibo, Puerto Rico owned by the US National Science Foundation (NSF). The observatory's main instrument was the Arecibo Telescope, a spherical reflector dish built into a natural sinkhole, with a cable-mount steerable receiver and several radar transmitters for emitting signals mounted above the dish. Completed in 1963, it was the world's largest single-aperture telescope for 53 years, surpassed in July 2016 by the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST) in China. Following two breaks in cables supporting the receiver platform in mid-2020, the NSF decommissioned the telescope. A partial collapse of the telescope occurred on December 1, 2020, before controlled demolition could be conducted. In 2022, the NSF announced the telescope will not be rebuilt, with an education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
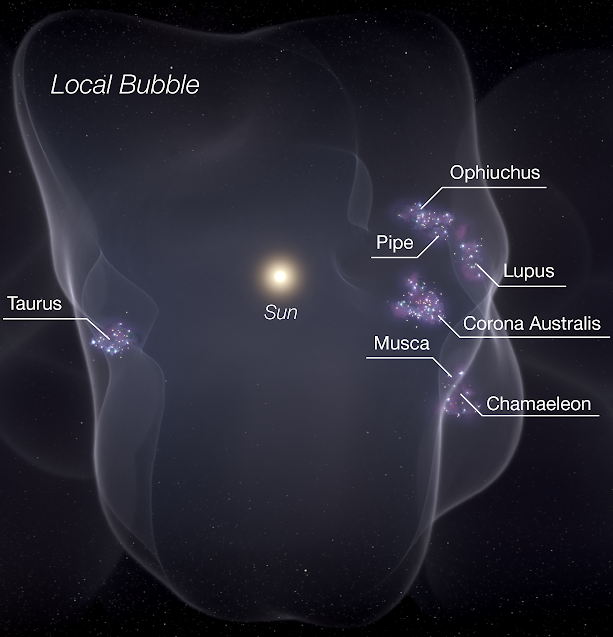
Local Bubble
The Local Bubble, or Local Cavity, is a relative cavity in the interstellar medium (ISM) of the Orion Arm in the Milky Way. It contains the closest of celestial neighbours and among others, the Local Interstellar Cloud (which contains the Solar System), the neighbouring G-Cloud, the Ursa Major Moving Group ( the closest stellar moving group) and the Hyades (the nearest open cluster). It is at least 300 light years across, and is defined by its neutral-hydrogen density of about 0.05 atoms/cm3, or approximately one tenth of the average for the ISM in the Milky Way (0.5 atoms/cm3), and one sixth that of the Local Interstellar Cloud (0.3 atoms/cm3). The exceptionally sparse gas of the Local Bubble is the result of supernovae that exploded within the past ten to twenty million years. Geminga, a pulsar in the constellation Gemini, was once thought to be the remnant of a single supernova that created the Local Bubble, but now multiple supernovae in sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner system planets—Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrestrial planets, being composed primarily of rock and metal. The four giant planets of the outer system a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstellar Medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar space and blends smoothly into the surrounding intergalactic space. The energy that occupies the same volume, in the form of electromagnetic radiation, is the interstellar radiation field. The interstellar medium is composed of multiple phases distinguished by whether matter is ionic, atomic, or molecular, and the temperature and density of the matter. The interstellar medium is composed, primarily, of hydrogen, followed by helium with trace amounts of carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen. The thermal pressures of these phases are in rough equilibrium with one another. Magnetic fields and turbulent motions also provide pressure in the ISM, and are typically more important, dynamically, than the thermal pressure is. In the interstellar medium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Encyclopedia Of Science
David Darling (born 29 July 1953 in Glossop, Derbyshire) is an English astronomer, freelance science writer, and musician. Darling has published numerous popular science works, including ''Life Everywhere: The Maverick Science of Astrobiology'' in 2001 and ''The Universal Book of Mathematics ''The Universal Book of Mathematics: From Abracadabra to Zeno's Paradoxes'' (2004) is a bestselling book by British author David Darling. Summary The book is presented in a dictionary format. The book is divided into headwords, which, as the ti ...'' in 2004. He maintains the online ''Internet Encyclopedia of Science''. A review of Darling's book ''Soul Search'', stated that "he develops a sort of scientific pantheism positing that, with death, we move from the narrow consciousness of our highly selective, reality-filtering brain to the wider, timeless consciousness of the unbound universe." [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. Supernovae are more energetic than novae. In Latin, ''nova'' means "new", referring astronomically to what appears to be a temporary new bright star. Adding the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word ''supernova'' was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1929. The last supernova to be directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Emission Spectroscopy
X-ray emission spectroscopy (XES) is a form of X-ray spectroscopy in which the X-ray line spectra are measured with a spectral resolution sufficient to analyze the impact of the chemical environment on the X-ray line energy and on branching ratios. This is done by exciting electrons out of their shell and then watching the emitted photons of the recombinating electrons. There are several types of XES and can be categorized as non-resonant XES (XES), which includes K_-measurements, valence-to-core (VtC/V2C)-measurements, and (K_)-measurements, or as resonant XES (RXES or RIXS), which includes XXAS+XES 2D-measurement, high-resolution XAS, 2p3d RIXS, and Mössbauer-XES-combined measurements.S. DeBeer''Advanced X-Ray Spectroscopy''(PDF) Juni 2016, last checked 26.02.2020 In addition, ''Soft X-ray emission spectroscopy'' (SXES) is used in determining the electronic structure of materials. History The first XES experiments were published by Lindh and Lundquist in 1924 In these earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |