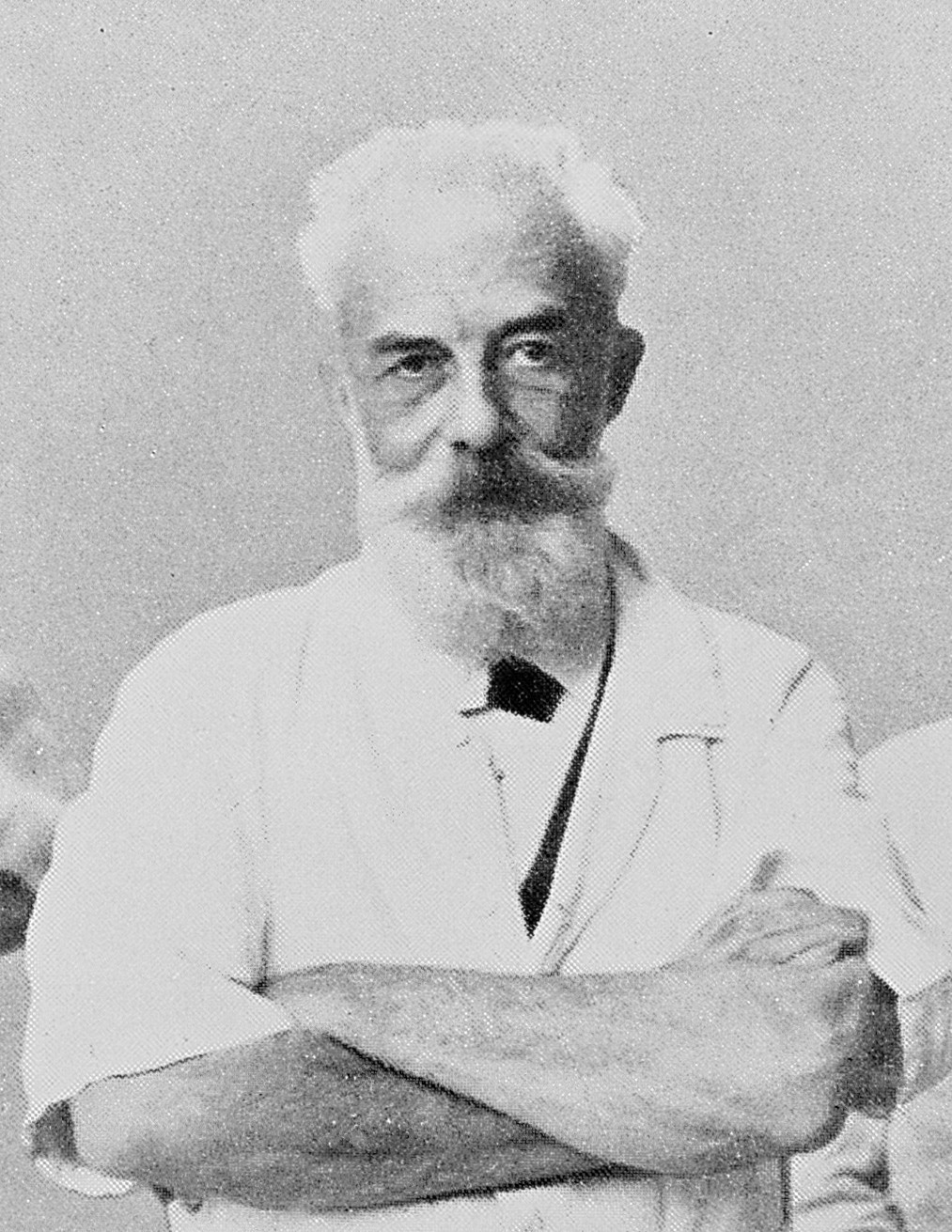|
Gall-bladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and stores it. The bile is then released via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of hemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Lymph Nodes
The hepatic lymph nodes consist of the following groups: * (a) hepatic, on the stem of the hepatic artery, and extending upward along the common bile duct, between the two layers of the lesser omentum, as far as the porta hepatis; the cystic gland, a member of this group, is placed near the neck of the gall-bladder; * (b) subpyloric, four or five in number, in close relation to the bifurcation of the gastroduodenal artery, in the angle between the superior and descending parts of the duodenum; an outlying member of this group is sometimes found above the duodenum on the right gastric (pyloric) artery. The lymph nodes of the hepatic chain receive Afferent lymphatics, afferents from the stomach, duodenum, liver, gall-bladder, and pancreas; their Efferent lymphatics, efferents join the celiac group of preaortic lymph nodes. Cancer prognosis and treatment Hepatic artery lymph nodes are commonly Resection (surgery), resected during a Whipple procedure. In a Whipple procedure, outcom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Duct
The cystic duct is the duct that (typically) joins the gallbladder and the common hepatic duct; the union of the cystic duct and common hepatic duct forms the bile duct (formerly known as the common bile duct). Its length varies. Anatomy The cystic duct typically measures (sources differ) 2–4 cm/2–3 cm in length (though its length has been known to range from 0.5 cm to 9 cm), and 2–3 mm in diameter. It is often tortuous. It is the distal continuation of the neck of the gallbladder, from where it is directed inferoposteriorly and to the left/medially (this occurs in half of individuals). It typically terminates by uniting with the common hepatic duct to form the bile duct (usually anterior to the right hepatic artery). It usually joins the common bile duct from the right lateral side (forming an oblique angle between the two), and at such a distance that the bile duct is twice as long as the common hepatic duct. It often fuses with the common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Hepatic Duct
The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. Structure The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the union of the right hepatic duct (which drains bile from the right functional lobe of the liver) and the left hepatic duct (which drains bile from the left functional lobe of the liver). The duct is about 3 cm long. The common hepatic duct is about 6 mm in diameter in adults, with some variation.Gray's Anatomy, 39th ed, p. 1228 Termination The common hepatic duct typically unites with the cystic duct some 1–2 cm superior to the duodenum and anterior to the right hepatic artery, with the cystic duct approaching the common hepatic duct from the right. Relations The right branch of the hepatic artery proper usually passes posterior to the duct, but may rarely pass anterior to it instead. Histology The inner surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Bile Duct
The common bile duct (also bile duct) is a part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the union of the common hepatic duct and cystic duct. It ends by uniting with the pancreatic duct to form the ampulla of Vater (hepatopancreatic ampulla). Its sphincter the sphincter of Oddi, enables the regulation of bile flow. Anatomy The bile duct is some 6–8 cm long, and normally up to 8 mm in diameter. Its proximal supraduodenal part is situated within the free edge of the lesser omentum. Its middle retroduodenal part is oriented inferiorly and right-ward, and is situated posterior to the first part of the duodenum, and anterior to the inferior vena cava. Its distal paraduodenal part is oriented still more right-ward, is accommodated by a groove upon (sometimes a channel within) the posterior aspect of the head of the pancreas, and is situated anterior to the right renal vein. The bile duct terminates by uniting with the pancreatic duct (at an angle of about 60°) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foregut
The foregut in humans is the anterior part of the alimentary canal, from the distal esophagus to the first half of the duodenum, at the entrance of the bile duct. Beyond the stomach, the foregut is attached to the abdominal walls by mesentery. The foregut arises from the endoderm, developing from the folding primitive gut, and is developmentally distinct from the midgut and hindgut. Although the term “foregut” is typically used in reference to the anterior section of the primitive gut, components of the adult gut can also be described with this designation. Pain in the epigastric region, just below the intersection of the ribs, typically refers to structures in the adult foregut. Adult foregut Components * Esophagus * Respiratory tract (lower respiratory tract) * Stomach * Duodenum (up to ampulla of vater) * Liver * Gallbladder * Pancreas * Spleen – The spleen arises from the mesodermal dorsal mesentery (the foregut arises from the endoderm not mesoderm). But the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin in the blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs (lungs or gills) to the other tissues of the body, where it releases the oxygen to enable aerobic respiration which powers an animal's metabolism. A healthy human has 12to 20grams of hemoglobin in every 100mL of blood. Hemoglobin is a metalloprotein, a chromoprotein, and a globulin. In mammals, hemoglobin makes up about 96% of a red blood cell's dry matter, dry weight (excluding water), and around 35% of the total weight (including water). Hemoglobin has an oxygen-binding capacity of 1.34mL of O2 per gram, which increases the total blood oxygen capacity seventy-fold compared to dissolved oxygen in blood plasma alone. The mammalian hemoglobin molecule can bind and transport up to four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brush Border
A brush border (striated border or brush border membrane) is the microvillus-covered surface of simple cuboidal and simple columnar epithelium found in different parts of the body. Microvilli are approximately 100 nanometers in diameter and their length varies from approximately 100 to 2,000 nanometers. Because individual microvilli are so small and are tightly packed in the brush border, individual microvilli can only be resolved using electron microscopes; with a light microscope they can usually only be seen collectively as a fuzzy fringe at the surface of the epithelium. This fuzzy appearance gave rise to the term brush border, as early anatomists noted that this structure appeared very much like the bristles of a paintbrush. Brush border cells are found mainly in the following organs: * The small intestine tract: This is where absorption takes place. The brush borders of the intestinal lining are the site of terminal carbohydrate digestions. The microvilli that constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columnar Epithelia
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder - Intermed Mag
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and stores it. The bile is then released via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of hemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celiac Lymph Nodes
The celiac lymph nodes are associated with the branches of the celiac artery. Other lymph nodes in the abdomen are associated with the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries. The celiac lymph nodes are grouped into three sets: the gastric, hepatic The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ... and splenic lymph nodes. They receive lymph from the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, spleen, liver, and gall bladder. Additional images File:illu_lymph_chain08.jpg, Lymph nodes of the abdominal cavity References External links Lymphatics of the torso {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Albert Hartmann
Henri Albert Hartmann (16 June 1860 – 1 January 1952) was a French surgeon. He wrote numerous papers on a wide variety of subjects, ranging from war injuries to shoulder dislocations to gastrointestinal cancer. Hartmann is best known for Hartmann's operation, a two-stage colectomy he devised for colon cancer and diverticulitis. Hartmann Day Hartmann Day is the 16 June, each year. "Hartmann Day" celebrates Henri Albert Charles Antoine Hartmann's (born 16 June 1860) invention of the surgical operation that is now known as the "Hartmann Procedure" that has saved many lives. It also celebrates the work of those who have performed the operation, and of those who have supported patients about to have, having, or have had the operation. This celebration was instituted in 2021, marking one hundred years since the publication of the operation. Hartmann Day card In June 2022 a grateful patient sent a Hartmann Day card to the group of Stoma Nurses who had helped the patient. The car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Segments
A liver segment is one of eight segments of the liver as described in the widely used Couinaud classification (named after Claude Couinaud) in the anatomy of the liver. This system divides the lobes of the liver into eight segments based on a transverse plane through the bifurcation of the main portal vein, arranged in a clockwise manner starting from the caudate lobe. Couinaud segments There are four lobes of the liver. The Couinaud classification of liver anatomy then further divides the liver into eight functionally independent segments. Each segment has its own vascular inflow, outflow and biliary drainage. In the centre of each segment there is a branch of the portal vein, hepatic artery and bile duct. In the periphery of each segment there is vascular outflow through the hepatic veins. The division of the liver into independent units means that segments can be resected without damaging the remaining segments. To preserve the viability of the liver following surgery, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |