|
Galindians
Galindians were two distinct, and now extinct, tribes of the Balts. Most commonly, Galindians refers to the Western Galindians who lived in the southeast part of Prussia. Less commonly, it is used for a tribe that lived in the area of what is today Moscow (). Etymology Johannes Voigt (supported by many others) suggested that name is derived from the Baltic word *''galas'' ("the end", probably synonymous to "located farthest", "located near the border of the territory or area"), alluding to the fact that they settled for some time further west and further east than any other Baltic tribe. Polish historian suggested another etymology: the name ''Galind''- may be derived from the hydronym of in the province of Olsztyn, in what was the very center of ancient ''Galindia''. J. Nalepa (1971) suggested the root *''gal''- was originally a different ablaut grade of the same root found in Lithuanian "''gilus''" – deep, and "''gelmė''" – depth. The original meaning referred to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golyad Language
Golyad () or East Galindian (, ) is a poorly attested extinct Baltic language of the Dnieper Balts living in the Protva basin in present-day Russia. The Golyad people are believed to have descended from the Moshchiny culture and are only known ethnonyn for the Dnieper-Oka language. Due to there being no known written documents of the Golyad language, the language is poorly known. The language went extinct in the 12th century due to Early Slavic migration and assimilation. It is believed the vernaculars of the Finno-Ugrians and Volga Finns adopted loanwords from East Galindian. Phonology Based on Baltic substratum and hydronomy in the Protva Basin, the following phonology can be reconstructed: Consonants Vowels Lexicon There are some Russian dialectal words from the Protva Basin region suspected to be of Baltic origin: It is believed that the hydronyms "Lama", " Yauza", "Nudol" and "Churilikha" have Baltic origins. Specifically, the Churilikha's name has orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples (, ) are a group of peoples inhabiting the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea who speak Baltic languages. Among the Baltic peoples are modern-day Lithuanians (including Samogitians) and Latvians (including Latgalians (modern), Latgalians) — all East Balts — as well as the Old Prussians, Curonians, Sudovians, Skalvians, Yotvingians and Galindians — the West Balts — whose languages and cultures are now extinct, but made a large influence on the living branches, especially on literary Lithuanian language. The Balts are descended from a group of Proto-Indo-Europeans, Proto-Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the lower Vistula and southeast shore of the Baltic Sea and upper Daugava and Dnieper rivers, and which over time became differentiated into West and East Balts. In the fifth century CE, parts of the eastern Baltic coast began to be settled by the ancestors of the Western Balts, whereas the East Balts lived in modern-day Belarus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
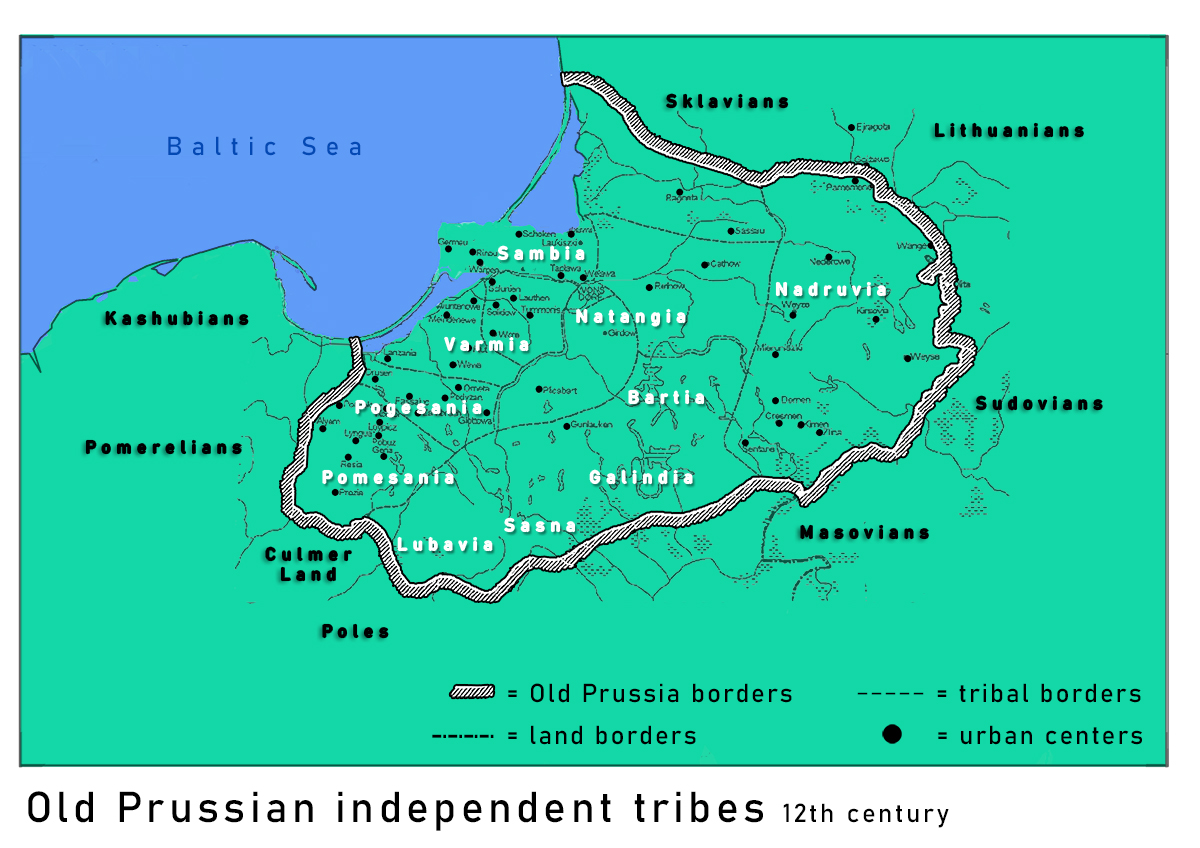
Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians were a Balts, Baltic people that inhabited the Prussia (region), region of Prussia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon to the east. As Balts, they spoke an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language of the Baltic languages, Baltic branch now known as Old Prussian language, Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian Prussian mythology, deities. Their ethnonym was later adopted by predominantly Low German language, Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region. The duchy of the Duchy of Poland (c. 960–1025), Polans under Mieszko I, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the State of the Teuton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshchiny Culture
The Moshchiny culture () was an archaeological culture of the Iron Age from the 4th to the 7th century in present-day western Russia. Distribution area The settlement area was located in the forest areas at the upper Dnieper, Dnepr and the upper Oka River, Oka in today's Russian Oblast Kaluga Oblast, Kaluga, Tula Oblast, Tula, Oryol Oblast, Oryol and Smolensk Oblast, Smolensk. It is named after a settlement near the village '' Moshchiny '' () in the Mosalsky District in the Kaluga Oblast. () Kaluga Oblast. Russia. Genesis The Moshchiny culture emerged in the 4th century from the '':ru:Юхновская культура, Yukhnov culture'', with influences from Zarubintsy c ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Tribes C 1200
Baltic may refer to: Peoples and languages *Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian *Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originating from the Baltic countries *Baltic Germans, historical ethnic German minority in Latvia and Estonia *Baltic Finnic peoples, the Finnic peoples historically inhabiting the area on the northeastern side of the Baltic sea Places Northern Europe * Baltic Sea, in Europe * Baltic region, an ambiguous term referring to the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea * Baltic states (also Baltic countries, Baltic nations, Baltics), a geopolitical term, currently referring to Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania * Baltic Provinces or governorates, former parts of the Swedish Empire and then Russian Empire (in modern Latvia, Estonia) * Baltic Shield, the exposed Precambrian northwest segment of the East European Craton * Baltic Plate, an ancient tectonic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borovsk
Borovsk () is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative center of Borovsky District of Kaluga Oblast, Russia, located on the Protva River just south from the oblast's border with Moscow Oblast. Population: 12,000 (1969). History It is known to have existed since 1356 as a part of the Principality of Ryazan. In the 14th century, it was owned by Vladimir the Bold, but passed to the Grand Duchy of Moscow when his granddaughter Maria of Borovsk married Vasily II of Moscow, Vasily II. In 1444, the St. Paphnutius Monastery was founded near Borovsk. Its strong walls, towers, and a massive cathedral survive from the reign of Boris Godunov. Two famous Old Believers—archpriest Avvakum, Avvakum Petrovich and boyarynya Feodosiya Morozova—were incarcerated at this monastery in the second half of the 17th century. The town was liberated by the Red Army on January 4, 1942. Administrative and municipal status Within the subdivisions of Russia#Administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vereya
Vereya () is the name of several inhabited localities in Russia. ;Urban localities *Vereya, Naro-Fominsky District, Moscow Oblast, a town in Naro-Fominsky District of Moscow Oblast ;Rural localities * Vereya, Orekhovo-Zuyevsky District, Moscow Oblast, a settlement in Vereyskoye Rural Settlement of Orekhovo-Zuyevsky District in Moscow Oblast * Vereya, Ramensky District, Moscow Oblast, a village in Vereyskoye Rural Settlement of Ramensky District in Moscow Oblast * Vereya, Ryazan Oblast, a village in Oskinsky Rural Okrug of Klepikovsky District in Ryazan Oblast * Vereya, Zabaykalsky Krai, a settlement in Priargunsky District of Zabaykalsky Krai Zabaykalsky Krai is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (a krai), located in the Russian Far East. Its administrative center is Chita, Zabaykalsky Krai, Chita. As of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census, the population was ... See also * Verkhnyaya Vereya {{Set index article, populated places in Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozhaysk
MozhayskAlternative transliterations include ''Mozhaisk'', ''Mozhajsk'', ''Mozhaĭsk'', and ''Možajsk''. (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative center of Mozhaysky District, Moscow Oblast, Mozhaysky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located to the west of Moscow, on the historic road leading to Smolensk and then to Poland. Population: History First mentioned in 1231 as an appanage of Principality of Chernigov, Chernigov; A theory says Mozhaysk took its name from the Mozhay (Mozhaya) River, whose name could be of Baltic origin (compare Lithuanian ''mažoji'' "small" - in contrast to the larger Moskva River nearby). Later Mozhaysk became an important stronghold of the Principality of Smolensk, Smolensk dynasty, in the 13th century ruled by Duke (later Saint) Theodore the Black. Muscovite Russia, Muscovites seized Mozhaysk in 1303, but in the course of the following century had serious troubles defending it against Algirdas (Grand Duke of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders of Russia, land borders with fourteen countries. Russia is the List of European countries by population, most populous country in Europe and the List of countries and dependencies by population, ninth-most populous country in the world. It is a Urbanization by sovereign state, highly urbanised country, with sixteen of its urban areas having more than 1 million inhabitants. Moscow, the List of metropolitan areas in Europe, most populous metropolitan area in Europe, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, while Saint Petersburg is its second-largest city and Society and culture in Saint Petersburg, cultural centre. Human settlement on the territory of modern Russia dates back to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protva
The Protva () is a river in the Moscow and Kaluga oblasts in Russia. It is a left tributary of the Oka. It is long, and has a drainage basin of .«Река ПРОТВА» Russian State Water Registry The area of its basin is . The Protva freezes up in early December and stays icebound until early April. Its main tributary is the . The towns of , , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Baltic Languages
The East Baltic languages are a group of languages that along with the extinct West Baltic languages belong to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. The East Baltic branch primarily consists of two extant languages— Latvian and Lithuanian. Occasionally, Latgalian and Samogitian are viewed as distinct languages, though they are traditionally regarded as dialects. It also includes now-extinct Selonian, Semigallian, and possibly Old Curonian. Lithuanian is the most-spoken East Baltic language, with more than 3 million speakers worldwide, followed by Latvian, with 1.75 million native speakers, then Samogitan with 500,000 native speakers, and lastly Latgalian with 150,000 native speakers. History Originally, East Baltic was presumably native to the north of Eastern Europe, which included modern Latvia, Lithuania, northern parts of current European Russia and Belarus. Dnieper Balts lived in the current territory of Moscow, which was the furthest undisput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old East Slavic
Old East Slavic (traditionally also Old Russian) was a language (or a group of dialects) used by the East Slavs from the 7th or 8th century to the 13th or 14th century, until it diverged into the Russian language, Russian and Ruthenian language, Ruthenian languages. Ruthenian eventually evolved into the Belarusian language, Belarusian, Rusyn language, Rusyn, and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian languages. Terminology The term ''Old East Slavic'' is used in reference to the modern family of East Slavic languages. However, it is not universally applied. The language is also traditionally known as ''Old Russian''; however, the term may be viewed as anachronistic, because the initial stages of the language which it denotes predate the dialectal divisions marking the nascent distinction between modern East Slavic languages, therefore a number of authors have proposed using ''Old East Slavic'' (or ''Common East Slavic'') as a more appropriate term. ''Old Russian'' is also used to descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |