|
Galeazzo Maria Sforza
Galeazzo Maria Sforza (24 January 1444 – 26 December 1476) was the fifth Duke of Milan from 1466 until 1476. He was born to Francesco Sforza, a popular condottiero and ally of Cosimo de' Medici who would gain the Duchy of Milan in 1450, and Bianca Maria Visconti. He married into the Gonzaga family; on the death of his first wife Dorotea Gonzaga, he married Bona of Savoy. Life Galeazzo Maria Sforza was born in Fermo, near the family's castle of Girifalco. He was the first son of Francesco Sforza and Bianca Maria Visconti. At the death of his father on 8 March 1466, Sforza was in France heading a military expedition to help King Louis XI against Charles I of Burgundy. Called back home by his mother, Sforza returned to Italy under a false name. The false identity was necessary as he had to pass by the territories of the family's enemy, the Duke of Savoy, who made an unsuccessful attempt on Sforza's life. He entered Milan on 20 March 1466, and was acclaimed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piero Benci
Piero del Pollaiuolo ( , , ; also spelled Pollaiolo; – by 1496), whose birth name was Piero Benci, was an Italian Renaissance painter from Florence. His older brother, by about ten years, was the artist Antonio del Pollaiuolo and the two frequently worked together. Their work shows both classical influences and an interest in human anatomy; according to Vasari, the brothers carried out dissections to improve their knowledge of the subject (though modern scholars tend to doubt this). Giorgio Vasari, who wrote several decades after both brothers were dead, includes a joint biography of Antonio and Piero del Pollaiuolo in his ''Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects''. Vasari says that Antonio was especially highly regarded for his ''disegno'' or drawing, and it may be that on shared works he did most of the underdrawing, leaving Piero and their assistants to complete the painting. Vasari began the tradition of stressing the contribution of Antonio ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condottiero
Condottieri (; singular: ''condottiero'' or ''condottiere'') were Italian military leaders active during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The term originally referred specifically to commanders of mercenary companies, derived from the Italian word ''condotta''—the contract under which they served a Italian city-states, city-state or lord. The word ''condottiero'' thus meant 'contractor'. Over time, however, in Italian usage, ''condottiero'' came to mean any 'commander' or 'military leader'. Mercenary captains Background In the 13th and 14th centuries, the Italian city-states of Republic of Venice, Venice, Republic of Florence, Florence, and republic of Genoa, Genoa were very rich from their trade with the Levant, yet possessed woefully small armies. In the event that foreign powers and envious neighbours attacked, the ruling nobles hired foreign mercenaries to fight for them. The military-service terms and conditions were stipulated in a (contract) between the city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Martini
Johannes Martini (c. 1440 – late 1497 or early 1498) was a Franco-Flemish composer of the Renaissance. Life He was born in Brabant around 1440, but information about his early life is scanty. He probably received his early training in Flanders, as did most of the composers of his generation. Sometime before 1473 he became associated with the ducal chapel in Ferrara, Italy, where Ercole I d'Este was attempting to build a musical establishment on the part of some of the other aristocratic centers in Italy. He was a member of the famous Milan chapel of the Sforza family in July 1474, along with Loyset Compère, Gaspar van Weerbeke, and some of the other composers from northern Europe who were part of the first wave of Franco-Flemish influence in Italy. In November he returned to Ferrara. What prompted him to leave and return is not known, but since the Milanese chapel was then the most renowned in Europe, it is possible he went to investigate the competition for his emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Agricola
Alexander Agricola (; born Alexander Ackerman; – 15 August 1506) was a Netherlandish composer of the Renaissance writing in the Franco-Flemish style. A prominent member of the ''Grande chapelle'', the Habsburg musical establishment, he was a renowned composer in the years around 1500, and his music was widely distributed throughout Europe. He composed music in all of the important sacred and secular styles of the time.Wegman/Fitch, Grove online Life Agricola was the son, born out of wedlock, of Lijsbette Naps, a wealthy female merchant who lived in Ghent. He was probably born sometime in the late 1450s and had a brother named Jan. A commemorative motet first published in 1538 gave his age as 60 at the time of his death in 1506, but that may be due to a medieval convention concerning the number 60. He may have received his musical training from the parish church of St Nicolas in Ghent, as his mother made a substantial donation to its musical establishment in 1467. In 1476 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motet
In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the preeminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to the English musicologist Margaret Bent, "a piece of music in several parts with words" is as precise a definition of the motet as will serve from the 13th to the late 16th century and beyond.Margaret Bent,The Late-Medieval Motet in ''Companion to Medieval & Renaissance Music'', edited by Tess Knighton and David Fallows, 114–19 (Berkeley, California: University of California Press, 1992): 114. . The late 13th-century theorist Johannes de Grocheo believed that the motet was "not to be celebrated in the presence of common people, because they do not notice its subtlety, nor are they delighted in hearing it, but in the presence of the educated and of those who are seeking out subtleties in the arts". Etymology In the early 20th century, it was ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass (music)
The Mass () is a form of sacred musical composition that sets the invariable portions of the Christian Eucharistic liturgy (principally that of the Catholic Church, the Anglican Communion, and Lutheranism), known as the Mass. Most Masses are settings of the liturgy in Latin, the sacred language of the Catholic Church's Roman Rite, but there are a significant number written in the languages of non-Catholic countries where vernacular worship has long been the norm. For example, there have been many Masses written in English for a United States context since the Second Vatican Council, and others (often called "communion services") for the Church of England. Masses can be ''a cappella'', that is, without an independent accompaniment, or they can be accompanied by instrumental '' obbligatos'' up to and including a full orchestra. Many masses, especially later ones, were never intended to be performed during the celebration of an actual mass. History Middle Ages The earliest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Countries
The Low Countries (; ), historically also known as the Netherlands (), is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower Drainage basin, basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting today of the three modern "Benelux" countries: Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands (, which is singular). Geographically and historically, the area can also include parts of France (such as Nord (French department), Nord and Pas-de-Calais) and the Germany, German regions of East Frisia, Geldern, Guelders and Cleves. During the Middle Ages, the Low Countries were divided into numerous semi-independent principalities. Historically, the regions without access to the sea linked themselves politically and economically to those with access to form various unions of ports and hinterland, stretching inland as far as parts of the German Rhineland. Because of this, nowadays not only physically low-altitude areas, but also some hilly or elevated regions are considered part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franco-Flemish School
The designation Franco-Flemish School, also called Netherlandish School, Burgundian School, Low Countries School, Flemish School, Dutch School, or Northern School, refers to the style of polyphonic vocal music composition originating from France and from the Burgundian Netherlands in the 15th and 16th centuries as well as to the composers who wrote it. The spread of their technique, especially after the revolutionary development of printing, produced the first true international style since the unification of Gregorian chant in the 9th century. Franco-Flemish composers mainly wrote sacred music, primarily masses, motets, and hymns. Term and controversy Several generations of Renaissance composers from the region loosely known as the Low Countries (Imperial and French fiefs ruled in personal union by the House of Valois-Burgundy in the period from 1384 to 1482)—i.e. present-day Northern France, Belgium and the Southern Netherlands—are grouped under "Franco-Flemish Sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counts And Dukes Of Savoy
The titles of the count of Savoy, and then duke of Savoy, are titles of nobility attached to the historical territory of Savoy. Since its creation, in the 11th century, the House of Savoy held the county. Several of these rulers ruled as kings at one point in history or another. The County of Savoy was elevated to a Duchy of Savoy, duchy at the beginning of the 15th century, bringing together all the territories of the Savoyard state and having Amadeus VIII, Duke of Savoy, Amadeus VIII as its first duke. In the 18th century, Duke Victor Amadeus II of Sardinia, Victor Amadeus II annexed the Kingdom of Sardinia to the historical possessions of the Duchy, and from then on, the Savoyard dukes also held the title of Kings of Sardinia. The House of Savoy later went on to rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 to 1946 when the monarchy was abolished. Victor Amadeus II was the longest reigning monarch of Savoy, followed by Charles Emmanuel I, Duke of Savoy, Charles Emmanuel I, and Charles I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
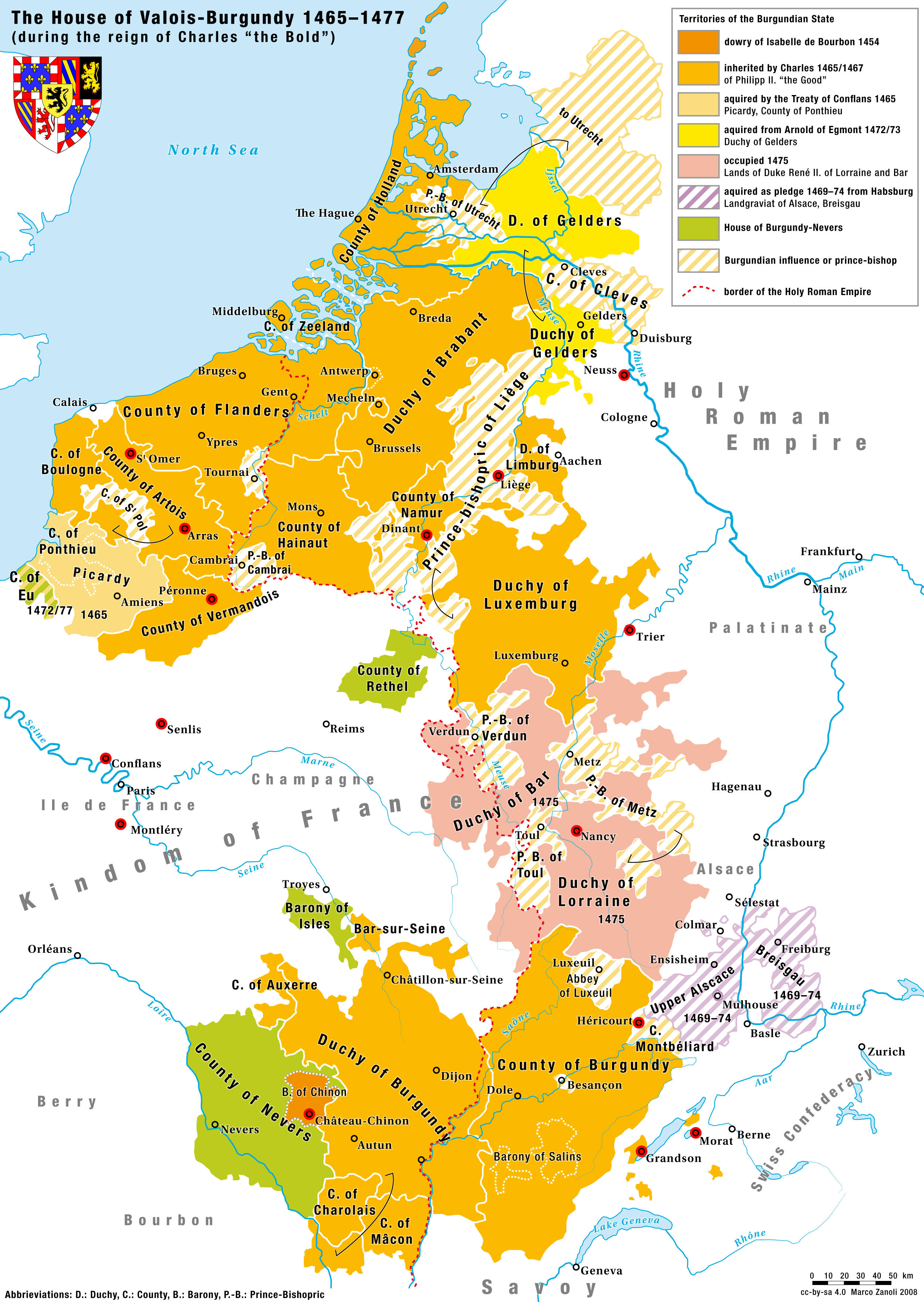
Charles The Bold
Charles Martin (10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), called the Bold, was the last duke of Burgundy from the House of Valois-Burgundy, ruling from 1467 to 1477. He was the only surviving legitimate son of Philip the Good and his third wife, Isabella of Portugal. As heir and as ruler, Charles vied for power and influence with rivals such as his overlord, King Louis XI of France. In 1465 Charles led a successful revolt of Louis's vassals in the War of the Public Weal. After becoming the Duke of Burgundy in 1467, Charles pursued his ambitions for a kingdom, independent from France, that would stretch contiguously from the North Sea in the north to the borders of Savoy in the south. For this purpose, he acquired Guelders and Upper Alsace; sought the title King of the Romans; and gradually became an enemy of the Germans. Charles married Margaret of York for an English alliance. He arranged the betrothal between his sole child, Mary, with Maximilian of Austria. A passiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis XI
Louis XI (3 July 1423 – 30 August 1483), called "Louis the Prudent" (), was King of France from 1461 to 1483. He succeeded his father, Charles VII. Louis entered into open rebellion against his father in a short-lived revolt known as the Praguerie in 1440. The king forgave his rebellious vassals, including Louis, to whom he entrusted the management of the Dauphiné, then a province in southeastern France. Louis's ceaseless intrigues, however, led his father to banish him from court. From the Dauphiné, Louis led his own political establishment and married Charlotte of Savoy, daughter of Louis, Duke of Savoy, against the will of his father. Charles VII sent an army to compel his son to his will, but Louis fled to Burgundy, where he was hosted by Philip the Good, the Duke of Burgundy, Charles's greatest enemy. When Charles VII died in 1461, Louis left the Burgundian court to take possession of his kingdom. His taste for intrigue and his intense diplomatic activity earned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |