|
GSLV F12
The GSLV F12 is the 15th flight of the GSLV and the 9th flight of Mk2 variant using indigenous Cryogenic engine. Launch Launch of GSLV F12 / NVS 01 Mission is Tentatively Scheduled for Monday, 29th May 2023 at 0512 hrs UTC from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Second Launch pad, Sriharikota Andhra Pradesh, India as Per Notam . Mission overview Primary payload: NVS-01 This also marks the 15th time that Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle will be launching the Satellites. This Launch Vehicle is an 3 Stage Launch Vehicle. The first stage of GSLV was also derived from the PSLV's PS1. The 138 tonne solid rocket motor is augmented by 4 liquid strap-ons which is Powered by Vikas (rocket engine) The Vikas (a portmanteau from initials of ''VIK''ram ''A''mbalal ''S''arabhai ) is a family of hypergolic liquid fuelled rocket engines conceptualized and designed by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) in the 1970s. The design was based .... References {{Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of GSLV Launches
This is a list of launches conducted by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) using Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) rockets. This list does not include LVM3 (formerly known as GSLV Mk III) launches, which can be found here. Notable missions GSLV MK. I flight D1 This was the first developmental flight of the GSLV Mk.I featuring Russian cryogenic engine KVD-1. It was used to place an experimental satellite GSAT-1 into the orbit. However, due to sub-optimal performance and lack of fuel the vehicle did not achieve the intended orbit and the satellite had to maneuver itself using onboard fuel to correct the shortfall. ISRO claims the launch to be successful. In a 2014 interview, ISRO Chairman K. Radhakrishnan attributed the failure to incorrect mixture ratio used in the cryogenic upper stage. GSLV MK. II flight D5 This was the second test flight with indigenous cryogenic stage CE-7.5 and the first successful launch with the CE-7.5. The flight lifte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Launch Pad
Satish Dhawan Space Centre – SDSC (formerly Sriharikota Range – SHAR) is the primary spaceport of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), located in Sriharikota, Tirupati district, Andhra Pradesh. The spaceport is located on an island off the east coast of India, surrounded by Pulicat Lake and the Bay of Bengal. The distance of Sriharikota from Chennai is . The Centre currently has three functioning launch pads used for launching sounding rockets, polar satellites and geosynchronous satellites. India's Lunar exploration probes Chandrayaan-1, Chandrayaan-2, Chandrayaan-3, Mars Orbiter Mission, solar research mission Aditya-L1 and space observatory XPoSat were also launched from SDSC. Originally called Sriharikota Range (SHAR), the centre was renamed on 5 September 2002 as a tribute to ISRO's former chairman Satish Dhawan with retaining its original acronym and is referred as SDSC-SHAR. History Sriharikota island was chosen in 1969 for a satellite launching statio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satish Dhawan Space Centre
Satish Dhawan Space Centre – SDSC (formerly Sriharikota Range – SHAR) is the primary spaceport of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), located in Sriharikota, Tirupati district, Andhra Pradesh. The spaceport is located on an island off the east coast of India, surrounded by Pulicat Lake and the Bay of Bengal. The distance of Sriharikota from Chennai is . The Centre currently has three functioning launch pads used for launching sounding rockets, polar satellites and geosynchronous satellites. India's Lunar exploration probes Chandrayaan-1, Chandrayaan-2, Chandrayaan-3, Mars Orbiter Mission, solar research mission Aditya-L1 and space observatory XPoSat were also launched from SDSC. Originally called Sriharikota Range (SHAR), the centre was renamed on 5 September 2002 as a tribute to ISRO's former chairman Satish Dhawan with retaining its original acronym and is referred as SDSC-SHAR. History Sriharikota island was chosen in 1969 for a satellite launchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NVS-01
NVS-01 is the first in the series of second generation navigation satellite and the ninth satellite in the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (NVS), with an alternate name of, IRNSS-1J. It will augment the existing satellite and bolster the capability of the NavIC constellation by adding more robustness and new features. ISRO already launched IRNSS 1A, 1B, 1C, 1D, 1E, 1F, 1G, 1H and 1I. The satellite is intended to replace IRNSS-1G and augment the constellation of geosynchronous navigation satellites after IRNSS-1I. Payload NVS-01 has two types of payloads, navigation payload and the ranging payload. The navigation payload transmits navigation service signals to the users. This payload is operating in L1 band, L5 band and S band. A highly stable Rubidium atomic clock is part of the navigation payload of the satellite. Failure of the imported Rubidium atomic clocks across the fleet of previous generation of satellite led to the creation of an indigenous optio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSLV
Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) is a class of expendable launch systems operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). GSLV has been used in fifteen launches since 2001. History The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) project was initiated in 1990 with the objective of acquiring an Indian launch capability for geosynchronous satellites. GSLV uses major components that are already proven in the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) launch vehicles in the form of the S125/S139 solid rocket booster and the liquid-fueled Vikas engine. Due to the thrust required for injecting the satellite in a geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) the third stage was to be powered by a LOX/ LH2 Cryogenic engine which at that time India did not possess or have the technological expertise to build. The aerodynamic characterization research was conducted at the National Aerospace Laboratories' 1.2m Trisonic Wind Tunnel Facility. The first development flight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
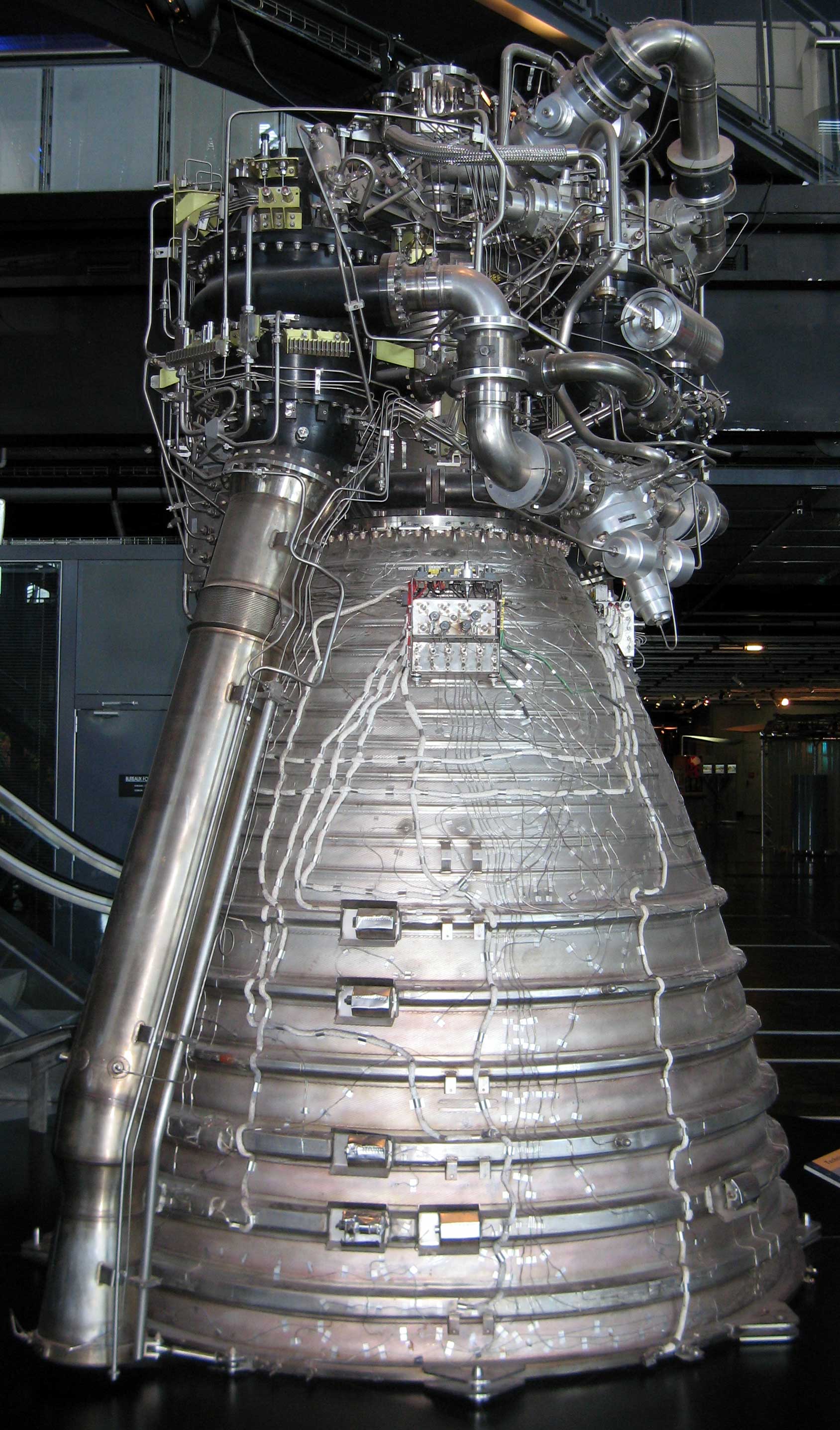
Cryogenic Rocket Engine
A cryogenic rocket engine is a rocket engine that uses a cryogenic fuel and oxidizer; that is, both its fuel and oxidizer are gases which have been liquefied and are stored at very low temperatures. These highly efficient engines were first flown on the US Atlas-Centaur and were one of the main factors of NASA's success in reaching the Moon by the Saturn V rocket. Rocket engines burning cryogenic propellants remain in use today on high performance upper stages and boosters. Upper stages are numerous. Boosters include ESA's Ariane 6, JAXA's H-II, ISRO's GSLV, LVM3, NASA's Space Launch System. The United States, Russia, India, Japan, France and China are the only countries that have operational cryogenic rocket engines. Cryogenic propellants Rocket engines need high mass flow rates of both oxidizer and fuel to generate useful thrust. Oxygen, the simplest and most common oxidizer, is in the gas phase at standard temperature and pressure, as is hydrogen, the simplest f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UTC
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is the primary time standard globally used to regulate clocks and time. It establishes a reference for the current time, forming the basis for civil time and time zones. UTC facilitates international communication, navigation, scientific research, and commerce. UTC has been widely embraced by most countries and is the effective successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) in everyday usage and common applications. In specialised domains such as scientific research, navigation, and timekeeping, other standards such as UT1 and International Atomic Time (TAI) are also used alongside UTC. UTC is based on TAI (International Atomic Time, abbreviated from its French name, ''temps atomique international''), which is a weighted average of hundreds of atomic clocks worldwide. UTC is within about one second of mean solar time at 0° longitude, the currently used prime meridian, and is not adjusted for daylight saving time. The coordination of time and frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle
Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) is a class of expendable launch systems operated by the ISRO, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). GSLV has been used in List of GSLV launches, fifteen launches since 2001. History The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) project was initiated in 1990 with the objective of acquiring an Indian launch capability for geosynchronous satellites. GSLV uses major components that are already proven in the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) launch vehicles in the form of the S125/S139 solid rocket booster and the Liquid-propellant rocket, liquid-fueled Vikas (rocket engine), Vikas engine. Due to the thrust required for injecting the satellite in a geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) the third stage was to be powered by a LOX/LH2, LH2 Cryogenic engine which at that time India did not possess or have the technological expertise to build. The aerodynamic characterization research was conducted at the National Aerospace Labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSLV
The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is an expendable medium-lift launch vehicle designed and operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It was developed to allow India to launch its Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellites into Sun-synchronous orbits, a service that was, until the advent of the PSLV in 1993, only commercially available from Russia. PSLV can also launch small size satellites into Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO). Some notable payloads launched by PSLV include India's first lunar probe Chandrayaan-1, India's first interplanetary mission, Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), India's first space observatory, Astrosat and India's first Solar mission, Aditya-L1. PSLV has gained credibility as a leading provider of rideshare services for small satellites, owing to its numerous multi-satellite deployment campaigns with auxiliary payloads, usually ride-sharing along with an Indian primary payload. As of June 2022, PSLV has launched 345 fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |