|
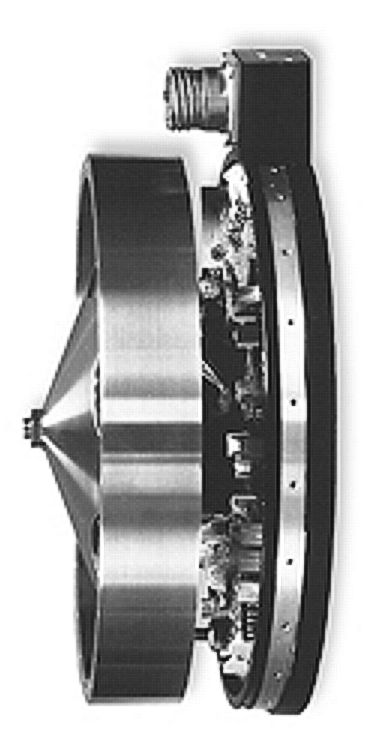
GPS Satellite Blocks
GPS satellite blocks are the various production generations of the Global Positioning System (GPS) used for satellite navigation. The first satellite in the system, Navstar 1, was launched by the United States Air Force on 22 February 1978. The GPS satellite constellation is now operated by the 2nd Navigation Warfare Squadron (2 NWS) of Mission Delta 31, United States Space Force. The GPS satellites circle the Earth at an altitude of about 20,000 km (12,427 miles) and complete two full orbits every day. Satellites by block Block I satellites Rockwell International was awarded a contract in 1974 to build the first eight Block I satellites. In 1978, the contract was extended to build an additional three Block I satellites. Beginning with Navstar 1 in 1978, ten "Block I" GPS satellites were successfully launched. One satellite, "Navstar 7", was lost due to an unsuccessful launch on 18 December 1981. The Block I satellites were launched from Vandenberg Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPS24goldenSMALL
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a Radionavigation-satellite service, satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the satellite navigation, global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geolocation and Time transfer, time information to a Satellite navigation device, GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephone or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls, and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver. Overview The GPS project was started by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn V
The Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, had multistage rocket, three stages, and was powered by liquid-propellant rocket, liquid fuel. Flown from 1967 to 1973, it was used for nine crewed flights to the Moon, and to launch Skylab, the first American space station. the Saturn V remains the only launch vehicle to have carried humans beyond low Earth orbit (LEO). The Saturn V holds the record for the largest payload capacity to low Earth orbit, , which included unburned propellant needed to send the Apollo command and service module and Apollo Lunar Module, Lunar Module to the Moon. The largest production model of the Saturn (rocket family), Saturn family of rockets, the Saturn V was designed under the direction of Wernher von Braun at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama; the lead contractors for construction of the rocket were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling; also spelled cesium in American English) is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium. It is pyrophoricity, pyrophoric and reacts with water even at . It is the least electronegativity, electronegative stable element, with a value of 0.79 on the Pauling scale. It has only one stable isotope, caesium-133. Caesium is mined mostly from pollucite. Caesium-137, a fission product, is extracted from waste produced by nuclear reactor technology, nuclear reactors. It has the largest atomic radius of all elements whose radii have been measured or calculated, at about 260 picometres. The German chemist Robert Bunsen and physicist Gustav Kirchhoff discovered caesium in 1860 by the new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubidium
Rubidium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have a density higher than Properties of water, water. On Earth, natural rubidium comprises two isotopes: 72% is a stable isotope Rb, and 28% is slightly radioactive Rb, with a half-life of 48.8 billion years – more than three times as long as the estimated age of the universe. German chemists Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff discovered rubidium in 1861 by the newly developed technique, Atomic emission spectroscopy#Flame emission spectroscopy, flame spectroscopy. The name comes from the Latin word , meaning deep red, the color of its emission spectrum. Rubidium's compounds have various chemical and electronic applications. Rubidium metal is easily vaporized and has a convenient spectral absorption range, making it a frequent target for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Wheel
A reaction wheel (RW) is an electric motor attached to a flywheel, which, when its rotation speed is changed, causes a counter-rotation proportionately through conservation of angular momentum. A reaction wheel can rotate only around its center of mass; it is not capable of moving from one place to another ( translational force). Reaction wheels are used primarily by spacecraft for three-axis attitude control, and do not require rockets or external applicators of torque, which reduces the mass fraction needed for fuel. They provide a high pointing accuracy, and are particularly useful when the spacecraft must be rotated by very small amounts, such as keeping a telescope pointed at a star. A reaction wheel is sometimes operated at a constant (or near-constant) rotation speed, to provide a satellite with a large amount of stored angular momentum. Doing so alters the spacecraft's rotational dynamics so that disturbance torques perpendicular to one axis of the satellite (the axis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Attitude Control
Spacecraft attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of a spacecraft (vehicle or satellite) with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc. Controlling vehicle attitude requires actuators to apply the torques needed to orient the vehicle to a desired attitude, and algorithms to command the actuators based on the current attitude and specification of a desired attitude. Before and during attitude control can be performed, spacecraft attitude determination must be performed, which requires sensors for absolute or relative measurement. The broader integrated field that studies the combination of sensors, actuators and algorithms is called ''guidance, navigation and control'', which also involves non-attitude concepts, such as position determination and navigation. Motivation A spacecraft's attitude must typically be stabilized and controlled for a variety of reasons. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Diego Air And Space Museum
The San Diego Air & Space Museum (SDASM) is an aviation and space exploration museum in San Diego, California. It is located in Balboa Park and is housed in the former Ford Building, which is listed on the US National Register of Historic Places. The museum was established by articles of incorporation on October 12, 1961, and opened to the public on February 15, 1963. History The museum was established on October 12, 1961, as the San Diego Aerospace Museum. The museum was first opened to the public on February 15, 1963, in the Food and Beverage Building, which had been built in 1915 for the Panama–California Exposition. In 1965 the museum was moved to the larger Electrical Building. On February 22, 1978, the Electrical Building and the museum were destroyed in an arson fire.. Several one-of-a-kind aircraft were destroyed, including the Beecraft Wee Bee, the world's lightest aircraft, and her sister's craft the Queen Bee. A reproduction of the ''Spirit of St. Louis'', built- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Article (aerospace)
A test article or pathfinder is a version of a spacecraft or related vehicle or equipment, built as a platform to perform testing on particular portions of a spaceflight regime. Test articles are built to the specifications necessary to replicate particular conditions and behaviors that are to be validated. Test articles may be built for flight testing or for non-flight testing. For space agencies with extensive flight certification procedures, they may be built without the certification and quality control steps taken with the versions intended for flight. Test articles are more complete than a boilerplate. Overview Some test articles are theoretically able to be modified and upgraded to flight-ready status. Of the 136 Space Shuttle external fuel tanks produced, one was retained as a test article. The contractor producing the tanks stated that that tank could be refurbished for flight use if necessary. Test articles are often displayed in museums because of their accurac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPS Signals
GPS signals are broadcast by Global Positioning System satellites to enable satellite navigation. Using these signals, receivers on or near the Earth's surface can determine their Position, Velocity and Time (PVT). The GPS satellite constellation is operated by the 2nd Space Operations Squadron (2SOPS) of Space Delta 8, United States Space Force. GPS signals include ranging signals, which are used to measure the distance to the satellite, and navigation messages. The navigation messages include ephemeris data which are used both in trilateration to calculate the position of each satellite in orbit and also to provide information about the time and status of the entire satellite constellation, called the almanac. There are four GPS signal specifications designed for civilian use. In order of date of introduction, these are: L1 C/A, L2C, L5 and L1C. L1 C/A is also called the ''legacy signal'' and is broadcast by all currently operational satellites. L2C, L5 and L1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L Band
The L band is the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) designation for the range of frequencies in the radio spectrum from 1 to 2 gigahertz (GHz). This is at the top end of the ultra high frequency (UHF) band, at the lower end of the microwave range. Applications Mobile service In Europe, the Electronic Communications Committee (ECC) of the European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications Administrations (CEPT) has harmonized part of the L band (1452–1492 MHz), allowing individual countries to adopt this spectrum for terrestrial mobile/fixed communications networks supplemental downlink (MFCN SDL). By means of carrier aggregation, an LTE-Advanced or UMTS/HSDPA base station could use this spectrum to provide additional bandwidth for communications from the base station to the mobile device; i.e., in the downlink direction. In the Americas, mobile services are operated between the 1.7 GHz to 2.1 GHz range in the PCS and AWS bands. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly hazardous unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine hydrate (). Hydrazine is mainly used as a foaming agent in preparing Polymeric foam, polymer foams, but applications also include its uses as a precursor (chemistry), precursor to pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, as well as a long-term storable propellant for in-outer space, space spacecraft propulsion. Additionally, hydrazine is used in various rocket propellant, rocket fuels and to prepare the gas precursors used in airbags. Hydrazine is used within both nuclear and conventional electrical power plant steam cycles as an oxygen scavenger to control concentrations of dissolved oxygen in an effort to reduce corrosion. , approximately 120,000 tons of hydrazine hydrate (corresponding to a 64% solution of hydrazine in water by weight) we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra High Frequency
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter (one decimetre). Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the super-high frequency (SHF) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF ( very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, satellite phones, and numerous other applications. The IEEE defines the UHF radar band as frequencies between 300 MHz and 1 GHz. Two other IEEE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |