Reaction wheel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
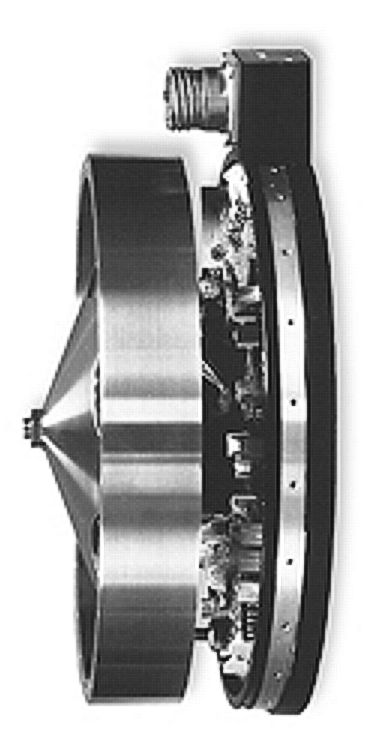
 A reaction wheel (RW) is an electric motor attached to a flywheel, which, when its rotation speed is changed, causes a counter-rotation proportionately through
A reaction wheel (RW) is an electric motor attached to a flywheel, which, when its rotation speed is changed, causes a counter-rotation proportionately through
NASA's NASA's Swift Observatory Returns to Science
NASA News, February 18, 2022, NASA. Retrieved April 16, 2023

 A reaction wheel (RW) is an electric motor attached to a flywheel, which, when its rotation speed is changed, causes a counter-rotation proportionately through
A reaction wheel (RW) is an electric motor attached to a flywheel, which, when its rotation speed is changed, causes a counter-rotation proportionately through conservation of angular momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total ang ...
. A reaction wheel can rotate only around its center of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the barycenter or balance point) is the unique point at any given time where the weight function, weighted relative position (vector), position of the d ...
; it is not capable of moving from one place to another ( translational force).
Reaction wheels are used primarily by spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
for three-axis attitude control, and do not require rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
s or external applicators of torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. Wh ...
, which reduces the mass fraction needed for fuel. They provide a high pointing accuracy, and are particularly useful when the spacecraft must be rotated by very small amounts, such as keeping a telescope pointed at a star.
A reaction wheel is sometimes operated at a constant (or near-constant) rotation speed, to provide a satellite with a large amount of stored angular momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total ang ...
. Doing so alters the spacecraft's rotational dynamics so that disturbance torques perpendicular to one axis of the satellite (the axis parallel to the wheel's spin axis) do not result directly in spacecraft angular motion about the same axis as the disturbance torque; instead, they result in (generally smaller) angular motion (precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In o ...
) of that spacecraft axis about a perpendicular axis. This has the effect of tending to stabilize that spacecraft axis to point in a nearly-fixed direction, allowing for a less-complicated attitude control system. Satellites using this "momentum-bias" stabilization approach include SCISAT-1; by orienting the momentum wheel's axis to be parallel to the orbit-normal vector, this satellite is in a "pitch momentum bias" configuration.
Design
For three-axis control, reaction wheels must be mounted along at least three directions, with extra wheels providing redundancy to the attitude control system. A redundant mounting configuration could consist of four wheels along tetrahedral axes, or a spare wheel carried in addition to a three axis configuration. Changes in speed (in either direction) are controlled electronically by computer. The strength of the materials used in a reaction wheel determine the speed at which the wheel would come apart, and therefore how much angular momentum it can store. Since the reaction wheel is a small fraction of the spacecraft's total mass, easily controlled, temporary changes in its speed result in small changes in angle. The wheels therefore permit very precise changes in a spacecraft'sattitude
Attitude or Attitude may refer to:
Philosophy and psychology
* Attitude (psychology), a disposition or state of mind
** Attitude change
* Propositional attitude, a mental state held towards a proposition
Science and technology
* Orientation ...
. For this reason, reaction wheels are often used to aim spacecraft carrying cameras or telescopes.
Over time, reaction wheels may build up enough stored momentum to exceed the maximum speed of the wheel, called saturation. However, slowing down the wheels imparts a torque causing undesired rotation. Designers therefore supplement reaction wheel systems with other attitude control mechanisms to cancel out the torque caused by "desaturating" the reaction wheels. Typically designers use "reaction control system
A reaction control system (RCS) is a spacecraft system that uses Thrusters (spacecraft), thrusters to provide Spacecraft attitude control, attitude control and translation (physics), translation. Alternatively, reaction wheels can be used for at ...
s"; arrays of small chemical rocket engines that fire as the wheels slow down to counter the torque the wheels are imparting on the spacecraft as they slow down.
More fuel efficient methods for reaction wheel desaturation have been developed over time. By reducing the amount of fuel the spacecraft needs to be launched with, they increase the useful payload that can be delivered to orbit. These methods include magnetorquers (better known as torque rods), which transfer angular momentum to the Earth through its planetary magnetic field requiring only electrical power and no fuel. They are however limited to areas of space with a sufficiently large magnetic field (such as in low Earth orbit). In the absence of a sufficiently strong magnetic field, the next most efficient practice is to use high-efficiency attitude jets such as ion thruster
An ion thruster, ion drive, or ion engine is a form of electric propulsion used for spacecraft propulsion. An ion thruster creates a cloud of positive ions from a neutral gas by ionizing it to extract some electrons from its atoms. The i ...
s.
Examples
Beresheet was launched on aFalcon 9
Falcon 9 is a Reusable launch system#Partial reusable launch systems, partially reusable, two-stage-to-orbit, medium-lift launch vehicle designed and manufactured in the United States by SpaceX. The first Falcon 9 launch was on June 4, 2010, an ...
rocket on 22 February 2019 1:45 UTC, with the goal of landing on the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
. Beresheet uses the low-energy transfer technique to save fuel. Since its fourth maneuver in its elliptical orbit, to prevent shakes when the amount of liquid fuel ran low, there was a need to use a reaction wheel.
The James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed to conduct infrared astronomy. As the largest telescope in space, it is equipped with high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments, allowing it to view objects too old, Lis ...
has six reaction wheels built by Rockwell Collins Deutschland.
LightSail 2 was launched on 25 June 2019, focused around the concept of a solar sail. LightSail 2 uses a reaction wheel system to change orientation by very small amounts, allowing it to receive different amounts of momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (: momenta or momentums; more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. ...
from the light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
across the sail, resulting in a higher altitude.
Failures and mission impact
The failure of one or more reaction wheels can cause a spacecraft to lose its ability to maintain attitude (orientation) and thus potentially cause a mission failure. Recent studies conclude that these failures can be correlated with space weather effects. These events probably caused failures by inducing electrostatic discharge in the steel ball bearings of Ithaco wheels, compromising the smoothness of the mechanism. Supporting this hypothesis, newer reaction wheels have non-conducting ceramic bearings, and none have failed in this manner. Two servicing missions to theHubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
have replaced a reaction wheel. In February 1997, the Second Servicing Mission ( STS-82) replaced one after 'electrical anomalies', rather than any mechanical problem. Study of the returned mechanism provided a rare opportunity to study equipment that had undergone long-term service (seven years) in space, particularly for the effects of vacuum on lubricant
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, ...
s. The lubricating compound was found to be in 'excellent condition'. In 2002, during Servicing Mission 3B ( STS-109), astronauts from the shuttle ''Columbia'' replaced another reaction wheel. Neither of these wheels had failed and Hubble was designed with four redundant wheels, and maintained pointing ability so long as three were functional.
In 2004, during the mission of the '' Hayabusa'' spacecraft, an X-axis reaction wheel failed. The Y-axis wheel failed in 2005, causing the craft to rely on chemical thrusters to maintain attitude control.
From July 2012 to May 11, 2013, two out of the four reaction wheels in the Kepler space telescope failed. This loss severely affected Kepler ability to maintain a sufficiently precise orientation to continue its original mission. On August 15, 2013, engineers concluded that Kepler's reaction wheels cannot be recovered and that planet-searching using the transit method (measuring changes in star brightness caused by orbiting planets) could not continue. Although the failed reaction wheels still function, they are experiencing friction exceeding acceptable levels, and consequently hindering the ability of the telescope to properly orient itself. The Kepler telescope was returned to its "point rest state", a stable configuration that uses small amounts of thruster fuel to compensate for the failed reaction wheels, while the Kepler team considered alternative uses for Kepler that do not require the extreme accuracy in its orientation needed by the original mission. On May 16, 2014, NASA extended the Kepler mission to a new mission named K2, which uses Kepler differently, but allows it to continue searching for exoplanets
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first detec ...
. On October 30, 2018, NASA announced the end of the Kepler mission after it was determined that the fuel supply had been exhausted.
The NASA space probe ''Dawn
Dawn is the time that marks the beginning of twilight before sunrise. It is recognized by the diffuse sky radiation, appearance of indirect sunlight being Rayleigh scattering, scattered in Earth's atmosphere, when the centre of the Sun's disc ha ...
'' had excess friction in one reaction wheel in June 2010. It was originally scheduled to depart Vesta and begin its two-and-a-half-year journey to Ceres on August 26, 2012; however, a problem with another of the spacecraft's reaction wheels forced ''Dawn'' to briefly delay its departure from Vesta's gravity until September 5, 2012, and it planned to use thruster jets instead of the reaction wheels during the three-year journey to Ceres. The loss of the reaction wheels limited the camera observations on the approach to Ceres.
On the evening of Tuesday, January 18, 2022, a possible failure of one of the Swift Observatory's reaction wheels caused the mission control team to power off the suspected wheel, putting the observatory in safe mode as a precaution. This was the first time a reaction wheel failed on Swift in 17 years. Swift resumed science operations on February 17, 2022.NASA News, February 18, 2022, NASA. Retrieved April 16, 2023
Similar devices
Acontrol moment gyroscope
A control moment gyroscope (CMG) is an attitude control device generally used in spacecraft attitude control systems. A CMG consists of a spinning rotor and one or more motorized gimbals that tilt the rotor’s angular momentum. As the rotor til ...
(CMG) is a related but different type of attitude actuator, generally consisting of a momentum wheel mounted in a one-axis or two-axis gimbal. When mounted to a rigid spacecraft, applying a constant torque to the wheel using one of the gimbal motors causes the spacecraft to develop a constant angular velocity about a perpendicular axis, thus allowing control of the spacecraft's pointing direction. CMGs are generally able to produce larger sustained torques than RWs with less motor heating, and are preferentially used in larger or more-agile (or both) spacecraft, including Skylab
Skylab was the United States' first space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three trios of astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Skylab was constructe ...
, Mir, and the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
.
See also
* * * *References
External links
* * * {{cite web , url=https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20110015369_2011016130.pdf , archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20221009/https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20110015369_2011016130.pdf , archive-date=2022-10-09 , url-status=live, last=Markley , first=F. Landis , author2=Reid G. Reynolds , author3=Frank X. Liu , author4= Kenneth L. Lebsock , title=Maximum Torque and Momentum Envelopes for Reaction Wheel Arrays , date=2009 Spacecraft attitude control Spacecraft propulsion Gyroscopes ca:Roda de reacció