|
GDDR7
Graphics Double Data Rate 7 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (GDDR7 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous graphics random-access memory (SGRAM) specified by the JEDEC Semiconductor Memory Standard, with a high bandwidth, "double data rate" interface, designed for use in graphics cards, game consoles, and high-performance computing. It is a type of GDDR SDRAM (graphics DDR SDRAM), and is the successor to GDDR6. History * At Samsung Tech Day 2022, Samsung announced GDDR7 as the successor of GDDR6X, which could deliver up to 36 GT/s. Samsung announced two months later that it would use PAM-3 signaling to achieve the highest transfer rate. * On March 8, 2023, Cadence announced the verification solution tool for preliminary GDDR7 SDRAM production. * On June 30, 2023, Micron announced that it will be manufactured using 1β node (equivalent to 12–10 nm process node), slated to release in H1 2024. * On July 18, 2023, Samsung announced the first generation of GDDR7, which can reach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GeForce RTX 50 Series
The GeForce RTX 50 series is a series of consumer graphics processing units (GPUs) developed by Nvidia as part of its GeForce line of graphics cards, succeeding the GeForce 40 series. Announced at CES 2025, it debuted with the release of the RTX 5080 and RTX 5090 on January 30, 2025. It is based on Nvidia's Blackwell architecture featuring Nvidia RTX's fourth-generation RT cores for hardware-accelerated real-time ray tracing, and fifth-generation deep-learning-focused Tensor Cores. The GPUs are manufactured by TSMC on custom 4N process node. Background In March 2024, Nvidia announced the Blackwell architecture for its datacenter products. Like Ampere, Blackwell is a shared architecture between both consumer and datacenter products rather than distinct architectures released simultaneously like Ada Lovelace for consumers and Hopper for datacenter. At the Game Awards in December 2024, a cinematic trailer for ''The Witcher IV'' was shown which had been pre-rendered on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
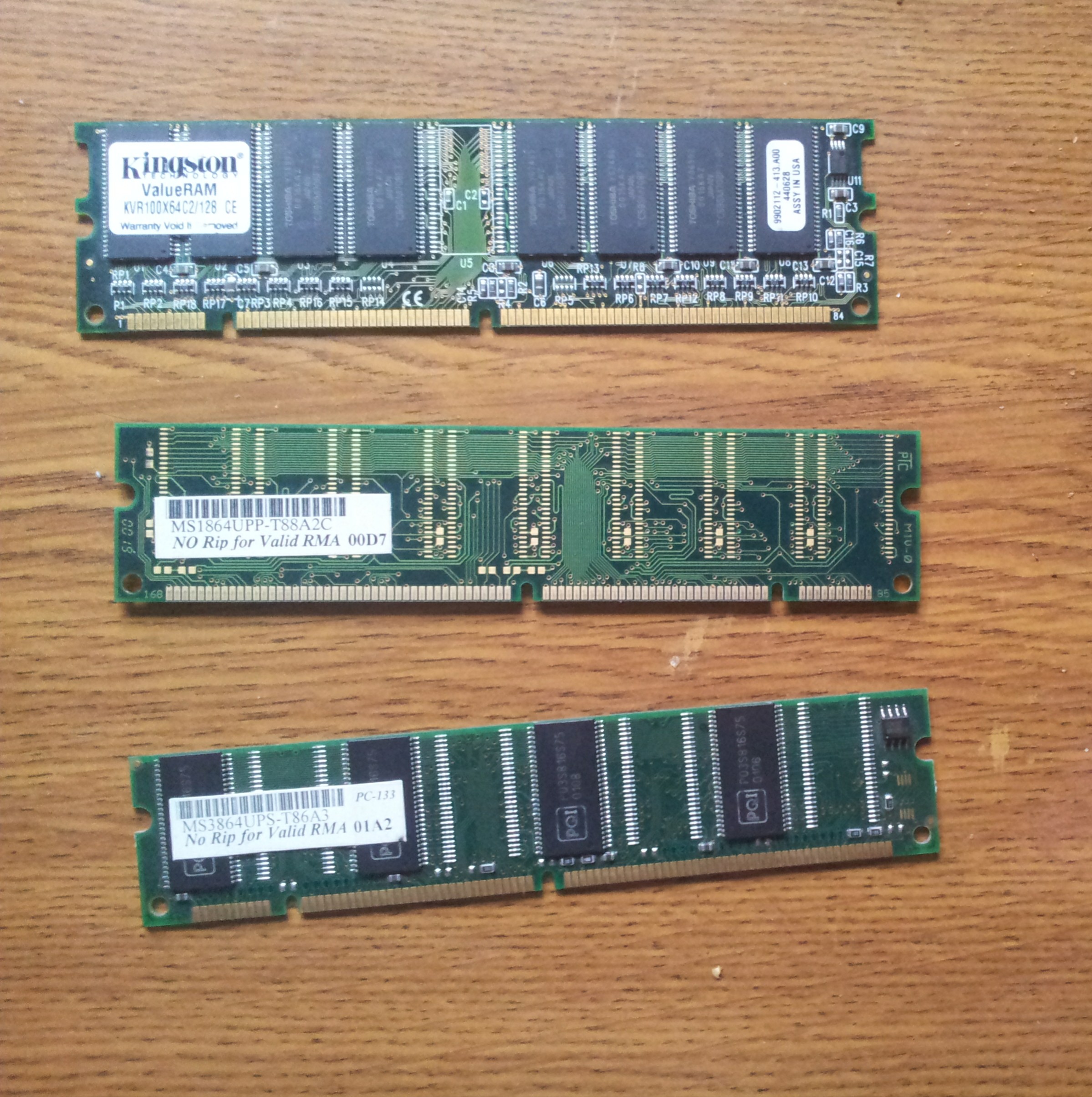
GDDR SDRAM
Graphics DDR SDRAM (GDDR SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) specifically designed for applications requiring high bandwidth, e.g. graphics processing units (GPUs). GDDR SDRAM is distinct from the more widely known types of DDR SDRAM, such as DDR4 and DDR5, although they share some of the same features—including double data rate (DDR) data transfers. , GDDR SDRAM has been succeeded by GDDR2, GDDR3, GDDR4, GDDR5, GDDR5X, GDDR6, GDDR6X, GDDR6W and GDDR7. Generations File:ATI Radeon X1300 256MB - Hynix HY5DU561622CTP-5-5390.jpg, Hynix GDDR SDRAM File:SAMSUNG@QDDR3-SDRAM@256MBit@K5J55323QF-GC16 Stack-DSC01234-DSC01284 - ZS-retouched.jpg, A Samsung GDDR3 256MBit package File:Sapphire Ultimate HD 4670 512MB - Qimonda HYB18H512321BF-10-93577.jpg, A 512 MBit Qimonda GDDR3 SDRAM package File:SAMSUNG@QDDR3-SDRAM@256MBit@K5J55323QF-GC16 Stack-DSC01340-DSC01367 - ZS-retouched.jpg, Inside a Samsung GDDR3 256MBit package DDR SGRAM GDDR was init ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-amplitude Modulation
Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) is a form of signal modulation in which the message information is encoded in the amplitude of a pulse train interrupting the carrier frequency. Demodulation is performed by detecting the amplitude level of the carrier at every single period. Types There are two types of pulse amplitude modulation: * In ''single polarity PAM'', a suitable fixed DC bias is added to the signal to ensure that all the pulses are positive. * In ''double polarity PAM'', the pulses are both positive and negative. Pulse-amplitude modulation is widely used in modulating signal transmission of digital data, with non- baseband applications having been largely replaced by pulse-code modulation, and, more recently, by pulse-position modulation. The number of possible pulse amplitudes in analog PAM is theoretically infinite. Digital PAM reduces the number of pulse amplitudes to some natural number. Uses Ethernet Some versions of the Ethernet communication standard are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronous Dynamic Random-access Memory
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to the early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions delayed only by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDDR6X
Graphics Double Data Rate 6 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (GDDR6 SDRAM) is a type of Synchronous dynamic random-access memory#Synchronous graphics RAM .28SGRAM.29, synchronous graphics random-access memory (SGRAM) with a high Bandwidth (computing), bandwidth, "double data rate" interface, designed for use in Video card, graphics cards, Video game console, game consoles, and High-throughput computing, high-performance computing. It is a type of GDDR SDRAM (graphics DDR SDRAM), and is the successor to GDDR5. Just like GDDR5X it uses QDR (quad data rate) in reference to the write command clock (WCK) and ODR (Octal Data Rate) in reference to the command clock (CK). Overview The finalized specification was published by JEDEC in July 2017. GDDR6 offers increased per-pin bandwidth (up to 16 Gbit/s) and lower operating voltages (1.35 V), increasing performance and decreasing power consumption relative to GDDR5X. Commercial implementation At Hot Chips 2016, Samsung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GDDR6 SDRAM
Graphics Double Data Rate 6 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (GDDR6 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous graphics random-access memory (SGRAM) with a high bandwidth, "double data rate" interface, designed for use in graphics cards, game consoles, and high-performance computing. It is a type of GDDR SDRAM (graphics DDR SDRAM), and is the successor to GDDR5. Just like GDDR5X it uses QDR (quad data rate) in reference to the write command clock (WCK) and ODR (Octal Data Rate) in reference to the command clock (CK). Overview The finalized specification was published by JEDEC in July 2017. GDDR6 offers increased per-pin bandwidth (up to 16 Gbit/s) and lower operating voltages (1.35 V), increasing performance and decreasing power consumption relative to GDDR5X. Commercial implementation At Hot Chips 2016, Samsung announced GDDR6 as the successor of GDDR5X. Samsung later announced that the first products would be 16 Gbit/s, 1.35 V chips. In January 2018, Sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10 Nm Process
In semiconductor fabrication, the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS) defines the "10 nanometer process" as the MOSFET technology node following the "14 nm" node. Since at least 1997, "process nodes" have been named purely on a marketing basis, and have no relation to the dimensions on the integrated circuit; neither gate length, metal pitch or gate pitch on a "10nm" device is ten nanometers. For example, GlobalFoundries' " 7 nm" processes are dimensionally similar to Intel's "10 nm" process. TSMC and Samsung's "10 nm" processes are somewhere between Intel's "14 nm" and "10 nm" processes in transistor density. The transistor density (number of transistors per square millimetre) is more important than transistor size, since smaller transistors no longer necessarily mean improved performance, or an increase in the number of transistors. All production "10 nm" processes are based on FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Scrubbing
Memory scrubbing consists of reading from each computer memory location, correcting bit errors (if any) with an error-correcting code ( ECC), and writing the corrected data back to the same location. Due to the high integration density of modern computer memory chips, the individual memory cell structures became small enough to be vulnerable to cosmic rays and/or alpha particle emission. The errors caused by these phenomena are called soft errors. Over 8% of dual in-line memory modules (DIMMs) experience at least one correctable error per year. This can be a problem for DRAM and SRAM based memories. The probability of a soft error at any individual memory bit is very small. However, together with the large amount of memory modern computersespecially serversare equipped with, and together with extended periods of uptime, the probability of soft errors in the total memory installed is significant. The information in an ECC memory is stored redundantly enough to correct single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Error Correction Code
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, forward error correction (FEC) or channel coding is a technique used for controlling errors in data transmission over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea is that the sender encodes the message in a redundant way, most often by using an error correction code, or error correcting code (ECC). The redundancy allows the receiver not only to detect errors that may occur anywhere in the message, but often to correct a limited number of errors. Therefore a reverse channel to request re-transmission may not be needed. The cost is a fixed, higher forward channel bandwidth. The American mathematician Richard Hamming pioneered this field in the 1940s and invented the first error-correcting code in 1950: the Hamming (7,4) code. FEC can be applied in situations where re-transmissions are costly or impossible, such as one-way communication links or when transmitting to multiple receivers in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom's Hardware
''Tom's Hardware'' is an online publication owned by Future plc and focused on technology. It was founded in 1996 by Thomas Pabst. It provides articles, news, price comparisons, videos and reviews on computer hardware and high technology. The site features coverage on CPUs, motherboards, RAM, PC cases, graphic cards, display technology, power supplies and displays, storage, smartphones, tablets, gaming, consoles, and computer peripherals. ''Tom's Hardware'' has a forum and featured blogs. History ''Tom's Hardware'' was founded in 1996 as ''Tom's Hardware Guide'' in Canada by Thomas Pabst. It started using the domain tomshardware.com in September 1997 and was followed by several foreign language versions, including Italian, French, Finnish and Russian based on franchise agreements. While the initial testing labs were in Germany and California, much of ''Tom's Hardware'''s testing now occurs in New York and a facility in Ogden, Utah owned by its parent company. In April 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-return-to-zero
In telecommunications, a non-return-to-zero (NRZ) line code is a binary code in which ones are represented by one significant condition, usually a positive voltage, while zeros are represented by some other significant condition, usually a negative voltage, with no other neutral or rest condition. For a given data signaling rate, i.e., bit rate, the NRZ code requires only half the baseband bandwidth required by the Manchester code (the passband bandwidth is the same). The pulses in NRZ have more energy than a return-to-zero (RZ) code, which also has an additional rest state beside the conditions for ones and zeros. When used to represent data in an asynchronous communication scheme, the absence of a neutral state requires other mechanisms for bit synchronization when a separate clock signal is not available. Since NRZ is not inherently a self-clocking signal, some additional synchronization technique must be used for avoiding bit slips; examples of such techniques are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |