|
Friedrich August Ukert
Friedrich August Ukert (28 October 1780 – 18 May 1851) was a German history scholar, teacher and humanitarian. He was born in Eutin, Bishopric of Lübeck. From 1800 he studied philology at the University of Halle as a student of Friedrich August Wolf, then continued his education at the University of Jena, where his instructors included Johann Heinrich Voss, Johann Jakob Griesbach and Christian Gottfried Schütz. After finishing his studies, he worked as a tutor, first in Danzig, then in Weimar, where he provided education for the two sons of the late Friedrich Schiller. In 1808 he relocated to Gotha and worked as an inspector at the Gymnasium Illustre. Shortly afterwards, he found employment as a librarian at the city's ducal library. At the time of his death, he held the title of chief librarian in Gotha. Deutsche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich August Ukert
Friedrich August Ukert (28 October 1780 – 18 May 1851) was a German history scholar, teacher and humanitarian. He was born in Eutin, Bishopric of Lübeck. From 1800 he studied philology at the University of Halle as a student of Friedrich August Wolf, then continued his education at the University of Jena, where his instructors included Johann Heinrich Voss, Johann Jakob Griesbach and Christian Gottfried Schütz. After finishing his studies, he worked as a tutor, first in Danzig, then in Weimar, where he provided education for the two sons of the late Friedrich Schiller. In 1808 he relocated to Gotha and worked as an inspector at the Gymnasium Illustre. Shortly afterwards, he found employment as a librarian at the city's ducal library. At the time of his death, he held the title of chief librarian in Gotha. Deutsche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukert (crater)
Ukert is a lunar impact crater that lies on a strip of rugged ground between Mare Vaporum to the north and Sinus Medii in the south. It was named after German historian Friedrich August Ukert. It is located to the north-northwest of the crater Triesnecker and northeast of the crater pair of Pallas Pallas may refer to: Astronomy * 2 Pallas asteroid ** Pallas family, a group of asteroids that includes 2 Pallas * Pallas (crater), a crater on Earth's moon Mythology * Pallas (Giant), a son of Uranus and Gaia, killed and flayed by Athena * Pa ... and Murchison. The outer rim of this crater is not quite circular, with outward bulges to the north and the east. The interior floor is irregular in places, with a central ridge running from crater midpoint down to the southern wall. There is a tiny craterlet along the northern rim, but otherwise the crater contains no impacts of note. Satellite craters By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Halle Alumni
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Eutin
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century German Historians
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1851 Deaths
Events January–March * January 11 – Hong Xiuquan officially begins the Taiping Rebellion. * January 15 – Christian Female College, modern-day Columbia College, receives its charter from the Missouri General Assembly. * January 23 – The flip of a coin, subsequently named Portland Penny, determines whether a new city in the Oregon Territory is named after Boston, Massachusetts, or Portland, Maine, with Portland winning. * January 28 – Northwestern University is founded in Illinois. * February 1 – ''Brandtaucher'', the oldest surviving submersible craft, sinks during acceptance trials in the German port of Kiel, but the designer, Wilhelm Bauer, and the two crew escape successfully. * February 6 – Black Thursday in Australia: Bushfires sweep across the state of Victoria, burning about a quarter of its area. * February 12 – Edward Hargraves claims to have found gold in Australia. * February 15 – In Boston, Massac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1780 Births
Year 178 ( CLXXVIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scipio and Rufus (or, less frequently, year 931 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 178 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Bruttia Crispina marries Commodus, and receives the title of '' Augusta''. * Emperor Marcus Aurelius and his son Commodus arrive at Carnuntum in Pannonia, and travel to the Danube to fight against the Marcomanni. Asia * Last (7th) year of ''Xiping'' era and start of ''Guanghe'' era of the Chinese Han Dynasty. * In India, the decline of the Kushan Empire begins. The Sassanides take over Central Asia. Religion * The Montanist heresy is condemned for the first time. Births * Lü Meng, Chinese general (d. 220) * Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
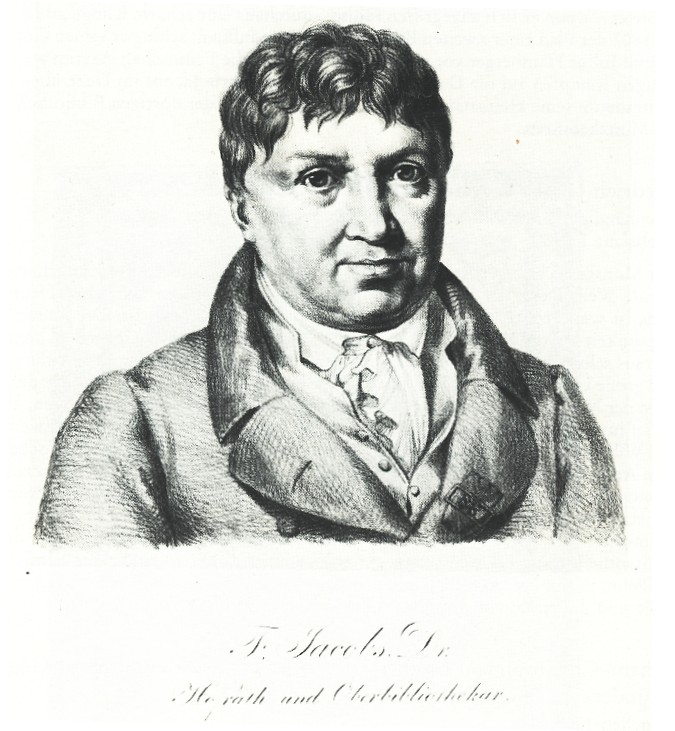
Christian Friedrich Wilhelm Jacobs
Christian Friedrich Wilhelm Jacobs (October 6, 1764 – March 30, 1847) a German classical scholar, was born at Gotha. After studying philology and theology at Jena and Göttingen, in 1785, Friedrich Jacobs (as he is known), became a teacher in the gymnasium of his native town, and in 1802 was appointed to an office in the public library. In 1807 he became classical tutor in the lyceum of Munich, but, disgusted at the attacks made upon him by the old Bavarian Catholic party, who resented the introduction of north German teachers, he returned to Gotha in 1810 to take charge of the library and the numismatic cabinet. He remained in Gotha till his death on 30 March 1847. Jacobs was an extremely successful teacher; he took great interest in the affairs of his country, and was a publicist of no mean order. But his great work was a huge critical commentary to the '' Greek Anthology'' in 13 volumes (1798–1814), followed by the first modern edition based on the ''Codex Palatinus'' (181 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadripart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, languages, and national identity have historically been based. Geographically, Kurdistan roughly encompasses the northwestern Zagros and the eastern Taurus mountain ranges. Kurdistan generally comprises the following four regions: southeastern Turkey ( Northern Kurdistan), northern Iraq ( Southern Kurdistan), northwestern Iran ( Eastern Kurdistan), and northern Syria ( Western Kurdistan). Some definitions also include parts of southern Transcaucasia. Certain Kurdish nationalist organizations seek to create an independent nation state consisting of some or all of these areas with a Kurdish majority, while others campaign for greater autonomy within the existing national boundaries. Historically, the word "Kurdistan" is first attested in 11th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Oxford Reference Online'' also place Armenia in Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region; and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia to the north, the Lachin corridor (under a Russian peacekeeping force) and Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran and the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan to the south. Yerevan is the capital, largest city and the financial center. Armenia is a unitary, multi-party, democratic nation-state with an ancient cultural heritage. The first Armenian state of Urartu was established in 860 BC, and by the 6th century BC it was replaced by the Satrapy of Armenia. The Kingdom of Armenia reached its height under Tigranes the Great in the 1st century BC and in the year 301 became the first state in the world to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1938.jpg)