|
Freygish
In music, the Phrygian dominant scale is the fifth mode of the harmonic minor scale, the fifth being the dominant.Dave Hunter (2005). ''Play Acoustic'', San Francisco: Backbeat, p. 226. . Also called the persian scale, altered Phrygian scale, dominant flat 2 flat 6 (in jazz), the Freygish scale (also spelled FraigishDick Weissman, Dan Fox (2009). ''A Guide to Non-Jazz Improvisation'', guitar edition, Pacific, Missouri: Mel Bay, p. 130. .), harmonic dominant, or simply the fifth mode of the harmonic minor scale. It resembles the scale of the Phrygian mode but has a major third. In the Berklee method, it is known as the Mixolydian 9 13 chord scale, a Mixolydian scale with a lowered 9th (2nd) and lowered 13th (6th), used in secondary dominant chord scales for V7/III and V7/VI. Bebop jazz pianist Barry Harris added a note to the scale and describes it as: For ii V in F minor (G-7b5 C7b9), play down from the 7th of the Eb7 dominant scale (Mixolydian) to E the 3rd of C7”. Harris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klezmer
Klezmer ( yi, קלעזמער or ) is an instrumental musical tradition of the Ashkenazi Jews of Central and Eastern Europe. The essential elements of the tradition include dance tunes, ritual melodies, and virtuosic improvisations played for listening; these would have been played at weddings and other social functions. The musical genre incorporated elements of many other musical genres including Ottoman (especially Greek and Romanian) music, Baroque music, German and Slavic folk dances, and religious Jewish music. As the music arrived in the United States, it lost some of its traditional ritual elements and adopted elements of American big band and popular music. Among the European-born klezmers who popularized the genre in the United States in the 1910s and 1920s were Dave Tarras and Naftule Brandwein; they were followed by American-born musicians such as Max Epstein, Sid Beckerman and Ray Musiker. After the destruction of Jewish life in Eastern Europe during the Holoca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gypsy Scale
The term ''Gypsy scale'' refers to one of several musical scales named after their support of and association with Romani or "Gypsy" music: * Double harmonic scale (major), the fifth mode of Hungarian minor, or Double Harmonic minor, scale, also known as the Byzantine scale. * Hungarian minor scale, minor scale with raised fourth and seventh degrees, also known as Double Harmonic minor scale. * Phrygian dominant scale In music, the Phrygian dominant scale is the fifth mode of the harmonic minor scale, the fifth being the dominant.Dave Hunter (2005). ''Play Acoustic'', San Francisco: Backbeat, p. 226. . Also called the persian scale, altered Phrygian scale, d ..., also known as Freygish or Jewish scale; Spanish Gypsy or Spanish Phrygian scale. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Gypsy scale Heptatonic scales Romani music Musical scales Musical scales with augmented seconds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D Freygish Noteworthy Composer
D, or d, is the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''dee'' (pronounced ), plural ''dees''. History The Semitic letter Dāleth may have developed from the logogram for a fish or a door. There are many different Egyptian hieroglyphs that might have inspired this. In Semitic, Ancient Greek and Latin, the letter represented ; in the Etruscan alphabet the letter was archaic, but still retained (see letter B). The equivalent Greek letter is Delta, Δ. Architecture The minuscule (lower-case) form of 'd' consists of a lower-story left bowl and a stem ascender. It most likely developed by gradual variations on the majuscule (capital) form 'D', and today now composed as a stem with a full lobe to the right. In handwriting, it was common to start the arc to the left of the vertical stroke, resulting in a serif at the top of the arc. This ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Music
Music has been an integral part of Egyptian culture since antiquity in Egypt. Egyptian music had a significant impact on the development of ancient Greek music, and via the Greeks it was important to early European music well into the Middle Ages. Due to the thousands of years long dominance of Egypt over its neighbors, Egyptian culture, including music and musical instruments, was very influential in the surrounding regions; for instance, the instruments claimed in the Bible to have been played by the ancient Hebrews are all Egyptian instruments as established by Egyptian archaeology. Egyptian modern music is considered as a main core of Middle Eastern and Oriental music as it has a huge influence on the region due to the popularity and huge influence of Egyptian cinema and music industries, owing to the political influence Egypt has on its neighboring countries, as well as Egypt producing the most accomplished musicians and composers in the region, specially in the 20th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castile (historical Region)
Castile or Castille (; ) is a territory of imprecise limits located in Spain. The invention of the concept of Castile relies on the assimilation (via a metonymy) of a 19th-century determinist geographical notion, that of Castile as Spain's ("tableland core", connected to the Meseta Central) with a long-gone historical entity of diachronically variable territorial extension (the Kingdom of Castile). The proposals advocating for a particular semantic codification/closure of the concept (a '' dialogical'' construct) are connected to essentialist arguments relying on the reification of something that does not exist beyond the social action of those building Castile not only by identifiying with it as a homeland of any kind, but also ''in opposition'' to it. A hot topic concerning the concept of Castile is its relation with Spain, insofar intellectuals, politicians, writers, or historians have either endorsed, nuanced or rejected the idea of the ''maternity'' of Spain by Castil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
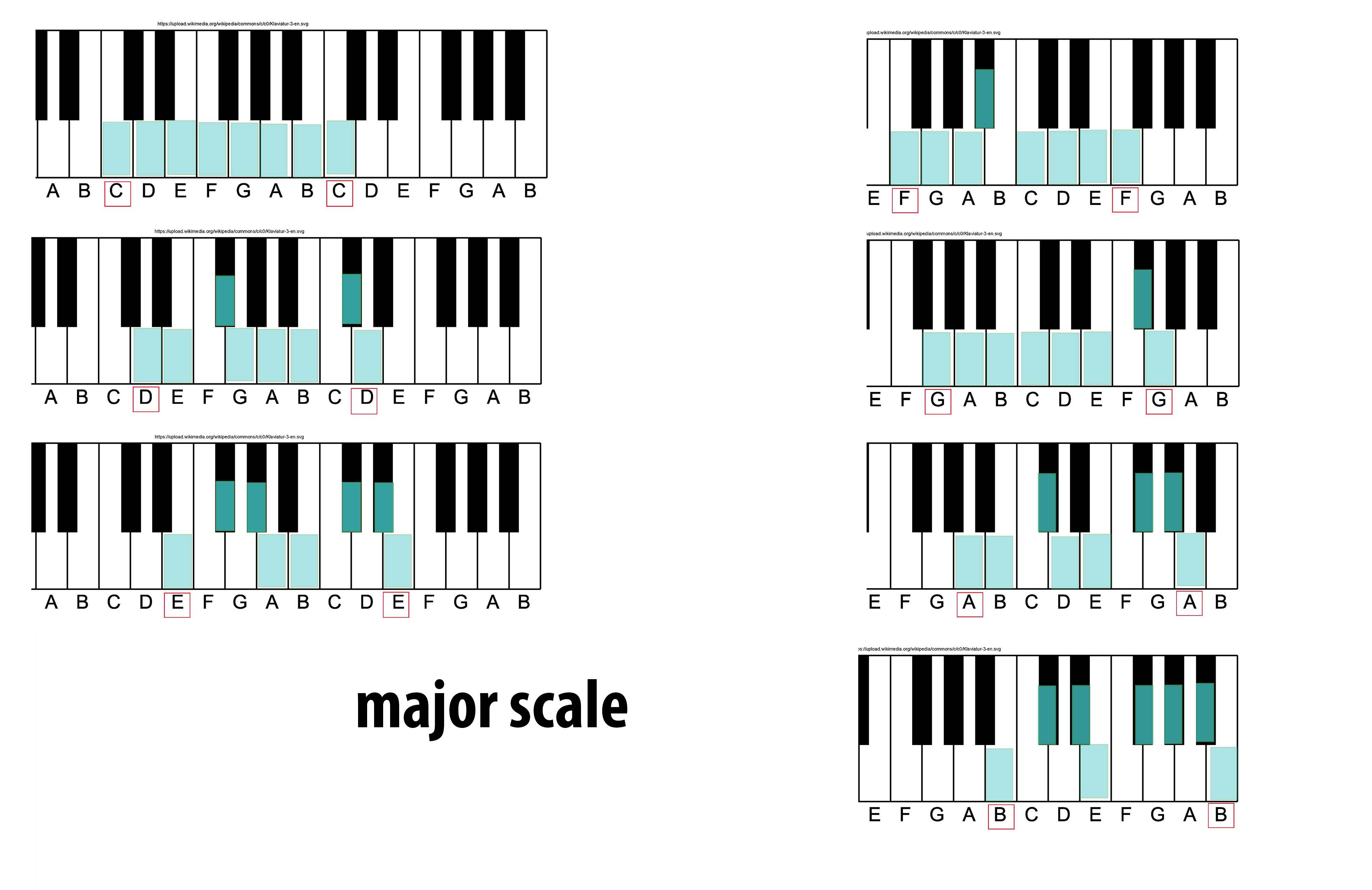
Major Scale
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale had a central importance in Western music, particularly in the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as '' Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as '' Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrygian Mode
The Phrygian mode (pronounced ) can refer to three different musical modes: the ancient Greek ''tonos'' or ''harmonia,'' sometimes called Phrygian, formed on a particular set of octave species or scales; the Medieval Phrygian mode, and the modern conception of the Phrygian mode as a diatonic scale, based on the latter. Ancient Greek Phrygian The octave species (scale) underlying the ancient-Greek Phrygian ''tonos'' (in its diatonic genus) corresponds to the medieval and modern Dorian mode. The terminology is based on the '' Elements'' by Aristoxenos (fl. c. 335 BC), a disciple of Aristotle. The Phrygian ''tonos'' or ''harmonia'' is named after the ancient kingdom of Phrygia in Anatolia. In Greek music theory, the ''harmonia'' given this name was based on a ''tonos'', in turn based on a scale or octave species built from a tetrachord which, in its diatonic genus, consisted of a series of rising intervals of a whole tone, followed by a semitone, followed by a whole tone. : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vakulabharanam
Vakulabharanam (pronounced ) is a rāgam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is the 14th '' melakarta'' rāgam in the 72 ''melakarta'' rāgam system of Carnatic music. It is called Dhātivasantabhairavi''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras or Vātivasantabhairavi in Muthuswami Dikshitar school of Carnatic music. In Western Music, it is E major. Structure and Lakshana It is the 2nd rāgam in the 3rd ''chakra Agni''. The mnemonic name is ''Agni-Sri''. The mnemonic phrase is ''sa ra gu ma pa dha ni''. Its ' structure (ascending and descending scale) is as follows (see ''swaras'' in Carnatic music for details on below notation and terms): * : * : ''Shuddha rishabham, antara gandharam, shuddha madhyamam, shuddha dhaivatham'' and '' kaisiki nishadham'' are the ''swaras'' used in this scale. As this scale is a ''melakarta'' rāgam, by de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnatic Music
Carnatic music, known as or in the South Indian languages, is a system of music commonly associated with South India, including the modern Indian states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala and Tamil Nadu, and Sri Lanka. It is one of two main subgenres of Indian classical music that evolved from ancient Hindu Texts and traditions, particularly the Samaveda. The other subgenre being Hindustani music, which emerged as a distinct form because of Persian or Islamic influences from Northern India. The main emphasis in Carnatic music is on vocal music; most compositions are written to be sung, and even when played on instruments, they are meant to be performed in ''gāyaki'' (singing) style. Although there are stylistic differences, the basic elements of (the relative musical pitch), (the musical sound of a single note), (the mode or melodic formulæ), and (the rhythmic cycles) form the foundation of improvisation and composition in both Carnatic and Hindustan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raga
A ''raga'' or ''raag'' (; also ''raaga'' or ''ragam''; ) is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a melodic mode. The ''rāga'' is a unique and central feature of the classical Indian music tradition, and as a result has no direct translation to concepts in classical European music. Each ''rāga'' is an array of melodic structures with musical motifs, considered in the Indian tradition to have the ability to "colour the mind" and affect the emotions of the audience. Each ''rāga'' provides the musician with a musical framework within which to improvise. Improvisation by the musician involves creating sequences of notes allowed by the ''rāga'' in keeping with rules specific to the ''rāga''. ''Rāga''s range from small ''rāga''s like Bahar and Shahana that are not much more than songs to big ''rāga''s like Malkauns, Darbari and Yaman, which have great scope for improvisation and for which performances can last over an hour. ''Rāga''s ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindustani Classical Music
Hindustani classical music is the classical music of northern regions of the Indian subcontinent. It may also be called North Indian classical music or, in Hindustani, ''shastriya sangeet'' (). It is played in instruments like the violin, sitar and sarod. Its origins from the 12th century CE, when it diverged from Carnatic music, the classical tradition in South India. Hindustani classical music arose in the Ganga-Jamuni Tehzeeb, a period of great influence of Perso-Arabic arts in the subcontinent, especially the Northern parts. This music combines the Indian classical music tradition with Perso-Arab musical knowledge, resulting in a unique tradition of gharana system of music education. History Around the 12th century, Hindustani classical music diverged from what eventually came to be identified as Carnatic classical music.The central notion in both systems is that of a melodic musical mode or '' raga'', sung to a rhythmic cycle or '' tala''. It is melodic music, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Classical Music
Persian traditional music or Iranian traditional music, also known as Persian classical music or Iranian classical music, refers to the classical music of Iran (also known as ''Persia''). It consists of characteristics developed through the country's classical, medieval, and contemporary eras. It also influenced areas and regions that are considered part of Greater Iran. Due to the exchange of musical science throughout history, many of Iran's classical modes are related to those of its neighboring cultures. Iran's classical art music continues to function as a spiritual tool, as it has throughout history, and much less of a recreational activity. It belongs for the most part to the social elite, as opposed to the folkloric and popular music, in which the society as a whole participates. However, components of Iran's classical music have also been incorporated into folk and pop music compositions. History The history of musical development in Iran dates back thousands of years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)





%2C_1660-1670_CE%2C_Golkonda.png)