|
Frame Semantics (linguistics)
Frame semantics is a theory of linguistic meaning developed by Charles J. Fillmore that extends his earlier case grammar. It relates linguistic semantics to encyclopedic knowledge. The basic idea is that one cannot understand the meaning of a single word without access to all the essential knowledge that relates to that word. For example, one would not be able to understand the word "sell" without knowing anything about the situation of commercial transfer, which also involves, among other things, a seller, a buyer, goods, money, the relation between the money and the goods, the relations between the seller and the goods and the money, the relation between the buyer and the goods and the money and so on. Thus, a word activates, or evokes, a frame of semantic knowledge relating to the specific concept to which it refers (or highlights, in frame semantic terminology). The idea of the encyclopedic organisation of knowledge itself is old and was discussed by Age of Enlightenment philo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the science, scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the Cognition, cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Evolution
Cultural evolution is an evolutionary theory of social change. It follows from the definition of culture as "information capable of affecting individuals' behavior that they acquire from other members of their species through teaching, imitation and other forms of social transmission". Cultural evolution is the change of this information over time. Cultural evolution, historically also known as sociocultural evolution, was originally developed in the 19th century by anthropologists stemming from Charles Darwin's research on evolution. Today, cultural evolution has become the basis for a growing field of scientific research in the social sciences, including anthropology, economics, psychology and organizational studies. Previously, it was believed that social change resulted from biological adaptations, but anthropologists now commonly accept that social changes arise in consequence of a combination of social, evolutionary and biological influences. There have been a number of di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald Langacker
Ronald Wayne Langacker (born December 27, 1942) is an American linguist and professor emeritus at the University of California, San Diego. He is best known as one of the founders of the cognitive linguistics movement and the creator of cognitive grammar. He has also made significant contributions to the comparative study of Uto-Aztecan languages, publishing several articles on historical Uto-Aztecan linguistics, as well as editing collections of grammar sketches of under-described Uto-Aztecan languages. Life Born in Fond du Lac, Wisconsin, Langacker received his Ph.D. from the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign in 1966. From 1966 until 2003, he was professor of linguistics at the University of California, San Diego. From 1997 until 1999 he also served as president of the International Cognitive Linguistics Association. Career Langacker develops the central ideas of cognitive grammar in his seminal, two-volume ''Foundations of Cognitive Grammar'', which became a maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
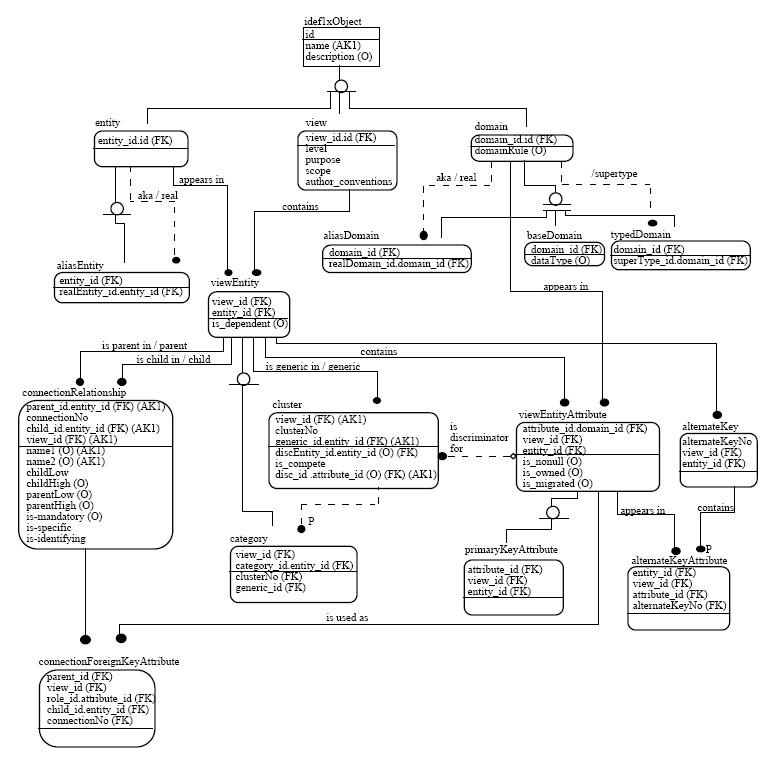
Gellish
Gellish is an ontology language for data storage and communication, designed and developed by Andries van Renssen since mid-1990s. It started out as an engineering modeling language ("Generic Engineering Language", giving it the name, "Gellish") but evolved into a universal and extendable conceptual data modeling language with general applications. Because it includes domain-specific terminology and definitions, it is also a semantic data modelling language and the Gellish modeling methodology is a member of the family of semantic modeling methodologies. Although its concepts have 'names' and definitions in various natural languages, Gellish is a natural-language-independent formal language. Any natural language variant, such as Gellish Formal English is a controlled natural language. Information and knowledge can be expressed in such a way that it is computer-interpretable, as well as system-independent and natural language independent. Each natural language variant is a structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Model
An information model in software engineering is a representation of concepts and the relationships, constraints, rules, and operations to specify data semantics for a chosen domain of discourse. Typically it specifies relations between kinds of things, but may also include relations with individual things. It can provide sharable, stable, and organized structure of information requirements or knowledge for the domain context.Y. Tina Lee (1999)"Information modeling from design to implementation"National Institute of Standards and Technology. Overview The term ''information model'' in general is used for models of individual things, such as facilities, buildings, process plants, etc. In those cases, the concept is specialised to facility information model, building information model, plant information model, etc. Such an information model is an integration of a model of the facility with the data and documents about the facility. Within the field of software engineering and data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Construction Grammar
Construction grammar (often abbreviated CxG) is a family of theories within the field of cognitive linguistics which posit that constructions, or learned pairings of linguistic patterns with meanings, are the fundamental building blocks of human language. Constructions include words (''aardvark'', ''avocado''), morphemes (''anti-'', ''-ing''), fixed expressions and idioms (''by and large'', ''jog X's memory''), and abstract grammatical rules such as the passive voice (''The cat was hit by a car'') or the ditransitive (''Mary gave Alex the ball''). Any linguistic pattern is considered to be a construction as long as some aspect of its form or its meaning cannot be predicted from its component parts, or from other constructions that are recognized to exist. In construction grammar, every utterance is understood to be a combination of multiple different constructions, which together specify its precise meaning and form. Advocates of construction grammar argue that language and cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Construction
In linguistics, a grammatical construction is any syntactic string of words ranging from sentences over phrasal structures to certain complex lexemes, such as phrasal verbs. Grammatical constructions form the primary unit of study in construction grammar theories. In construction grammar, cognitive grammar, and cognitive linguistics, a grammatical construction is a syntactic template that is paired with conventionalized semantic and pragmatic content. In generative frameworks, constructions are generally treated as epiphenomenal, being derived by the general syntactic rules of the language in question. See also * Construction grammar * Formal grammar In formal language theory, a grammar (when the context is not given, often called a formal grammar for clarity) describes how to form strings from a language's alphabet that are valid according to the language's syntax. A grammar does not describe ... References * Ronald W. Langacker, ''Foundations of Cognitive Grammar Volume I'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexeme
A lexeme () is a unit of lexical meaning that underlies a set of words that are related through inflection. It is a basic abstract unit of meaning, a unit of morphological analysis in linguistics that roughly corresponds to a set of forms taken by a single root word. For example, in English, ''run'', ''runs'', ''ran'' and ''running'' are forms of the same lexeme, which can be represented as . One form, the lemma (or citation form), is chosen by convention as the canonical form of a lexeme. The lemma is the form used in dictionaries as an entry's headword. Other forms of a lexeme are often listed later in the entry if they are uncommon or irregularly inflected. Description The notion of the lexeme is central to morphology, the basis for defining other concepts in that field. For example, the difference between inflection and derivation can be stated in terms of lexemes: * Inflectional rules relate a lexeme to its forms. * Derivational rules relate a lexeme to another lexe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Semantics
Lexical semantics (also known as lexicosemantics), as a subfield of linguistic semantics, is the study of word meanings.Pustejovsky, J. (2005) Lexical Semantics: Overview' in Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics, second edition, Volumes 1-14Taylor, J. (2017) Lexical Semantics'. In B. Dancygier (Ed.), The Cambridge Handbook of Cognitive Linguistics (Cambridge Handbooks in Language and Linguistics, pp. 246-261). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. It includes the study of how words structure their meaning, how they act in grammar and compositionality, and the relationships between the distinct senses and uses of a word. The units of analysis in lexical semantics are lexical units which include not only words but also sub-words or sub-units such as affixes and even compound words and phrases. Lexical units include the catalogue of words in a language, the lexicon. Lexical semantics looks at how the meaning of the lexical units correlates with the structure of the language or s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestalt Psychology
Gestalt-psychology, gestaltism, or configurationism is a school of psychology that emerged in the early twentieth century in Austria and Germany as a theory of perception that was a rejection of basic principles of Wilhelm Wundt's and Edward Titchener's elementalist and structuralist psychology.Mather, George (2006) Foundations of Perception, Psychology Pressch.1 p.32 As used in Gestalt psychology, the German word ''Gestalt'' ( , ; meaning "form") is interpreted as "pattern" or "configuration". Gestalt psychologists emphasize that organisms perceive entire patterns or configurations, not merely individual components. The view is sometimes summarized using the adage, "the whole is more than the sum of its parts." Gestalt psychology was founded on works by Max Wertheimer, Wolfgang Köhler, and Kurt Koffka. Origin and history Max Wertheimer (1880–1943), Kurt Koffka (1886–1941), and Wolfgang Köhler (1887-1967) founded Gestalt psychology in the early 20th century. The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherentism
In philosophical epistemology, there are two types of coherentism: the coherence theory of truth; and the coherence theory of justification (also known as epistemic coherentism). Coherent truth is divided between an anthropological approach, which applies only to localized networks ('true within a given sample of a population, given our understanding of the population'), and an approach that is judged on the basis of universals, such as categorical sets. The anthropological approach belongs more properly to the correspondence theory of truth, while the universal theories are a small development within analytic philosophy. The coherentist theory of justification, which may be interpreted as relating to either theory of coherent truth, characterizes epistemic justification as a property of a belief only if that belief is a member of a coherent set. What distinguishes coherentism from other theories of justification is that the set is the primary bearer of justification. As an ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech recognition, computer vision, translation between (natural) languages, as well as other mappings of inputs. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' of Oxford University Press defines artificial intelligence as: the theory and development of computer systems able to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and translation between languages. AI applications include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google), recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon and Netflix), understanding human speech (such as Siri and Alexa), self-driving cars (e.g., Tesla), automated decision-making and competing at the highest level in strategic game systems (such as chess and G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |