|
Fairey Seafox
The Fairey Seafox was a 1930s British reconnaissance floatplane designed and built by Fairey for the Fleet Air Arm. It was designed to be catapulted from the deck of a light cruiser and served in the Second World War. Sixty-six were built, with two finished without floats and used as landplanes. Design and development The Fairey Seafox was built to satisfy Air Ministry Specification S.11/32 for a two-seat spotter-reconnaissance floatplane. The first of two prototypes appeared in 1936, first flying on 27 May 1936,Taylor 1974, p.285. and the first of the 64 production aircraft were delivered in 1937.Taylor 1974, p.287. The flights were organised as 700 Naval Air Squadron of the Fleet Air Arm. The fuselage was of all-metal monocoque construction, the wings being covered with metal on the leading edge, otherwise fabric. It was powered by a 16-cylinder 395 hp (295 kW) air-cooled Napier Rapier H engine. It cruised at 106 mph (171 km/h), and had a range of 44 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
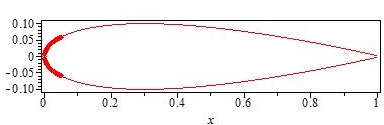
Leading Edge
The leading edge of an airfoil surface such as a wing is its foremost edge and is therefore the part which first meets the oncoming air.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 305. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Characteristics Sweep Seen in plan the leading edge may be straight, curved, kinked or a combination of these. A straight leading edge may be swept or unswept, while curves or kinks always mean that part of the leading edge is swept. On a swept wing the sweep angle may differ from that of the wing, as wing sweep is conventionally measured at the airfoil 25% chord line. However on a delta wing the leading edge sweep defines the wing sweep. Radius and stagnation point A rounded leading edge helps to maintain a smooth airflow at varying angles of incidence to the airflow. Most subsonic airfoils therefore have a rounded leading edge. The degree of rounding is characterised by the profile radius at that point. The airflow divides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
754 Naval Air Squadron
754 Naval Air Squadron (754 NAS) was a Naval Air Squadron of the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm. It was active as an Observer Training Squadron from 1939 to 1944 as part of No.2 Observer School, forming out of the School of Naval Co-operation, in May 1939. It initially operated out of RNAS Lee-on-Solent (HMS Daedalus), however, after the Naval Air Station was attacked and bombed, it then moved to RNAS Arbroath (HMS Condor), in September 1940. Here, it provided training for Observers and also Air Gunners and where four years later, in March 1944, it disbanded. The squadron then briefly reformed as a Training Squadron, as part of No. 1 Naval Air Gunners School, when 744 Naval Air Squadron was re-designated 754 Naval Air Squadron, in June 1944, at RN Air Section Yarmouth, Nova Scotia, Canada, untildisbanding again, in March 1945. History of 754 NAS Observer Training Squadron (1939 - 1944) 754 Naval Air Squadron formed at RNAS Lee-on-Solent (HMS Daedalus), situated near Lee-on-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
718 Naval Air Squadron
718 Naval Air Squadron (718 NAS) was a Naval Air Squadron of the Royal Navy created on 15 July 1936 to serve as a Catapult Flight of the Fleet Air Arm. It was elevated to squadron status at the end of 1937, before being disbanded on 21 January 1940. It was re-formed on 5 June 1944 to operate as the Army Co-operation Naval Operational Training Unit before being disbanded again on 1 November 1945. On 23 August 1946 it was reformed for the third time to operate as a Seafire Conversion Squadron but was disbanded less than one year later, on 17 March 1947. On 25 April 1955, after almost a decade, the squadron was reformed once more to train RNVR on jet aircraft. Once this work was complete, it was disbanded for the final time on 31 December 1955. History Initial Formation 718 NAS originally came into being as a Flight-sized unit following a renumbering of the No. 433 (Catapult) Flight and operated in the 8th Cruiser Squadron in the America and West Indies Station. The unit was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
716 Naval Air Squadron
716 Naval Air Squadron (716 NAS) was a List of Fleet Air Arm aircraft squadrons, Naval Air Squadron of the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm. References Citations Bibliography * 700 series Fleet Air Arm squadrons Military units and formations established in 1936 Military units and formations of the Royal Navy in World War II {{UK-navy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
714 Naval Air Squadron
714 Naval Air Squadron was a squadron of the British Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm. It was first formed as 714 (Catapult) Flight on 15 July 1936, by renumbering 406 (Catapult) Flight, and operated Fairey IIIF floatplanes from cruisers in the East Indies (probably principally 4th Cruiser Squadron). The Fairey IIFs were quickly replaced by Hawker Osprey floatplanes and Supermarine Walrus flying boats, and in 1937 these were supplemented by Fairey Seafox floatplanes. By July 1938 it had consolidated on the Walrus as equipment, and in early 1939 it was upgraded to full squadron status. It was disbanded on 21 January 1940, when all the Fleet Air Arm's catapult units were merged to form 700 Naval Air Squadron. The squadron was reformed on 1 August 1944 at RNAS Fearn near Tain, Scotland, as an operational training squadron equipped with the Fairey Barracuda. It moved to RNAS Rattray (HMS ''Merganser'') near Crimond, Aberdeenshire in October 1944. Its commanding officers included Lieuten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
713 Naval Air Squadron
713 Naval Air Squadron (713 NAS) was a List of Fleet Air Arm aircraft squadrons, Naval Air Squadron of the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm. References Citations Bibliography * 700 series Fleet Air Arm squadrons Military units and formations established in 1936 Military units and formations of the Royal Navy in World War II {{UK-navy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
703 Naval Air Squadron
703 Naval Air Squadron of the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy was formed as a long-range catapult squadron on 3 March 1942 at RNAS Lee-on-Solent. During the Cold War, it was reformed as an experimental trials unit, and then as a helicopter training squadron. Since 2003, the squadron has formed the Royal Naval wing of the Defence Elementary Flying Training School at RAF Barkston Heath. History World War II On 3 June 1942, 703 Naval Air Squadron was formed at RNAS Lee-on-Solent to operate floatplanes off catapult-equipped Armed Merchant Cruisers. It was initially equipped with Vought Kingfishers, supplementing these with Fairey Seafox and Fairey Swordfish floatplanes. The squadron also operated three Supermarine Walrus amphibian aircraft from Walvis Bay in southern Africa. On 1 May 1944, the squadron was disbanded. Air Sea Warfare Development Unit (1945 - 1950) In April 1945, the squadron was reformed as the naval component of the RAF's Air Sea Warfare Development Unit (ASWD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
702 Naval Air Squadron
702 Naval Air Squadron (702 NAS) was a naval squadron of the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm. It was based at RNAS Yeovilton in Somerset and earlier at RNAS Portland in Dorset. As a training Squadron it trained all ground and air crew for the sister front-line maritime Lynx squadron, 815 NAS It merged with 700(W) NAS to form 825 NAS. 702 NAS disbanded on 1 August 2014. History Formation and WWII (1936 - 1945) 702 NAS was founded on 15 July 1936 to operate aircraft from the ships of the 2nd Battle Squadron. Operating Supermarine Walrus and Fairey Seal aircraft from its base at RAF Mount Batten initially, later these were replaced by the Fairey Swordfish float-plane. Granted Squadron status in 1939, and briefly disbanded in 1940, 702 Naval Air Squadron reformed as a Long Range Catapult squadron with Fairey Seafoxes for duty in Armed Merchant Cruisers for much of the Second World War. Naval Jet Evaluation Training Unit In 1949 the squadron reformed at RNAS Culdrose as the Naval J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armed Merchantmen
An armed merchantman is a merchant ship equipped with guns, usually for defensive purposes, either by design or after the fact. In the days of sail, piracy and privateers, many merchantmen would be routinely armed, especially those engaging in long distance and high value trade. In more modern times, auxiliary cruisers were used offensively as merchant raiders to disrupt trade chiefly during both World War I and World War II, particularly by Germany. While armed merchantmen are clearly inferior to purpose-built warships, sometimes they have scored successes in combat against them. Examples include East Indiamen mimicking ships of the line and chasing off regular French warships in the Battle of Pulo Aura in 1804, and the sinking the Australian light cruiser in their battle in 1941, although ''Kormoran'' was also destroyed and had to be scuttled. Pre-20th century East Indiamen of various European countries were heavily armed for their long journeys to the Far East. In part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery Observer
An artillery observer, artillery spotter or forward observer (FO) is responsible for directing artillery and mortar fire onto a target. It may be a ''forward air controller'' (FAC) for close air support (CAS) and spotter for naval gunfire support (NGSF). Also known as fire support specialist (FiSTer), an artillery observer usually accompanies a tank or infantry maneuver unit. Spotters ensure that indirect fire hits targets which the troops at the fire support base cannot see. Because artillery is an indirect fire weapon system, the guns are rarely in line-of-sight of their target, often located miles away. The observer serves as the eyes of the guns, by sending target locations and if necessary corrections to the fall of shot, usually by radio. More recently, a mission controller for an Army Unmanned Air System (UAS) may also perform this function, and some armies use special artillery patrols behind the enemy's forward elements. Special forces such as the British SAS, US SE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutschland-class Cruiser
The ''Deutschland'' class was a series of three ''Panzerschiffe'' (armored ships), a form of heavily armed cruiser, built by the '' Reichsmarine'' officially in accordance with restrictions imposed by the Treaty of Versailles. The ships of the class, , , and , were all stated to displace in accordance with the Treaty, though they actually displaced at standard displacement. The design for the ships incorporated several radical innovations, including the first major use of welding in a warship and all- diesel propulsion. Due to their heavy armament of six guns and lighter weight, the British began referring to the vessels as "pocket battleships". The ''Deutschland''-class ships were initially classified as ''Panzerschiffe'', but the '' Kriegsmarine'' reclassified them as heavy cruisers in February 1940. The three ships were built between 1929 and 1936 by the Deutsche Werke in Kiel and the ''Reichsmarinewerft'' in Wilhelmshaven, seeing much service with the German Navy. All ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |