|
Ford Fox Platform
The Ford Fox platform is an Car platform, automobile platform that was used by Ford Motor Company from the 1978 to 1993 model years. Originally introduced to underpin compact sedans, the Fox architecture was utilized for a wide variety of vehicle designs for Ford and Lincoln-Mercury vehicles. Serving as the direct replacement for the long-running Ford Falcon (North America), Ford Falcon architecture, the downsizing of intermediate-size cars expanded its use, with the Fox platform also replacing the Ford Torino platform. For the 1980s, the chassis came into wider use, supporting both the Ford Mustang and the Ford Thunderbird. Designed to be relatively lightweight and simple, the Fox platform was a rear-wheel drive chassis that utilized a wide variety of powertrains. Along with the sedans, coupes, and station wagons introduced by the inaugural Ford Fairmont and Mercury Zephyr, models were offered as hatchbacks, convertibles, and as a coupe utility. In addition to pony cars and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational corporation, multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. The company sells automobiles and commercial vehicles under the List of Ford vehicles, Ford brand, and luxury cars under its Lincoln Motor Company, Lincoln brand. The company is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the single-letter ticker symbol F and is controlled by the Ford family (Michigan), Ford family. They have minority ownership but a plurality of the voting power. Ford introduced methods for large-scale manufacturing of cars and large-scale management of an industrial workforce using elaborately engineered manufacturing sequences typified by moving assembly lines. By 1914, these methods were known around the world as Fordism. Ford's former British subsidiaries Jaguar Cars, Jaguar and Land Rover, acquired in 1989 and 2000, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatchback
A hatchback is a car body style, car body configuration with a rear door that swings upward to provide access to the main interior of the car as a cargo area rather than just to a separated trunk. Hatchbacks may feature fold-down second-row seating, where the interior can be reconfigured to prioritize passenger or cargo volume. While early examples of the body configuration can be traced to the 1930s, the Merriam-Webster dictionary dates the term itself to 1970. The hatchback body style has been marketed worldwide on cars ranging in size from supermini car, superminis to small family cars, as well as executive cars and some sports cars. They are a primary component of sport utility vehicles. Characteristics The distinguishing feature of a hatchback is a rear door that opens upwards and is hinged at roof level (as opposed to the boot/trunk lid of a sedan (car), saloon/sedan, which is hinged below the rear window). Most hatchbacks use a Three-box styling#, two-box design bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lee Iacocca
Lido Anthony "Lee" Iacocca ( ; October 15, 1924 – July 2, 2019) was an American automobile executive who developed the Ford Mustang, Lincoln Continental Mark III, and Ford Pinto cars while at the Ford Motor Company in the 1960s, and then revived the Chrysler, Chrysler Corporation as its CEO during the 1980s. He was president of Chrysler from 1978 to 1991 and chairman and CEO from 1979 until his retirement at the end of 1992. He was one of the few executives to preside over the operations of two of the United States' Big Three (automobile manufacturers), Big Three automakers. Iacocca authored or co-authored several books, including ''Iacocca: An Autobiography'' (with William Novak), and ''Where Have All the Leaders Gone?.'' Early life and education Iacocca was born in Allentown, Pennsylvania, on October 15, 1924, to Nicola Iacocca and Antonietta Perrotta, Italian Americans from San Marco dei Cavoti, who settled in the steel producing region of the Lehigh Valley in eastern Pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Ford II
Henry Ford II (September 4, 1917 – September 29, 1987), commonly known as Hank the Deuce, was an American businessman in the automotive industry. He was the oldest son of Edsel Ford I and oldest grandson of Henry Ford. He served as president of the Ford Motor Company from 1945 to 1960, chief executive officer (CEO) from 1947 to 1979, and chairman of the board of directors from 1960 to 1980. Under his leadership, Ford Motor Company became a publicly traded corporation in 1956. From 1943 to 1950, he also served as president of the Ford Foundation. Early life and education Henry Ford II was born in Detroit, Michigan, to Eleanor Clay Ford and Edsel Ford on September 4, 1917. He, brothers Benson and William, and sister Josephine, grew up amid affluence. He graduated from The Hotchkiss School in 1936. He attended Yale University — where he served on the business staff of '' The Yale Record'', the campus humor magazine — but left in 1940 before graduation. During this time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
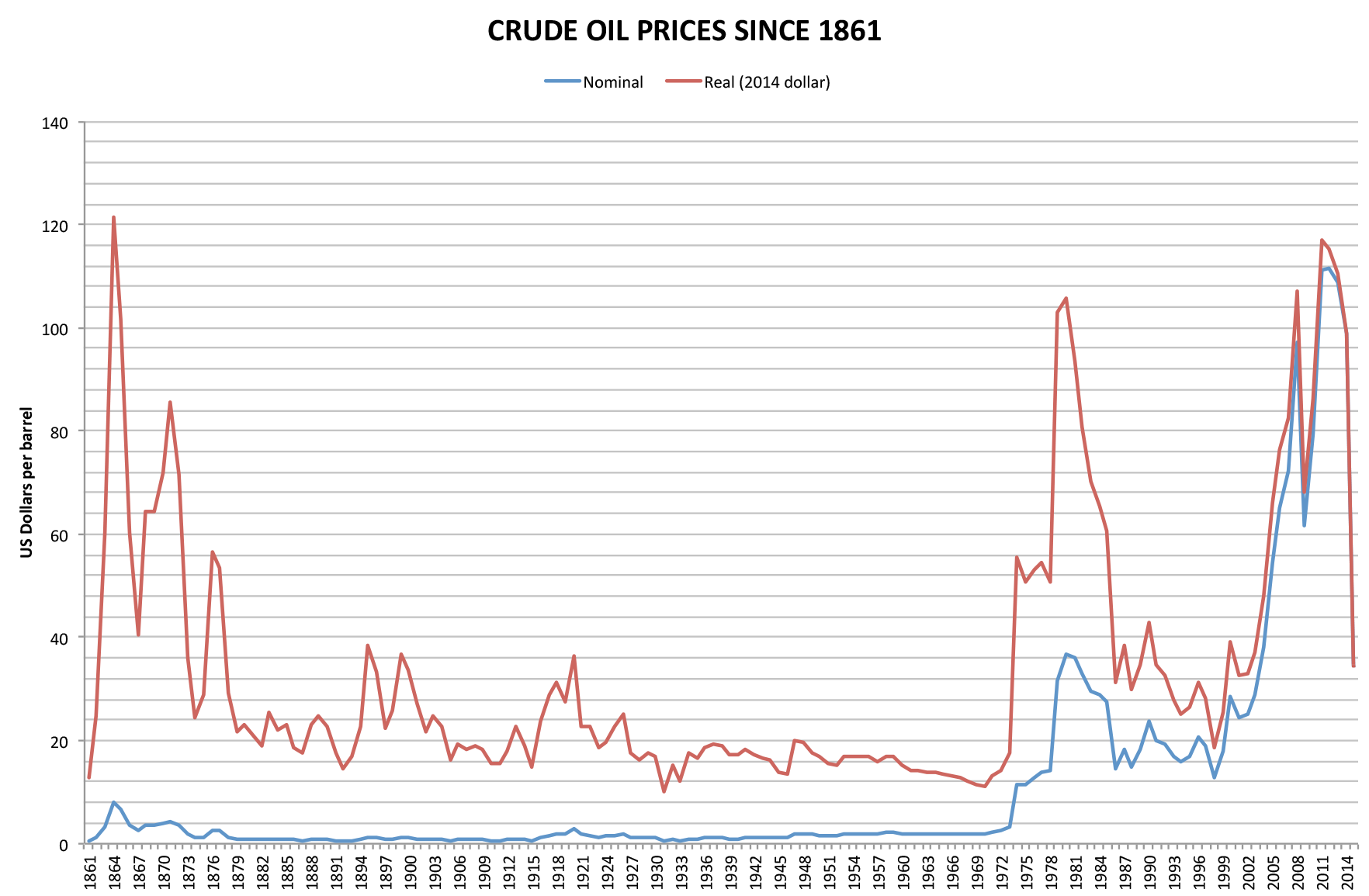
1973 Oil Crisis
In October 1973, the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) announced that it was implementing a total oil embargo against countries that had supported Israel at any point during the 1973 Yom Kippur War, which began after Egypt and Syria launched a large-scale surprise attack in an ultimately unsuccessful attempt to recover the territories that they had lost to Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War. In an effort that was led by Faisal of Saudi Arabia, the initial countries that OAPEC targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and the United States. This list was later expanded to include Estado Novo (Portugal), Portugal, Rhodesia, and South Africa. In March 1974, OAPEC lifted the embargo, but the price of oil had risen by nearly 300%: from US to nearly US globally. Prices in the United States were significantly higher than the global average. After it was implemented, the embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Guzzler Tax
The Energy Tax Act (, , enacted November 9, 1978) is a law passed by the U.S. Congress as part of the National Energy Act. The objective of this law, passed during the 1970s energy crisis, was to reduce demand for oil and gas supply by promoting fuel efficiency and renewable energy through taxes and tax credits. Tax credits for conservation This law gave an income tax credit to private residents who use solar, wind, or geothermal sources of energy. The credit is equal to 30% of the cost of the equipment up to $2000, as well as 20% of costs greater than $2000, up to a maximum of $10,000. There were also tax credits to businesses for renewable energy equipment, amounting to a maximum of 25% of the cost of the equipment. The renewable energy credits of this law were increased by the Crude Oil Windfall Profits Tax Act of 1980. Gas Guzzler Tax The Act also created the Gas Guzzler Tax which applies to the sales of vehicles with official EPA-estimated gas mileage below cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent agency of the United States government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on December 2, 1970, after Nixon signed an executive order. The order establishing the EPA was ratified by committee hearings in the House and Senate. The agency is led by its administrator, who is appointed by the president and approved by the Senate. The current administrator is Lee Zeldin. The EPA is not a Cabinet department, but the administrator is normally given cabinet rank. The EPA has its headquarters in Washington, D.C. There are regional offices for each of the agency's ten regions, as well as 27 laboratories around the country. The agency conducts environmental assessment, research, and education. It has the responsibility of maintaining and enforcing national standards under a variety of environmental laws, in consultat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automotive Industry In The United States
In the United States, the automotive industry began in the 1890s and, as a result of the size of the domestic market and the use of mass production, rapidly evolved into the largest in the world. The United States was the first country in the world to have a mass market for vehicle production and sales and is a pioneer of the automotive industry and mass market production process. During the 20th century, global competitors emerged, especially in the second half of the century primarily across European and Asian markets, such as Germany, France, Italy, Japan and South Korea. The U.S. is currently second among the List of countries by motor vehicle production, largest manufacturers in the world by volume. By value, the U.S. was the world's largest importer and fourth-largest exporter of cars in 2023. American manufacturers produce approximately 10 million units annually. Notable exceptions were 5.7 million automobiles manufactured in 2009 (due to Effects of the 2008–10 aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford Mustang (fourth Generation)
The fourth-generation Ford Mustang is a pony car produced by the Ford Motor Company for the 1994 through 2004 model years. Marking the first major redesign of the Ford Mustang in fifteen years, the fourth generation of the pony car was introduced in November 1993 with the launch taking place on December 9, 1993. The design (which was code-named "SN95" by Ford), was based on an updated version of the Ford Fox platform, Fox platform and was the final vehicle underpinned with this platform. It featured styling by Bud Magaldi that incorporated some stylistic elements from the classic Mustangs. A convertible model returned, but the previous notchback and hatchback bodystyles were discontinued in favor of a conventional 2-door coupe design. Prior to the redesigned Mustang's launch, a two-seater concept car, show car was designed by Darrell Behmer and Bud Magaldi. Called the Ford Mustang variants#Initial Concepts, Mustang Mach III, it was shown at the North American International Auto Sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Car Platform
A car platform is a shared set of common design, engineering, and production efforts, as well as major components, over a number of outwardly distinct models and even types of cars, often from different, but somewhat related, marques. It is practiced in the automotive industry to reduce the costs associated with the development of products by basing those products on a smaller number of platforms. This further allows companies to create distinct models from a design perspective on similar underpinnings. A car platform is not to be confused with a platform chassis, although such a chassis can be part of an automobile's design platform, as noted below. Definition and benefits A basic definition of a platform in cars, from a technical point of view, includes underbody and suspensions (with axles) — where the underbody is made of the front floor, rear floor, engine compartment, and frame (reinforcement of underbody). Key mechanical components that define an automobile platform in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford Fox Platform
The Ford Fox platform is an Car platform, automobile platform that was used by Ford Motor Company from the 1978 to 1993 model years. Originally introduced to underpin compact sedans, the Fox architecture was utilized for a wide variety of vehicle designs for Ford and Lincoln-Mercury vehicles. Serving as the direct replacement for the long-running Ford Falcon (North America), Ford Falcon architecture, the downsizing of intermediate-size cars expanded its use, with the Fox platform also replacing the Ford Torino platform. For the 1980s, the chassis came into wider use, supporting both the Ford Mustang and the Ford Thunderbird. Designed to be relatively lightweight and simple, the Fox platform was a rear-wheel drive chassis that utilized a wide variety of powertrains. Along with the sedans, coupes, and station wagons introduced by the inaugural Ford Fairmont and Mercury Zephyr, models were offered as hatchbacks, convertibles, and as a coupe utility. In addition to pony cars and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |