|
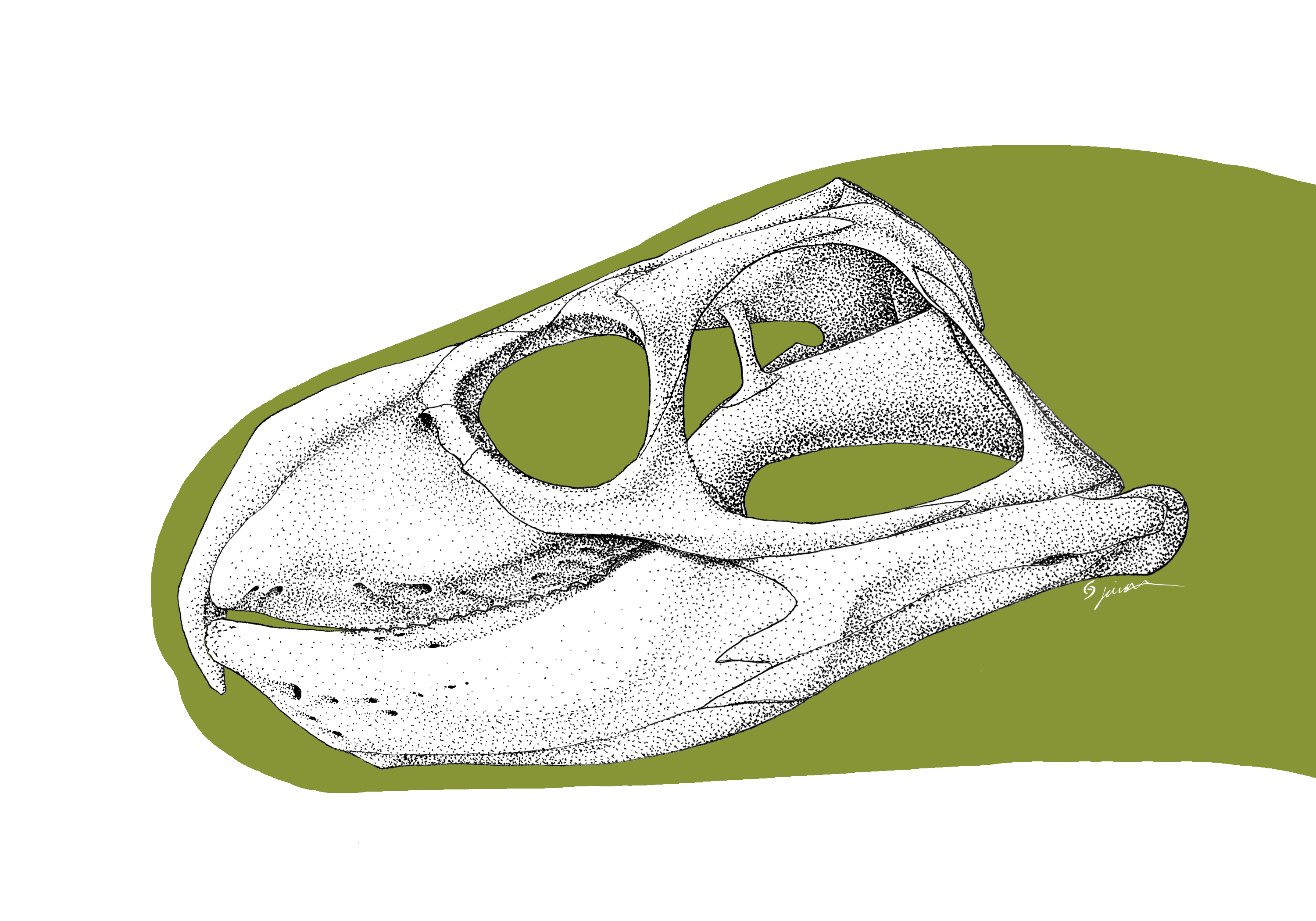
Fodonyx
''Fodonyx'' (meaning "digging claw") is an extinct genus of rhynchosaur from the middle Triassic epoch of Devon in England. Its fossils (25 specimens) were discovered in Otter Sandstone Formation (late Anisian age) and were first assigned to '' Rhynchosaurus spenceri''. This species was reassigned to its own genus, ''Fodonyx'' (the type and only species is ''Fodonyx spenceri'') the holotype of which iEXEMS 60/1985/292, that described by David W. E. Hone and Michael J. Benton in 2008. More recently, one skull was reassigned to the new genus '' Bentonyx''. It is distinguished from other rhynchosaurs by a single autapomorphy, the ventral angling of the paraoccipital processes. In all other rhynchosaurs these processes angle dorsally or are horizontal. It is not known if this conferred any advantage to ''Fodonyx. Fodonyx'' was between 40 and 50 cm long. Features Skull and lower jaw The two premaxillae are very long and run up over the snout to meet the prefrontals at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchosaur
Rhynchosaurs are a group of extinct herbivorous Triassic archosauromorph reptiles, belonging to the order Rhynchosauria. Members of the group are distinguished by their triangular skulls and elongated, beak like premaxillary bones. Rhynchosaurs first appeared in the Middle Triassic or possibly the Early Triassic, before becoming abundant and globally distributed during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. Description Rhynchosaurs were herbivores, and at times abundant (in some fossil localities accounting for 40 to 60% of specimens found), with stocky bodies and a powerful beak. Early primitive forms, like '' Mesosuchus'' and ''Howesia'', were generally small and more typically lizard-like in build, and had skulls rather similar to the early diapsid '' Youngina'', except for the beak and a few other features. Later and more advanced genera grew to medium to medium large size, up to two meters in length. The skull in these forms were short, broad, and triangular, becoming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bentonyx
''Bentonyx'' (meaning "Bentons' claw") is an extinct genus of rhynchosaur from the middle Triassic epoch of Devon in England. Its fossil, a well preserved skullBRSUG 27200 was discovered in Otter Sandstone Formation (late Anisian age) and was first assigned to '' Rhynchosaurus spenceri'', that is known from 25 specimens. This species was reassigned to its own genus, ''Fodonyx'', that was first described by David W. E. Hone and Michael Benton in 2008. More recently, this skull was reassigned to this genus by Max C. Langer, Felipe C. Montefeltro, David E. Hone, Robin Whatley and Cesar L. Schultz in 2010 and the type species is ''Bentonyx sidensis''. The Cladogram below is based on work by Martin Ezcurra Martin may refer to: Places * Martin City (other) * Martin County (other) * Martin Township (other) Antarctica * Martin Peninsula, Marie Byrd Land * Port Martin, Adelie Land * Point Martin, South Orkney Islands Austr ... ''et al''. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchosaurus
''Rhynchosaurus'' (''beaked lizard'') is a genus of rhynchosaur that lived during the Middle Triassic period. It lived in Europe. It was related to the archosaurs, but not within that group. The type species of ''Rhynchosaurus'' is ''R. articeps''. Michael Benton named two additional species, ''R. spenceri'' and ''R. brodiei'', but they were subsequently renamed '' Fodonyx'' and '' Langeronyx'' respectively.Martín D. Ezcurra, Felipe Montefeltro and Richard J. Butler (2016). "The Early Evolution of Rhynchosaurs". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 3: Article 142. doi:10.3389/fevo.2015.00142. Fossils of ''Rhynchosaurus'' have been found in the Tarporley Siltstone Formation (Mercia Mudstone Group) and possibly the Sherwood Sandstone Group of the United Kingdom.''Rhynchosaurus'' at |
Middle Triassic
In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian ages or stages. Formerly the middle series in the Triassic was also known as Muschelkalk. This name is now only used for a specific unit of rock strata with approximately Middle Triassic age, found in western Europe. Middle Triassic fauna Following the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the most devastating of all mass-extinctions, life recovered slowly. In the Middle Triassic, many groups of organisms reached higher diversity again, such as the marine reptiles (e.g. ichthyosaurs, sauropterygians, thallatosaurs), ray-finned fish and many invertebrate g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: they convey blood between the arterioles and venules. These microvessels are the site of exchange of many substances with the interstitial fluid surrounding them. Substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in the microcirculation. During early embryonic development, new capillaries are formed through vasculogenesis, the process of blood vessel formation that occurs through a '' de novo'' production of endothelial cells that then form vascular tubes. The term '' angiogenesis'' denotes the formation of new capillaries from pre-existing blood vessels and already pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Plate
A plate in animal anatomy may refer to several things: Flat bones (examples: bony plates, dermal plates) of vertebrates * an appendage of the Stegosauria group of dinosaurs * articulated armoured plates covering the head of thorax of Placodermi (literally "plate-skinned"), an extinct class of prehistoric fish (including skull, thoracic and tooth plates) * bony shields of the Ostracoderms (armored jawless fishes) such as the dermal head armour of members of the class Pteraspidomorphi that include dorsal, ventral, rostral and pineal plates * plates of a carapace, such as the dermal plates of the shell of a turtle * dermal plates partly or completely covering the body of the fish in the order Gasterosteiformes that includes the sticklebacks and relatives * plates of dermal bones of the armadillo * Zygomatic plate, a bony plate derived from the flattened front part of the zygomatic arch (cheekbone) in rodent anatomy Other flat structures * hairy plate-like keratin scales of the pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen
In anatomy and osteology, a foramen (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. plural foramina, or foramens ) is an open hole that is present in extant or extinct s. Foramina inside the body of animals typically allow nerves, arteries, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon, within the nerve, is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Bone
The nasal bones are two small oblong bones, varying in size and form in different individuals; they are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and by their junction, form the bridge of the upper one third of the nose. Each has two surfaces and four borders. Structure The two nasal bones are joined at the midline internasal suture and make up the bridge of the nose. Surfaces The ''outer surface'' is concavo-convex from above downward, convex from side to side; it is covered by the procerus and nasalis muscles, and perforated about its center by a foramen, for the transmission of a small vein. The ''inner surface'' is concave from side to side, and is traversed from above downward, by a groove for the passage of a branch of the nasociliary nerve. Articulations The nasal articulates with four bones: two of the cranium, the frontal and ethmoid, and two of the face, the opposite nasal and the maxilla. Other animals In primitive bony fish and tetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gums
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation. Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types, the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and harder, derived forms found only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacrimal Canaliculi
The lacrimal canaliculi, (sing. canaliculus), are the small channels in each eyelid that drain lacrimal fluid, from the lacrimal puncta to the lacrimal sac. This forms part of the lacrimal apparatus that drains lacrimal fluid from the surface of the eye to the nasal cavity. Structure There is a single lacrimal canaliculus in each eyelid An eyelid is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. The human eyel ..., a superior lacrimal canaliculus in the upper eyelid and an inferior lacrimal canaliculus in the lower eyelid. The canaliculi travel vertically and then turn medially to travel towards the lacrimal sac. At the bend, the canaliculus is dilated and called the ampulla. Usually, the superior and inferior lacrimal canaliculi join to form a common passage that enters the lateral wall of the lacrimal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |